Scan chain testing enhances digital circuit validation by connecting flip-flops in series, allowing easier fault detection during manufacturing, while boundary scan focuses on testing interconnections between integrated circuits without physical access. Explore the rest of the article to understand how each method can optimize Your testing strategy.
Table of Comparison
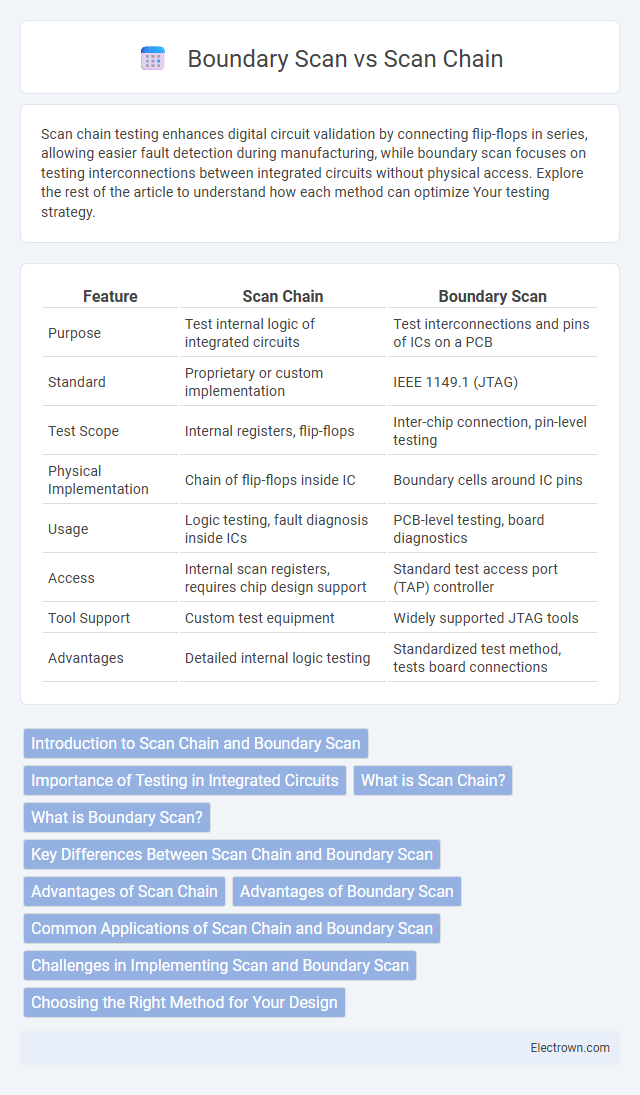
| Feature | Scan Chain | Boundary Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Test internal logic of integrated circuits | Test interconnections and pins of ICs on a PCB |
| Standard | Proprietary or custom implementation | IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) |
| Test Scope | Internal registers, flip-flops | Inter-chip connection, pin-level testing |
| Physical Implementation | Chain of flip-flops inside IC | Boundary cells around IC pins |
| Usage | Logic testing, fault diagnosis inside ICs | PCB-level testing, board diagnostics |
| Access | Internal scan registers, requires chip design support | Standard test access port (TAP) controller |
| Tool Support | Custom test equipment | Widely supported JTAG tools |
| Advantages | Detailed internal logic testing | Standardized test method, tests board connections |
Introduction to Scan Chain and Boundary Scan
Scan Chain and Boundary Scan are testing techniques used to improve fault detection in integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. Scan Chain tests internal registers by linking them into a serial chain, enabling efficient shift and capture of test data. Boundary Scan, defined by the IEEE 1149.1 standard, facilitates testing of interconnects and board-level faults by adding test cells at I/O pins, allowing you to verify connections without physical probes.
Importance of Testing in Integrated Circuits
Testing integrated circuits (ICs) ensures functionality, performance, and reliability, making Scan Chain and Boundary Scan critical methodologies. Scan Chain testing enhances fault detection within sequential logic by converting flip-flops into a shift register, facilitating efficient internal state observation. Boundary Scan, standardized by IEEE 1149.1, enables direct testing of interconnects and pins, improving system-level testability without physical probing.
What is Scan Chain?
Scan Chain is a testing methodology used in integrated circuits to enhance fault detection by connecting flip-flops in a sequential chain, enabling serial shifting of test data and observation of output responses. This technique facilitates easier debugging and validation of complex digital designs by allowing internal circuit states to be monitored and controlled during test operations. Scan Chain implementation is essential for improving test coverage and identifying manufacturing defects efficiently.
What is Boundary Scan?
Boundary Scan is a testing methodology standardized by IEEE 1149.1 that facilitates the detection of faults in integrated circuits and printed circuit boards without physical probing. It uses a serial shift register directly embedded into the device's boundary pins to control and observe signals, enabling efficient testing of interconnects between components. Your hardware debugging process benefits from Boundary Scan by allowing precise fault localization and testing access in complex electronic assemblies.
Key Differences Between Scan Chain and Boundary Scan
Scan chain focuses on testing internal logic by linking flip-flops in a controlled sequence, enabling efficient fault detection within integrated circuits. Boundary scan targets interconnect testing at the chip's pins and board-level integration by embedding test access ports compliant with the IEEE 1149.1 standard. The key difference lies in scan chain's internal circuit fault diagnosis versus boundary scan's external connectivity and system-level test capabilities.
Advantages of Scan Chain
Scan Chain offers distinct advantages in integrated circuit testing, including faster fault detection and easier diagnosis of manufacturing defects. It simplifies the testing process by reducing the complexity of test pattern generation and supports higher fault coverage through efficient serial data shifting. Your testing procedures benefit from Scan Chain's compatibility with standard design flows and lower hardware overhead compared to Boundary Scan.
Advantages of Boundary Scan
Boundary scan offers significant advantages over traditional scan chains by enabling testing and debugging of complex digital circuits without physical access to internal nodes. This method allows for faster fault detection and isolation through standardized IEEE 1149.1 protocols, improving test coverage and reducing manufacturing costs. Your design benefits from enhanced testability, especially in multi-layer PCB assemblies and densely packed integrated circuits.
Common Applications of Scan Chain and Boundary Scan
Scan Chain is commonly applied in integrated circuit testing for detecting manufacturing defects by shifting test data through a series of flip-flops, enabling efficient fault diagnosis in chip designs. Boundary Scan, standardized in IEEE 1149.1, is widely used for testing interconnections on printed circuit boards (PCBs) without physical probe access, facilitating board-level debugging and validation. Both techniques enhance test coverage and reduce time-to-market in semiconductor manufacturing and electronic assembly processes.
Challenges in Implementing Scan and Boundary Scan
Implementing scan chain testing faces challenges such as managing increased complexity in routing and ensuring minimal timing impact on critical paths. Boundary scan implementation requires careful consideration of pin multiplexing and standard compliance, which can complicate design verification and increase test setup time. Both approaches demand meticulous integration to balance test coverage and performance without compromising chip functionality.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Design
Choosing between Scan Chain and Boundary Scan depends on your design's complexity and testing requirements; Scan Chain excels in internal logic testing by linking flip-flops into shift registers, enabling efficient fault detection within integrated circuits. Boundary Scan focuses on testing interconnects between components at the board level, making it ideal for verifying solder joints and pin integrity without physical probing. Your decision should prioritize internal fault coverage with Scan Chain for logic-dense designs or use Boundary Scan when board-level connectivity and system integration testing are critical.
Scan Chain vs Boundary Scan Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com