Load pull and source pull are key techniques in RF design used to optimize device performance by varying load and source impedances respectively, enabling precise control of output power, gain, and linearity. Understanding these methods is essential for improving your circuit's efficiency and effectiveness, so continue reading to explore the detailed comparisons and applications.
Table of Comparison
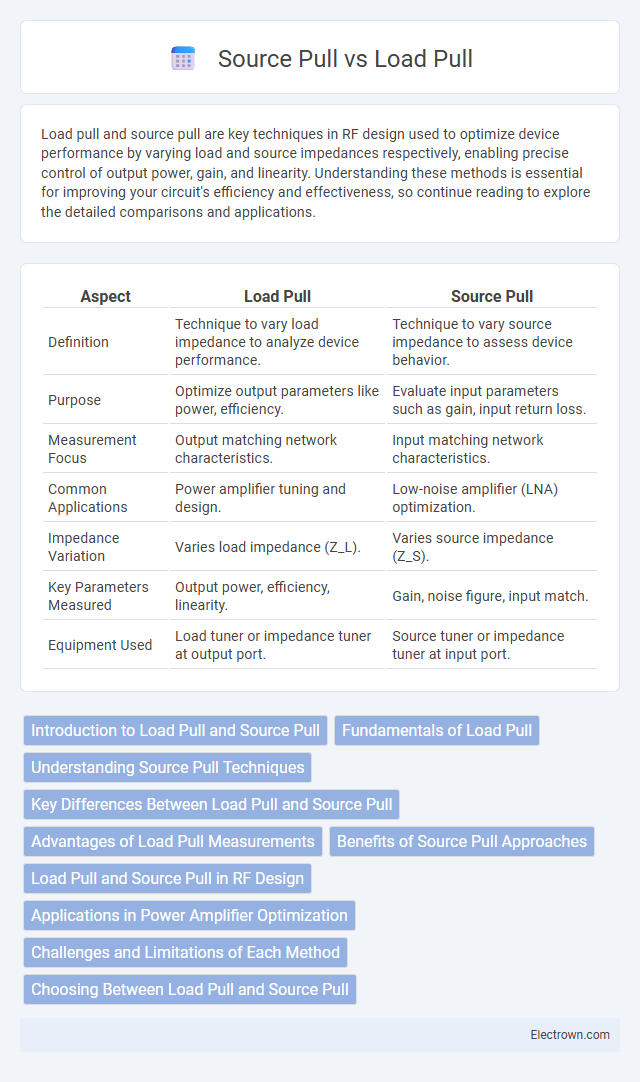
| Aspect | Load Pull | Source Pull |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique to vary load impedance to analyze device performance. | Technique to vary source impedance to assess device behavior. |
| Purpose | Optimize output parameters like power, efficiency. | Evaluate input parameters such as gain, input return loss. |
| Measurement Focus | Output matching network characteristics. | Input matching network characteristics. |
| Common Applications | Power amplifier tuning and design. | Low-noise amplifier (LNA) optimization. |
| Impedance Variation | Varies load impedance (Z_L). | Varies source impedance (Z_S). |
| Key Parameters Measured | Output power, efficiency, linearity. | Gain, noise figure, input match. |
| Equipment Used | Load tuner or impedance tuner at output port. | Source tuner or impedance tuner at input port. |
Introduction to Load Pull and Source Pull
Load pull and source pull are essential techniques in RF and microwave engineering used to characterize and optimize nonlinear devices like transistors. Load pull involves varying the load impedance presented to the device to analyze its performance under different conditions, while source pull adjusts the source impedance to assess the device's input characteristics. Your understanding of these methods helps in designing high-efficiency amplifiers by accurately determining optimal impedance matches for maximum gain, power, or linearity.
Fundamentals of Load Pull
Load Pull measures the impact of varying load impedances on an RF device's performance, enabling optimization of output power, efficiency, and linearity by systematically changing the load presented to the device. Source Pull evaluates the effects of different source impedances on input parameters such as gain and input match, crucial for achieving optimal device input conditions. Both techniques rely on precision impedance tuners and accurate network analyzers to characterize nonlinear behavior for robust RF design.
Understanding Source Pull Techniques
Source pull techniques are essential in RF amplifier design for optimizing input impedance to maximize performance parameters like gain and linearity. By varying source impedance during testing, engineers can characterize device behavior under different load conditions, facilitating precise matching network designs. This method contrasts with load pull, which focuses on output impedance, enabling comprehensive device optimization through iterative impedance tuning.
Key Differences Between Load Pull and Source Pull
Load pull and source pull are essential measurement techniques in RF design used to optimize device performance by varying impedance conditions. Load pull focuses on altering the load impedance presented to the device under test to maximize parameters such as output power and efficiency, while source pull adjusts the source impedance to improve input matching and device gain. The key difference lies in their application: load pull targets output-side optimization, whereas source pull concentrates on input-side impedance tuning for enhanced overall device characterization.
Advantages of Load Pull Measurements
Load pull measurements provide precise control of impedance conditions, enabling accurate evaluation of power amplifier performance under realistic operating environments. By varying the load impedances systematically, you can optimize device characteristics such as gain, efficiency, and linearity more effectively than with source pull methods alone. These measurements enhance the design process by offering detailed insight into the impacts of load variations on device behavior, ensuring improved circuit reliability and performance.
Benefits of Source Pull Approaches
Source pull approaches offer precise control over input impedance, enabling accurate characterization of nonlinear devices under real operating conditions. These techniques enhance measurement flexibility and repeatability compared to load pull, allowing you to optimize device performance efficiently. By directly adjusting the source impedance, source pull methods provide improved insight into device behavior, leading to better design outcomes.
Load Pull and Source Pull in RF Design
Load Pull and Source Pull are critical techniques in RF design for optimizing transistor performance by varying impedance conditions at the output and input terminals, respectively. Load Pull focuses on adjusting the load impedance to maximize power, gain, or efficiency, while Source Pull adjusts the source impedance to enhance linearity or noise figure. Your RF design process benefits significantly from applying both methods to achieve optimal device matching and performance across frequency bands.
Applications in Power Amplifier Optimization
Load pull techniques are critical in power amplifier optimization for identifying the optimal impedance that maximizes output power and efficiency by varying the load conditions. Source pull complements this by adjusting the source impedance to enhance the stability and linearity of the amplifier, aiding in bias point optimization and gain improvement. Together, load pull and source pull measurements enable precise impedance tuning, crucial for designing high-performance power amplifiers in RF and microwave systems.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Load pull techniques face challenges in accurately representing nonlinear device behavior under high-power conditions, often limited by the available tuner dynamic range and calibration complexity. Source pull methods struggle with isolating the intrinsic device characteristics due to the difficulty in precisely controlling and measuring source impedance, which can lead to less reliable parameter extraction. Your choice between load pull and source pull should consider these limitations to optimize design accuracy and measurement efficiency.
Choosing Between Load Pull and Source Pull
Choosing between load pull and source pull depends on the specific amplifier or transistor characterization needs. Load pull is used to optimize output matching for maximum power or efficiency by varying the load impedance, while source pull focuses on input impedance to enhance gain or linearity. Proper selection improves device performance by targeting either output conditions or input matching based on design goals.
Load Pull vs Source Pull Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com