Frequency counters measure the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time, providing precise frequency measurements essential for signal analysis, whereas timer counters track elapsed time intervals or count specific events, often used for timing operations and event sequencing. Discover how understanding these distinctions can enhance Your ability to select the right tool for your electronic measurement needs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
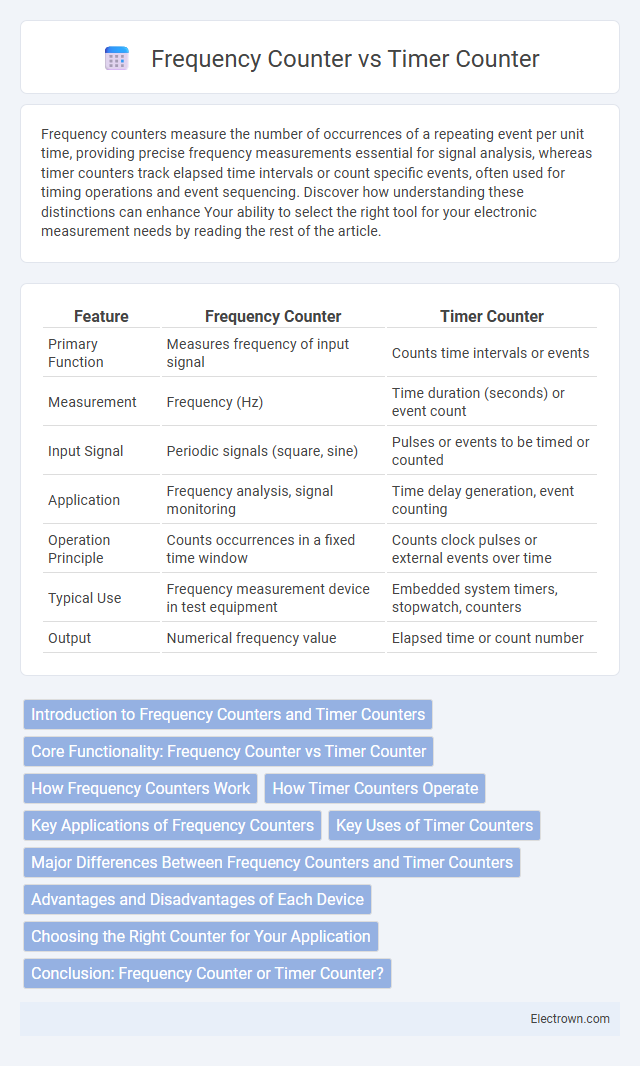
| Feature | Frequency Counter | Timer Counter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Measures frequency of input signal | Counts time intervals or events |
| Measurement | Frequency (Hz) | Time duration (seconds) or event count |
| Input Signal | Periodic signals (square, sine) | Pulses or events to be timed or counted |
| Application | Frequency analysis, signal monitoring | Time delay generation, event counting |
| Operation Principle | Counts occurrences in a fixed time window | Counts clock pulses or external events over time |
| Typical Use | Frequency measurement device in test equipment | Embedded system timers, stopwatch, counters |
| Output | Numerical frequency value | Elapsed time or count number |
Introduction to Frequency Counters and Timer Counters
Frequency counters measure the number of signal cycles per second to accurately determine the frequency of electronic signals, essential in communication systems and signal processing. Timer counters track elapsed time or count events by utilizing oscillator pulses, playing a critical role in timing applications, event measurement, and microcontroller functions. Understanding your choice between these tools depends on whether precise frequency measurement or time interval counting is required for your project.
Core Functionality: Frequency Counter vs Timer Counter
Frequency counters specialize in measuring the frequency of an input signal by counting the number of pulses within a specific time interval, providing precise frequency readings in hertz (Hz). Timer counters measure elapsed time intervals or generate accurate time delays by counting clock pulses, often used in timing applications and event counting. Understanding your core requirement--whether measuring signal frequency or timing intervals--determines the optimal choice between a frequency counter and a timer counter for your application.
How Frequency Counters Work
Frequency counters measure the rate of an input signal by counting the number of pulses within a specific time interval, using a high-precision time base to ensure accuracy. The device typically employs a quartz crystal oscillator to generate a stable reference clock, and the frequency counter increments the count each time it detects a signal pulse during the gate time. By dividing the total pulse count by the gate time, the frequency counter calculates the frequency of the input signal with high resolution and accuracy.
How Timer Counters Operate
Timer counters operate by incrementing or decrementing a counter register at each pulse of a fixed-frequency clock, allowing precise measurement of time intervals or event durations. They utilize internal clock sources or external signals to count pulses, triggering interrupts or actions upon reaching predefined thresholds or overflow conditions. These counters enable accurate timing control in embedded systems, microcontrollers, and digital circuits by regulating delays, pulse widths, and periodic events.
Key Applications of Frequency Counters
Frequency counters are essential in telecommunications for measuring signal frequencies to ensure accurate transmission and reception. They are widely used in electronics testing and validation to verify oscillator stability and signal integrity in RF circuits and microcontrollers. Additionally, frequency counters play a critical role in calibrating equipment in laboratories, maintaining precision in frequency standards and network analyzers.
Key Uses of Timer Counters
Timer counters are primarily used for measuring time intervals, generating precise time delays, and creating PWM signals in embedded systems and microcontrollers. They enable accurate scheduling of tasks, event counting, and frequency measurement by counting clock pulses over a set period. Key applications include controlling motor speeds, timing events in real-time operating systems, and managing communication protocols where precise timing is critical.
Major Differences Between Frequency Counters and Timer Counters
Frequency counters measure the number of pulses or cycles per second to determine the frequency of a signal, while timer counters measure time intervals between events or the duration of a pulse. Frequency counters often feature high accuracy in measuring periodic signals, whereas timer counters excel at timing operations, pulse width measurements, and event counting. Your choice depends on whether you need precise frequency measurement or detailed timing analysis for electronic signals.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Device
Frequency counters provide precise measurement of signal frequency, offering high accuracy for repetitive signals but struggle with low-frequency or non-periodic waveforms. Timer counters excel in measuring time intervals and pulse durations, making them versatile for varied signal types but often have limited frequency resolution compared to dedicated frequency counters. The choice depends on application needs: frequency counters are ideal for stable signals with known frequency ranges, while timer counters suit time-based measurements and event counting with moderate frequency accuracy.
Choosing the Right Counter for Your Application
Selecting the right counter depends on whether your application requires measuring signal frequency or precise time intervals. Frequency counters excel at determining how many cycles occur per second, making them ideal for frequency analysis and tuning applications. Timer counters provide accurate time measurement between events, which is essential for tasks like pulse width modulation and event timing, ensuring your system captures the necessary temporal details.
Conclusion: Frequency Counter or Timer Counter?
Frequency counters excel at precisely measuring signal frequency, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate frequency analysis. Timer counters offer versatile timing and event counting capabilities, suitable for measuring pulse width, time intervals, and counting events. Your choice depends on whether accuracy in frequency measurement or flexible timing functions are the priority for your project.
frequency counter vs timer counter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com