Soft recovery diodes feature reduced reverse recovery time and lower switching losses compared to standard diodes, enhancing efficiency and performance in high-frequency applications. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your choice of diode impacts circuit reliability and thermal management.
Table of Comparison
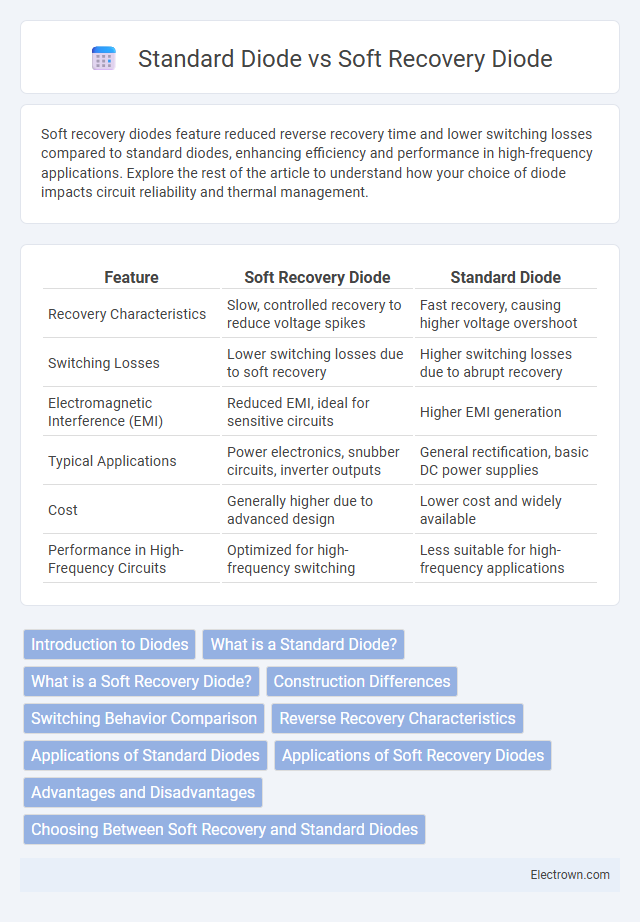
| Feature | Soft Recovery Diode | Standard Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery Characteristics | Slow, controlled recovery to reduce voltage spikes | Fast recovery, causing higher voltage overshoot |
| Switching Losses | Lower switching losses due to soft recovery | Higher switching losses due to abrupt recovery |
| Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) | Reduced EMI, ideal for sensitive circuits | Higher EMI generation |
| Typical Applications | Power electronics, snubber circuits, inverter outputs | General rectification, basic DC power supplies |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced design | Lower cost and widely available |
| Performance in High-Frequency Circuits | Optimized for high-frequency switching | Less suitable for high-frequency applications |
Introduction to Diodes
Soft recovery diodes offer reduced switching losses and lower electromagnetic interference compared to standard diodes due to their controlled reverse recovery characteristics. Unlike standard diodes, which exhibit abrupt switching and generate higher peak currents, soft recovery diodes improve efficiency and reliability in high-frequency power electronics applications. Your choice between these diodes impacts overall circuit performance, especially in switching power supplies and inverter designs.
What is a Standard Diode?
A standard diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction, commonly used for rectification in power supplies. It typically exhibits a fast recovery time but generates higher switching losses and more electromagnetic interference during turn-off. Understanding these characteristics helps you choose between a standard diode and a soft recovery diode for improved efficiency in your electronic circuits.
What is a Soft Recovery Diode?
A Soft Recovery Diode is designed to reduce switching losses and electromagnetic interference by controlling the rate of current decrease during the diode's turn-off period, unlike a Standard Diode which typically exhibits a rapid and harsh recovery. This diode uses tailored semiconductor structures to minimize voltage spikes and oscillations, improving efficiency in high-frequency applications such as power converters and motor drives. Your choice of a Soft Recovery Diode can significantly enhance system reliability and reduce noise in switching circuits.
Construction Differences
Soft recovery diodes feature a specialized semiconductor structure with a softer reverse recovery characteristic, utilizing graded junctions or tailored doping profiles to minimize voltage spikes and reduce electromagnetic interference. Standard diodes have a simpler, abrupt PN junction design that leads to a rapid transition from conducting to blocking state, causing higher switching losses and increased voltage overshoot. Understanding these construction differences enables you to select the ideal diode type for efficient power switching applications requiring low noise and reduced electromagnetic emissions.
Switching Behavior Comparison
Soft recovery diodes exhibit a smoother switching behavior with reduced reverse recovery current and lower voltage spikes compared to standard diodes, enhancing efficiency in high-frequency applications. The controlled recombination process in soft recovery diodes minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI) and switching losses, resulting in improved thermal performance and reliability. Standard diodes typically generate higher reverse recovery charges, causing increased power dissipation and stress on circuit components during switching transitions.
Reverse Recovery Characteristics
Soft recovery diodes exhibit significantly reduced reverse recovery time and lower peak reverse recovery current compared to standard diodes, resulting in minimized switching losses and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Their controlled recovery behavior prevents voltage spikes and ringing during the transition from conducting to blocking state, enhancing circuit reliability and efficiency. Standard diodes typically experience abrupt switching with higher reverse recovery charge, leading to increased power dissipation and stress on circuit components.
Applications of Standard Diodes
Standard diodes are widely used in applications such as rectification in power supplies, voltage clamping, and signal demodulation due to their fast switching speeds and low cost. They are preferred in circuits where high efficiency and minimal switching losses are not critical factors. Common uses include AC to DC conversion in power adapters, voltage protection in electronic devices, and general switching tasks in low-frequency circuits.
Applications of Soft Recovery Diodes
Soft recovery diodes are essential in high-efficiency power electronics, where minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and voltage spikes during switching is critical. These diodes are widely used in applications such as power supplies, motor drives, and renewable energy inverters to enhance performance and reduce energy loss. Your circuits benefit from improved reliability and lower switching noise when integrating soft recovery diodes compared to standard diodes.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Soft recovery diodes offer reduced switching losses and minimized electromagnetic interference compared to standard diodes, making them ideal for high-frequency applications. However, they typically have higher manufacturing costs and lower current ratings, which may limit their use in heavy-duty circuits. Your choice between these diodes depends on prioritizing efficiency and noise reduction versus cost and current capacity.
Choosing Between Soft Recovery and Standard Diodes
Soft recovery diodes are designed to minimize voltage spikes and switching losses by controlling the diode's reverse recovery behavior, making them ideal for high-frequency and high-efficiency power applications. Standard diodes exhibit faster reverse recovery but can generate higher electromagnetic interference and increased switching losses, suitable for low-cost and less demanding circuits. Selecting between soft recovery and standard diodes depends on the application's switching speed, efficiency requirements, and tolerance for electromagnetic noise.
Soft recovery diode vs Standard diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com