PMMA light guides offer excellent optical clarity and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for applications requiring efficient light transmission and lightweight design. Discover how polycarbonate light guides compare in impact resistance and durability to ensure Your project achieves the best performance by reading further.
Table of Comparison
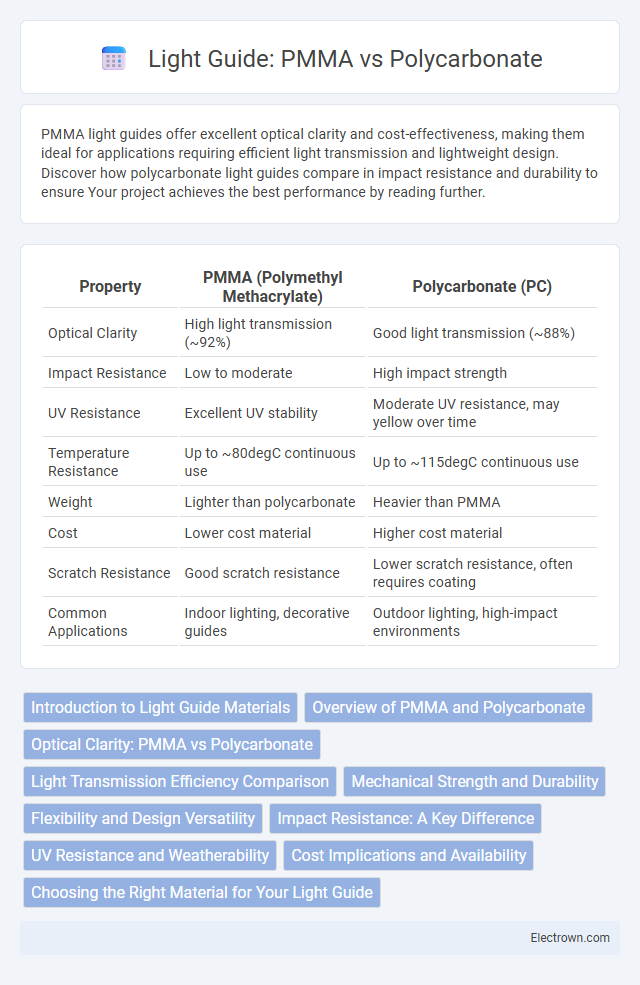
| Property | PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Clarity | High light transmission (~92%) | Good light transmission (~88%) |
| Impact Resistance | Low to moderate | High impact strength |
| UV Resistance | Excellent UV stability | Moderate UV resistance, may yellow over time |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to ~80degC continuous use | Up to ~115degC continuous use |
| Weight | Lighter than polycarbonate | Heavier than PMMA |
| Cost | Lower cost material | Higher cost material |
| Scratch Resistance | Good scratch resistance | Lower scratch resistance, often requires coating |
| Common Applications | Indoor lighting, decorative guides | Outdoor lighting, high-impact environments |
Introduction to Light Guide Materials
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) and Polycarbonate are widely used materials in light guide applications due to their excellent optical clarity and light transmission properties. PMMA offers higher light transmittance, typically around 92-94%, making it ideal for applications requiring superior brightness and clarity. Polycarbonate provides greater impact resistance and durability, with a refractive index close to PMMA, balancing optical performance with mechanical strength for robust light guide solutions.
Overview of PMMA and Polycarbonate
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent light transmittance and optical clarity, commonly used in light guides for its low cost and good UV resistance. Polycarbonate, another transparent thermoplastic, offers superior impact resistance and higher heat tolerance, making it ideal for light guides in demanding environments. Both materials differ in mechanical properties and environmental durability, influencing their selection based on application-specific requirements.
Optical Clarity: PMMA vs Polycarbonate
PMMA offers superior optical clarity with light transmittance up to 92%, making it ideal for applications requiring bright, clear light guides. Polycarbonate typically transmits around 88% of light but provides higher impact resistance and heat tolerance, which can affect clarity under stress or prolonged use. Your choice depends on prioritizing either maximum transparency with PMMA or durability with polycarbonate for light guide performance.
Light Transmission Efficiency Comparison
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) light guides typically offer higher light transmission efficiency, with values around 92-94%, due to their excellent optical clarity and low absorption rates. Polycarbonate light guides, while more impact-resistant, usually have slightly lower transmission efficiency, approximately 88-90%, because of higher internal scattering and absorption. Choosing PMMA will maximize your light guide's brightness and clarity in applications where optical performance is critical.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polycarbonate light guides exhibit superior mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to PMMA, making them ideal for applications requiring high durability and toughness. While PMMA offers good optical clarity, it is more prone to cracking and abrasion under mechanical stress, limiting its lifespan in demanding environments. Choosing polycarbonate enhances the longevity and reliability of Your light guide system in robust, high-impact settings.
Flexibility and Design Versatility
PMMA light guides offer excellent design versatility due to their ease of machining and ability to form complex shapes with high optical clarity. Polycarbonate light guides provide superior flexibility and impact resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring robust bending and durability. Both materials support tailored light distribution, but polycarbonate excels in flexible designs where mechanical stress is a concern.
Impact Resistance: A Key Difference
Polycarbonate light guides exhibit superior impact resistance compared to PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate), making them ideal for applications requiring high durability and toughness. PMMA, while offering excellent optical clarity, tends to be more brittle and susceptible to cracking under mechanical stress. The enhanced impact resistance of polycarbonate ensures longer lifespan and reliability in demanding lighting environments.
UV Resistance and Weatherability
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) exhibits excellent UV resistance, maintaining clarity and structural integrity under prolonged sunlight exposure, making it ideal for outdoor light guide applications. Polycarbonate, while tougher and more impact-resistant, is less UV stable and tends to yellow or degrade faster without UV-stabilizing additives. Your choice should consider the environmental conditions, as PMMA offers superior weatherability and long-term performance in UV-intensive settings.
Cost Implications and Availability
PMMA light guides are generally more cost-effective due to lower material and manufacturing expenses, making them suitable for budget-sensitive projects. Polycarbonate light guides offer superior durability and impact resistance but come at a higher price and may require specialized suppliers, affecting availability. You should weigh the balance between cost efficiency and material performance based on project demands and supply chain access.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Light Guide
PMMA offers excellent optical clarity and is cost-effective, making it ideal for light guides requiring high light transmission and aesthetic appeal. Polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and thermal stability, suitable for environments with mechanical stress or temperature variations. Choosing the right material for your light guide depends on balancing optical performance with durability demands specific to your application.
PMMA vs Polycarbonate light guide Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com