LED displays use light-emitting diodes for backlighting, offering bright visuals and energy efficiency, while OLED screens feature organic compounds that emit light individually, resulting in deeper blacks and superior contrast. Discover how these differences impact your viewing experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
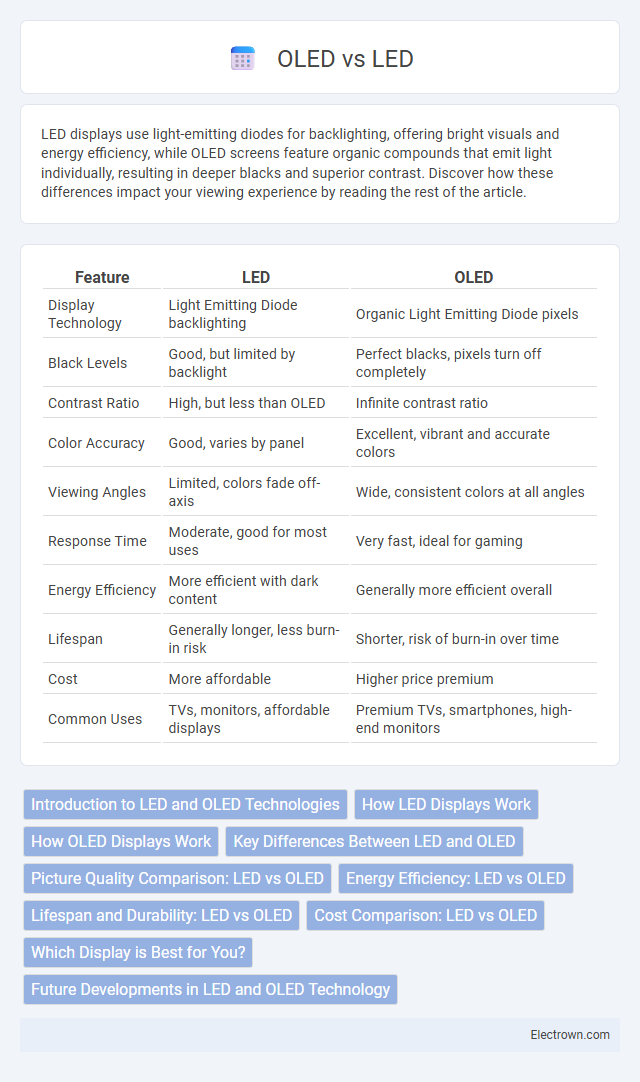
| Feature | LED | OLED |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Light Emitting Diode backlighting | Organic Light Emitting Diode pixels |
| Black Levels | Good, but limited by backlight | Perfect blacks, pixels turn off completely |
| Contrast Ratio | High, but less than OLED | Infinite contrast ratio |
| Color Accuracy | Good, varies by panel | Excellent, vibrant and accurate colors |
| Viewing Angles | Limited, colors fade off-axis | Wide, consistent colors at all angles |
| Response Time | Moderate, good for most uses | Very fast, ideal for gaming |
| Energy Efficiency | More efficient with dark content | Generally more efficient overall |
| Lifespan | Generally longer, less burn-in risk | Shorter, risk of burn-in over time |
| Cost | More affordable | Higher price premium |
| Common Uses | TVs, monitors, affordable displays | Premium TVs, smartphones, high-end monitors |
Introduction to LED and OLED Technologies
LED technology uses light-emitting diodes to produce images by illuminating an LCD panel, offering bright displays with energy efficiency and long lifespan. OLED, or organic light-emitting diode, features self-illuminating pixels that provide superior contrast, deeper blacks, and wider viewing angles compared to traditional LEDs. Your choice between LED and OLED impacts display quality, with OLED excelling in color accuracy and LED often being more cost-effective.
How LED Displays Work
LED displays work by using light-emitting diodes as backlighting sources behind an LCD panel, where each LED illuminates the pixels selectively to produce images with high brightness and energy efficiency. The LEDs emit white or colored light, which passes through liquid crystal layers that modulate the light based on electrical signals to create color and contrast. This technology allows precise control over brightness levels and improves display durability compared to traditional LCD screens.
How OLED Displays Work
OLED displays operate through organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through them, enabling each pixel to produce its own light independently. This self-emissive technology allows OLED screens to achieve true blacks and high contrast ratios by turning off pixels completely in dark areas. The absence of a backlight in OLED panels also results in thinner displays with faster response times compared to traditional LED screens.
Key Differences Between LED and OLED
LED displays use a backlight to illuminate pixels, resulting in lower contrast ratios and less vibrant colors compared to OLED screens. OLED technology features self-emissive pixels, allowing for true blacks, higher contrast, and better energy efficiency in dark scenes. OLED panels typically offer faster response times and wider viewing angles than traditional LED displays.
Picture Quality Comparison: LED vs OLED
OLED displays deliver superior picture quality with deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios compared to LED screens, thanks to their self-emissive pixels that can turn off individually. LED TVs rely on backlighting, which often results in less accurate black levels and potential light bleed, reducing overall image sharpness and color vibrancy. OLED technology excels in color accuracy and viewing angles, providing a more immersive and true-to-life visual experience than traditional LED panels.
Energy Efficiency: LED vs OLED
LED displays typically consume less power than OLEDs because they use a backlight that can be dimmed or turned off selectively, improving energy efficiency in bright scenes. OLED panels feature individually lit pixels that emit their own light, providing perfect blacks but generally drawing more power in bright or colorful images. Your choice between LED and OLED should consider your typical usage patterns and energy consumption preferences to optimize efficiency.
Lifespan and Durability: LED vs OLED
LED displays generally offer a longer lifespan and greater durability compared to OLED screens, with LED panels often lasting over 50,000 hours without significant brightness loss. OLED technology, while delivering superior contrast and color accuracy, is more prone to burn-in and gradual pixel degradation over time, which can reduce overall display longevity. Choosing an LED display can better suit your needs if durability and extended lifespan are critical factors for your device usage.
Cost Comparison: LED vs OLED
LED displays generally cost less than OLED screens due to simpler manufacturing processes and more established production lines. OLED technology, featuring self-emissive pixels, tends to be pricier but offers superior contrast and color accuracy, impacting the overall value proposition. Your choice between LED and OLED should consider budget constraints alongside the desired picture quality and long-term investment.
Which Display is Best for You?
OLED displays offer superior contrast ratios and deeper blacks due to their self-emissive pixels, making them ideal for dark-room viewing and vibrant colors. LED screens, often more affordable and energy-efficient, provide brighter displays suitable for well-lit environments and prolonged use. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize vivid picture quality with OLED or budget-friendly brightness with LED.
Future Developments in LED and OLED Technology
Future developments in LED technology emphasize mini-LED and micro-LED innovations, promising higher brightness, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced lifespan compared to traditional LEDs. OLED advancements focus on flexible, transparent displays and increased durability through improved organic materials and encapsulation techniques. Both technologies aim to revolutionize display quality in smartphones, televisions, and wearable devices by enhancing color accuracy, contrast ratios, and power consumption.
LED vs OLED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com