Ball Grid Array (BGA) offers higher pin density and better thermal performance compared to Quad Flat Package (QFP), making it ideal for complex, high-speed applications. Discover the key differences and how each package can impact Your electronic designs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
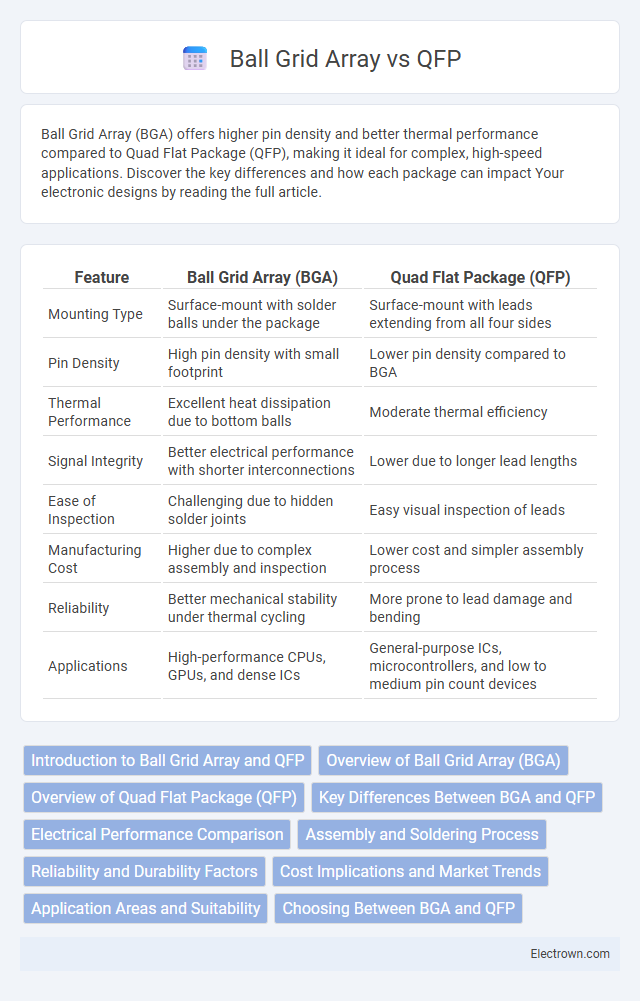
| Feature | Ball Grid Array (BGA) | Quad Flat Package (QFP) |
|---|---|---|
| Mounting Type | Surface-mount with solder balls under the package | Surface-mount with leads extending from all four sides |
| Pin Density | High pin density with small footprint | Lower pin density compared to BGA |
| Thermal Performance | Excellent heat dissipation due to bottom balls | Moderate thermal efficiency |
| Signal Integrity | Better electrical performance with shorter interconnections | Lower due to longer lead lengths |
| Ease of Inspection | Challenging due to hidden solder joints | Easy visual inspection of leads |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher due to complex assembly and inspection | Lower cost and simpler assembly process |
| Reliability | Better mechanical stability under thermal cycling | More prone to lead damage and bending |
| Applications | High-performance CPUs, GPUs, and dense ICs | General-purpose ICs, microcontrollers, and low to medium pin count devices |
Introduction to Ball Grid Array and QFP
Ball Grid Array (BGA) and Quad Flat Package (QFP) are two prominent types of surface-mount integrated circuit packaging used in electronics manufacturing. BGA features an array of solder balls on the underside of the package, providing superior electrical performance and heat dissipation compared to the flat leads of QFP, which extend from all four sides of the package. You should consider BGA for high-density applications due to its smaller footprint and better thermal management, while QFP is often chosen for its ease of inspection and cost-effectiveness.
