DB9 connectors feature 9 pins primarily used for serial communication in RS-232 interfaces, while DB25 connectors have 25 pins supporting a broader range of parallel and serial applications. Understanding these differences will help you select the right connector for your device--explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
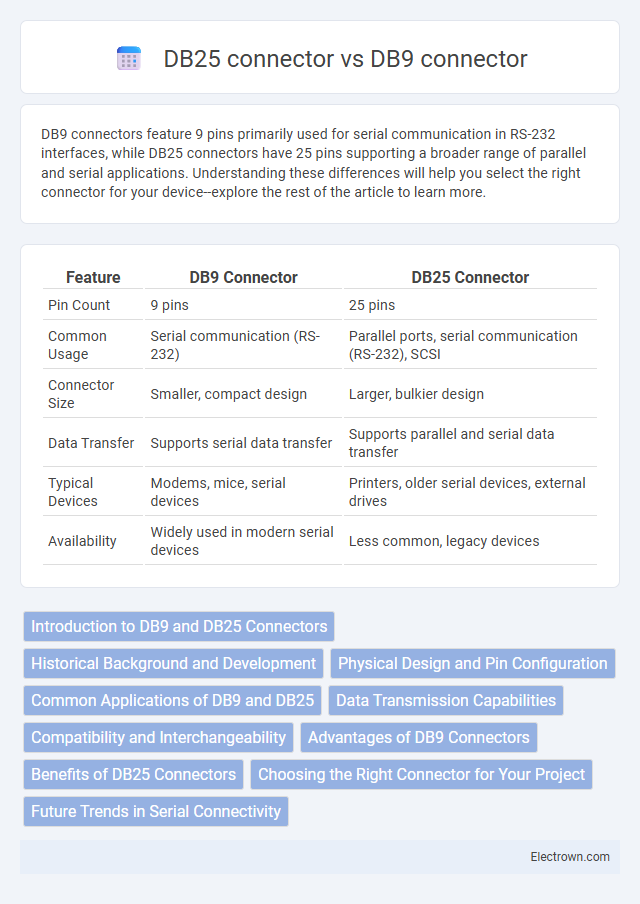
| Feature | DB9 Connector | DB25 Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Pin Count | 9 pins | 25 pins |
| Common Usage | Serial communication (RS-232) | Parallel ports, serial communication (RS-232), SCSI |
| Connector Size | Smaller, compact design | Larger, bulkier design |
| Data Transfer | Supports serial data transfer | Supports parallel and serial data transfer |
| Typical Devices | Modems, mice, serial devices | Printers, older serial devices, external drives |
| Availability | Widely used in modern serial devices | Less common, legacy devices |
Introduction to DB9 and DB25 Connectors
DB9 and DB25 connectors are widely used D-subminiature connectors distinguished by their pin count and applications. The DB9 connector features 9 pins arranged in two rows, commonly utilized in serial communication interfaces such as RS-232 for connecting peripherals like modems and mice. The DB25 connector contains 25 pins in two rows, supporting parallel and serial communication protocols, often employed in older printer connections and SCSI interfaces.
Historical Background and Development
The DB9 connector, introduced in the 1980s, emerged as a compact alternative to the larger DB25 connector, which was originally developed in the 1970s for parallel and serial communications in early computing systems. The DB25 connector became widely known for its use in parallel port connections and RS-232 serial interfaces, while the DB9 connector gained popularity for serial communication due to its smaller size and ease of use. Understanding the historical development of these connectors helps you appreciate their roles in the evolution of computer hardware and communication standards.
Physical Design and Pin Configuration
The DB9 connector features a compact 9-pin configuration arranged in two rows--five pins on top and four on bottom--making it ideal for serial port connections with minimal space requirements. The DB25 connector, larger in size, houses 25 pins arranged in two rows with 13 pins on top and 12 on bottom, providing greater versatility for parallel ports, SCSI interfaces, and other multi-signal applications. Your choice between DB9 and DB25 connectors depends on the device's physical space constraints and the number of signals needed for communication.
Common Applications of DB9 and DB25
DB9 connectors are commonly used in serial communication interfaces such as RS-232 ports for computer peripherals like mice, modems, and industrial equipment. DB25 connectors, with their higher pin count, support parallel port connections for printers and SCSI devices as well as more complex serial communication setups. Understanding the typical applications of DB9 and DB25 connectors can help you choose the right interface for specialized networking, legacy hardware, or industrial control systems.
Data Transmission Capabilities
DB9 connectors support serial communication with up to 9 pins, enabling basic data transmission typically used for RS-232 protocols, ideal for low-speed or legacy serial devices. DB25 connectors have 25 pins, providing broader functionality, including parallel and serial data transmission, supporting higher data rates and more complex signal configurations. Your choice between DB9 and DB25 depends on the required data transmission speed and the specific communication standard for your device.
Compatibility and Interchangeability
The DB9 connector, featuring 9 pins, is often used for serial communication interfaces, whereas the DB25 connector, with 25 pins, supports parallel and serial connections, making compatibility between the two limited without adapters. Interchangeability is restricted due to their differing pin counts and signal configurations, so directly swapping DB9 and DB25 connectors can result in improper connections and device malfunction. Your choice should consider the specific device requirements and interface standards to ensure seamless communication and avoid compatibility issues.
Advantages of DB9 Connectors
DB9 connectors offer a more compact design compared to DB25 connectors, making them ideal for space-constrained applications such as serial communication in industrial equipment and networking devices. Their reduced pin count simplifies wiring and maintenance, lowering the risk of connection errors and improving overall reliability. DB9 connectors also support faster data transmission rates in RS-232 and RS-485 standards, enhancing performance for modern serial communication protocols.
Benefits of DB25 Connectors
DB25 connectors offer increased pin count with 25 contacts, enabling support for multiple signal channels and enhanced data transmission capabilities compared to the 9-pin DB9 connectors. Their versatility makes them ideal for parallel and serial communication interfaces, providing robust connectivity in industrial and networking applications. Your setup benefits from the DB25 connector's ability to handle complex wiring configurations and higher device compatibility, ensuring efficient and reliable performance.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your Project
Selecting between DB9 and DB25 connectors depends on the specific project requirements, such as the number of data lines and signal types. The DB9 connector, with 9 pins, is ideal for serial communication and compact designs, while the DB25 connector offers 25 pins suited for parallel connections and higher data throughput. Evaluating pin count, device compatibility, and signal integrity ensures optimal performance and reliability for the intended application.
Future Trends in Serial Connectivity
The DB9 connector, commonly used for RS-232 serial communication, is gradually being replaced by more compact and versatile interfaces like USB and Thunderbolt, reflecting a shift towards faster, more flexible connectivity solutions. The DB25 connector, once standard for parallel and serial ports, is now largely obsolete due to its size and limited data transfer rates compared to modern alternatives. Your choice in serial connectivity should prioritize emerging standards supporting higher bandwidth and wider compatibility, ensuring future-proofing in evolving technological environments.
DB9 connector vs DB25 connector Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com