Analog controllers in SMPS offer simplicity and fast transient response, while digital controllers provide enhanced flexibility, programmability, and precise control over multiple parameters. Explore the detailed comparison to determine which controller best suits Your power supply needs.
Table of Comparison
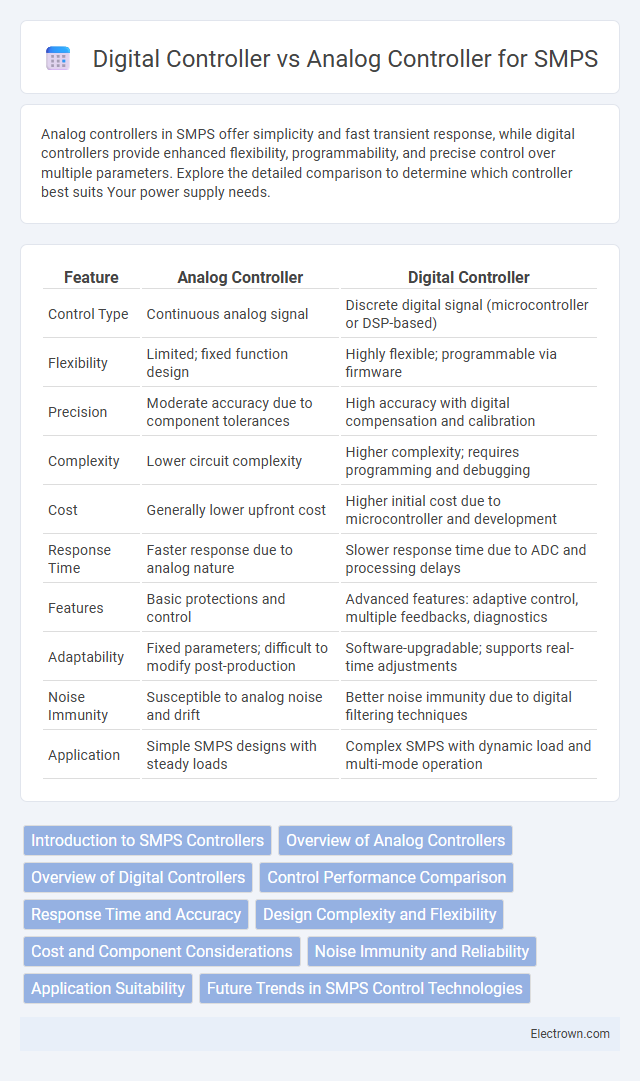
| Feature | Analog Controller | Digital Controller |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Continuous analog signal | Discrete digital signal (microcontroller or DSP-based) |
| Flexibility | Limited; fixed function design | Highly flexible; programmable via firmware |
| Precision | Moderate accuracy due to component tolerances | High accuracy with digital compensation and calibration |
| Complexity | Lower circuit complexity | Higher complexity; requires programming and debugging |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost due to microcontroller and development |
| Response Time | Faster response due to analog nature | Slower response time due to ADC and processing delays |
| Features | Basic protections and control | Advanced features: adaptive control, multiple feedbacks, diagnostics |
| Adaptability | Fixed parameters; difficult to modify post-production | Software-upgradable; supports real-time adjustments |
| Noise Immunity | Susceptible to analog noise and drift | Better noise immunity due to digital filtering techniques |
| Application | Simple SMPS designs with steady loads | Complex SMPS with dynamic load and multi-mode operation |
Introduction to SMPS Controllers
SMPS controllers regulate the power supply by managing voltage and current to ensure efficient energy conversion. Analog controllers use continuous signals to adjust the duty cycle, offering simplicity and low latency, while digital controllers employ microprocessors for precise control, programmability, and advanced features. Choosing the right controller for your SMPS depends on the balance between flexibility, complexity, and performance requirements.
Overview of Analog Controllers
Analog controllers for SMPS use continuous voltage or current signals to regulate power conversion, offering simplicity and low latency in response to load changes. These controllers rely on classic operational amplifier circuits and error amplifiers to maintain output voltage stability, making them effective for basic and cost-sensitive applications. You can expect analog controllers to excel in scenarios demanding real-time adjustments with minimal processing overhead.
Overview of Digital Controllers
Digital controllers for SMPS provide precise regulation through programmable algorithms and real-time feedback, enhancing efficiency and adaptability in power management. They support complex control strategies such as PID, adaptive control, and fault diagnostics, which improve performance over traditional analog controllers. Your SMPS design benefits from increased flexibility, easier firmware updates, and integration with digital interfaces for monitoring and control.
Control Performance Comparison
Analog controllers in SMPS offer fast response times and simple circuit designs, ensuring low latency in voltage regulation. Digital controllers provide superior precision and flexibility due to programmable parameters and advanced compensation algorithms, allowing adaptive control under varying load conditions. Overall, digital control achieves higher accuracy and stability in complex applications, while analog control excels in cost-effective and low-latency scenarios.
Response Time and Accuracy
Analog controllers in SMPS offer faster response times due to continuous signal processing, enabling quick adjustments to load variations and minimizing output voltage ripple. Digital controllers provide higher accuracy through precise computational algorithms, adaptive tuning, and error correction capabilities, ensuring stable output under varying conditions. Your choice depends on prioritizing swift response for transient loads (analog) or fine-tuned accuracy and programmability (digital).
Design Complexity and Flexibility
Analog controllers for SMPS feature simpler design complexity with fewer components, making them easier to implement but less adaptable to varying load conditions. Digital controllers offer greater design flexibility through programmable parameters and adaptive algorithms, enabling precise control and optimization for diverse applications. The software-centric nature of digital controllers allows rapid updates and complex control strategies that analog designs cannot easily replicate.
Cost and Component Considerations
Analog controllers for SMPS typically offer lower initial cost and simpler design with fewer components, making them suitable for cost-sensitive applications. Digital controllers, while generally more expensive due to microcontrollers and firmware development, enable integration of advanced features that can reduce overall system complexity and component count. Component considerations favor analog designs for minimal BOM cost, whereas digital controllers can optimize performance and flexibility despite higher upfront expenses.
Noise Immunity and Reliability
Analog controllers in SMPS offer superior noise immunity due to their continuous signal processing, which reduces susceptibility to high-frequency electromagnetic interference commonly encountered in switching environments. Digital controllers provide enhanced reliability through precise programming, facilitating adaptive control and fault detection that minimize component stress and extend system lifespan. Noise immunity in digital controllers depends largely on robust firmware and hardware design, while analog solutions benefit from inherent signal filtering capabilities.
Application Suitability
Analog controllers in SMPS are well-suited for applications requiring simplicity, low cost, and fast transient response, often found in low to mid-power supplies. Digital controllers excel in applications demanding precise regulation, adaptive control, and complex system integration, such as high-performance computing and telecommunications equipment. Their programmability allows for advanced features like fault diagnostics and multi-mode operation, making them ideal for sophisticated power management solutions.
Future Trends in SMPS Control Technologies
Future trends in SMPS control technologies emphasize the shift from analog controllers to digital controllers due to their enhanced precision, flexibility, and real-time monitoring capabilities. Digital controllers enable advanced features such as adaptive control algorithms, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with IoT devices, which improve efficiency and reliability for your power supply systems. The transition supports scalable and programmable designs, allowing manufacturers to optimize performance and implement rapid firmware updates without hardware changes.
analog controller vs digital controller for smps Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com