RS485 offers robust multi-point communication over long distances with high noise immunity, whereas RS232 is designed for short-distance, point-to-point connections with simpler wiring. Explore the rest of this article to understand which protocol best suits Your communication needs.
Table of Comparison
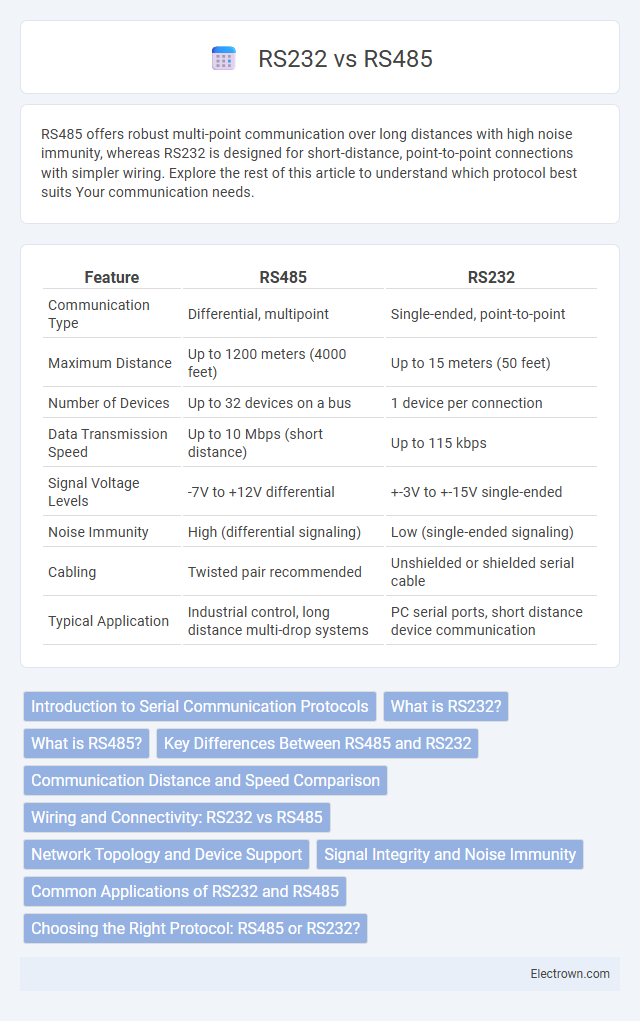
| Feature | RS485 | RS232 |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Differential, multipoint | Single-ended, point-to-point |
| Maximum Distance | Up to 1200 meters (4000 feet) | Up to 15 meters (50 feet) |
| Number of Devices | Up to 32 devices on a bus | 1 device per connection |
| Data Transmission Speed | Up to 10 Mbps (short distance) | Up to 115 kbps |
| Signal Voltage Levels | -7V to +12V differential | +-3V to +-15V single-ended |
| Noise Immunity | High (differential signaling) | Low (single-ended signaling) |
| Cabling | Twisted pair recommended | Unshielded or shielded serial cable |
| Typical Application | Industrial control, long distance multi-drop systems | PC serial ports, short distance device communication |
Introduction to Serial Communication Protocols
Serial communication protocols like RS485 and RS232 serve as essential standards for data transmission between devices, with RS232 primarily supporting short-distance, point-to-point connections using single-ended signaling and lower noise immunity. RS485 enables multi-point, long-distance communication through differential signaling, offering higher noise resistance and the ability to connect up to 32 devices on a single bus. Understanding these protocols' electrical characteristics and network topologies is crucial for selecting the appropriate interface in industrial automation and embedded systems.
What is RS232?
RS232 is a standard protocol for serial communication that enables data exchange between computers and peripheral devices using voltage signals on a single-ended line. It typically supports short-distance communication up to 15 meters with data rates up to 115.2 kbps, making it suitable for connecting devices like modems and printers. RS232 uses unbalanced signaling, where one wire carries the signal and a common ground serves as reference, which makes it more susceptible to noise compared to differential methods like RS485.
What is RS485?
RS485 is a robust serial communication standard widely used for industrial automation and control systems due to its ability to support long-distance data transmission up to 1,200 meters and multi-point connections with up to 32 devices. It operates on differential signaling, providing enhanced noise immunity and reliable communication in electrically noisy environments compared to RS232. RS485's half-duplex and full-duplex capabilities enable flexible network topologies, making it ideal for applications requiring multiple devices on a single communication bus.
Key Differences Between RS485 and RS232
RS485 supports multi-point communication with up to 32 devices on a single bus, while RS232 is designed for point-to-point connections between two devices. RS485 operates over longer distances, up to 1200 meters, and uses differential signaling for improved noise immunity, whereas RS232 is limited to about 15 meters with single-ended signaling. Voltage levels and data transmission speeds also differ significantly, with RS485 handling higher speeds and industrial environments more effectively than RS232.
Communication Distance and Speed Comparison
RS485 supports communication distances up to 1,200 meters while RS232 is limited to about 15 meters, making RS485 ideal for long-distance data transmission. In terms of speed, RS232 typically operates at speeds up to 115.2 kbps, whereas RS485 can reach speeds exceeding 10 Mbps depending on cable length. Your choice between RS485 and RS232 should consider these distance and speed differences to ensure optimal communication performance.
Wiring and Connectivity: RS232 vs RS485
RS485 supports multi-point connections with a differential two-wire or four-wire system allowing up to 32 devices to communicate on a single bus, whereas RS232 uses single-ended signaling with one transmitter and one receiver, limiting it to point-to-point communication. RS485 wiring is designed for long-distance and noise-resistant communication up to 1200 meters, while RS232 is typically restricted to 15 meters. The balanced, differential nature of RS485 wiring significantly enhances signal integrity in industrial environments compared to the unbalanced, single-ended RS232 wiring.
Network Topology and Device Support
RS485 supports multi-point network topology allowing up to 32 devices on a single bus, enabling robust communication in complex systems. RS232, in contrast, typically operates point-to-point, supporting only one transmitter and one receiver, limiting its use for simple, direct device connections. The differential signaling of RS485 enhances noise immunity and distance capabilities, making it ideal for industrial and automation networks requiring multiple device support.
Signal Integrity and Noise Immunity
RS485 offers superior signal integrity and noise immunity compared to RS232, supporting balanced differential signaling that reduces electromagnetic interference and crosstalk in industrial environments. Its twisted-pair cabling minimizes signal degradation over longer distances up to 1,200 meters, making it ideal for noise-prone applications. Your communication system benefits from RS485's robustness, ensuring data accuracy and reliable performance in electrically noisy settings.
Common Applications of RS232 and RS485
RS232 is commonly used for short-distance serial communication in computer peripherals, industrial equipment, and point-of-sale systems due to its simple, single-ended signaling. RS485 excels in longer-distance, multi-point applications such as building automation, industrial control networks, and HVAC systems thanks to its differential signaling and multi-drop capability. Both standards support reliable serial data transmission, but RS485's noise immunity and ability to connect multiple devices on the same bus make it ideal for harsh environments and complex configurations.
Choosing the Right Protocol: RS485 or RS232?
RS485 offers robust long-distance communication up to 1200 meters and supports multi-drop networks with up to 32 devices on a single bus, making it ideal for industrial environments requiring noise immunity and high data integrity. RS232 is suited for short-distance, point-to-point connections typically under 15 meters, commonly used in computer serial ports and simple device interfaces. Selecting between RS485 and RS232 depends on the application's distance requirements, network topology, and environmental conditions impacting signal reliability.
RS485 vs RS232 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com