Overview of Ball Grid Array (BGA)
Ball Grid Array (BGA) is a surface-mount packaging technology used for integrated circuits, characterized by an array of solder balls on the underside of the component that facilitates efficient electrical connection and heat dissipation. Compared to Quad Flat Package (QFP), BGA offers superior performance in terms of signal integrity and mechanical stability due to its shorter interconnect paths and lower inductance. Your choice of BGA can enhance circuit reliability and assembly density, making it ideal for high-performance applications in modern electronics.
Overview of Quad Flat Package (QFP)
The Quad Flat Package (QFP) features a square or rectangular body with leads extending from all four sides, commonly used in microcontrollers and integrated circuits. QFPs provide good thermal performance and ease of manual assembly due to their flat leads, making them suitable for medium to high pin count applications. Understanding the distinction between QFP and Ball Grid Array (BGA) helps optimize Your PCB design for space, reliability, and manufacturing processes.
Key Differences Between BGA and QFP
Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages use an array of solder balls on the underside for electrical connections, providing a smaller footprint and better heat dissipation compared to Quad Flat Package (QFP), which uses gull-wing leads extending from the sides. BGA offers superior performance in high-density applications due to its increased pin count and minimized inductance, while QFP is easier to inspect and solder with standard surface-mount technology processes. The choice between BGA and QFP depends on factors like assembly complexity, thermal management, and electrical performance requirements in electronic device design.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages offer superior electrical performance compared to Quad Flat Package (QFP) due to shorter interconnect lengths and lower parasitic inductance, which enhances signal integrity and reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI). BGAs enable higher pin density and improved thermal management, resulting in better power distribution and clock speed capabilities for high-frequency applications. In contrast, QFP's longer lead lengths increase the risk of signal degradation and limit their effectiveness in high-speed or high-density circuit designs.
Assembly and Soldering Process
Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages require precise alignment and controlled reflow soldering, as solder balls under the component melt to form robust, reliable joints on the PCB, enabling superior electrical performance and heat dissipation. Quad Flat Package (QFP) assembly involves soldering fine-pitched leads around the component's perimeter, which is more susceptible to bridging and requires meticulous inspection for solder joint quality. Your choice impacts soldering complexity and inspection methods, with BGA demanding X-ray inspection whereas QFP allows visual inspection of the solder joints.
Reliability and Durability Factors
Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages offer superior reliability and durability compared to Quad Flat Package (QFP) designs due to their robust solder ball connections that provide better stress distribution and reduced risk of solder joint fatigue. BGA's lower profile and evenly spaced solder balls enhance thermal performance and mechanical stability, minimizing issues like warping and cracking commonly seen in QFP's fine leads. The encapsulated balls in BGA also improve resistance to vibration and thermal cycling, which are critical factors in long-term electronic device performance and lifespan.
Cost Implications and Market Trends
Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages generally incur higher initial manufacturing costs compared to Quad Flat Package (QFP) due to their complex assembly and superior thermal performance, which benefits high-density and high-speed applications. Market trends indicate increasing adoption of BGA in consumer electronics and automotive sectors driven by miniaturization demands, while QFP remains cost-effective for lower pin-count and legacy designs. Understanding your project's volume and performance requirements can help optimize cost efficiency between these two packaging options.
Application Areas and Suitability
Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages are highly suitable for high-performance applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and high pin density, such as modern processors, GPUs, and complex communication devices. Quad Flat Package (QFP) designs are favored in consumer electronics, automotive control systems, and industrial equipment where moderate pin counts and ease of inspection or rework are critical. BGA is optimal for compact, densely packed circuit boards, whereas QFP provides better mechanical robustness and simpler manual soldering for medium-complexity assemblies.
Choosing Between BGA and QFP
Choosing between Ball Grid Array (BGA) and Quad Flat Package (QFP) depends on factors such as PCB space, thermal management, and signal integrity. BGA offers higher pin density and better heat dissipation, making it ideal for high-performance applications and compact designs. QFP is easier to inspect and rework, suitable for prototypes and lower pin count designs where cost and simplicity are priorities.
Ball Grid Array vs QFP Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com