LCL filters offer superior harmonic attenuation and reduced switching ripple compared to traditional LC filters, making them ideal for applications requiring enhanced power quality, such as grid-connected inverters. Discover how choosing the right filter can optimize your system's performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
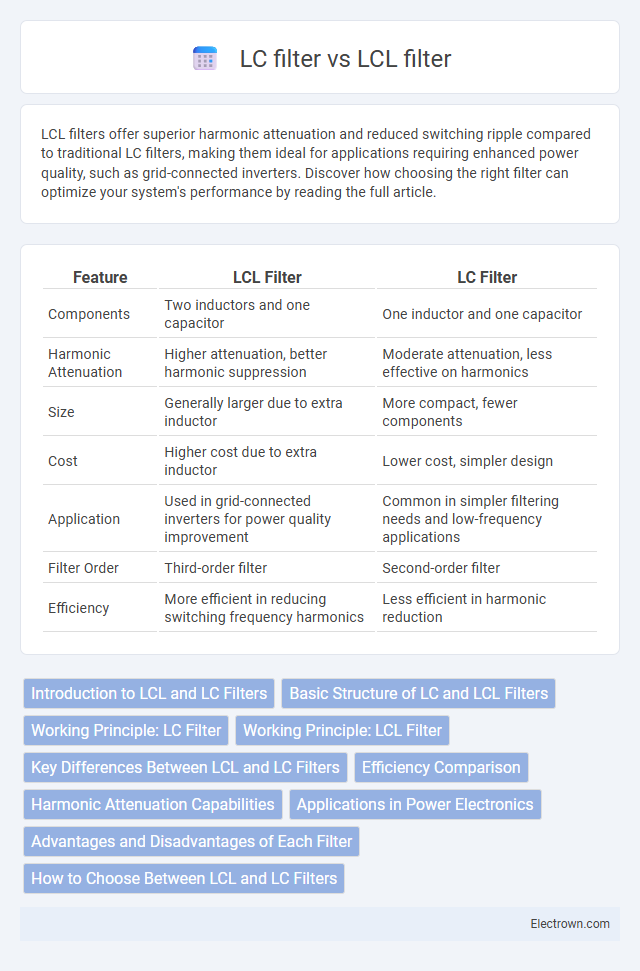
| Feature | LCL Filter | LC Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Components | Two inductors and one capacitor | One inductor and one capacitor |
| Harmonic Attenuation | Higher attenuation, better harmonic suppression | Moderate attenuation, less effective on harmonics |
| Size | Generally larger due to extra inductor | More compact, fewer components |
| Cost | Higher cost due to extra inductor | Lower cost, simpler design |
| Application | Used in grid-connected inverters for power quality improvement | Common in simpler filtering needs and low-frequency applications |
| Filter Order | Third-order filter | Second-order filter |
| Efficiency | More efficient in reducing switching frequency harmonics | Less efficient in harmonic reduction |
Introduction to LCL and LC Filters
LCL and LC filters are essential components in power electronics for reducing harmonic distortion and improving power quality in inverter-based systems. An LC filter consists of one inductor and one capacitor connected in series or parallel to attenuate high-frequency switching harmonics, while an LCL filter adds an extra inductor and capacitor stage, enhancing harmonic attenuation and reducing grid current distortion. The LCL filter's design complexity and improved filtering performance make it preferable for high-power applications requiring stringent harmonic standards such as IEEE 519.
Basic Structure of LC and LCL Filters
LC filters consist of a single inductor and capacitor arranged in series or parallel to smooth voltage and current waveforms. LCL filters incorporate an additional inductor and capacitor stage, forming a three-component network that enhances harmonic attenuation and reduces high-frequency noise more effectively. Your choice between LC and LCL filters depends on the required filtering performance and system complexity.
Working Principle: LC Filter
The LC filter operates by utilizing an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C) connected in series or parallel to form a resonant circuit that attenuates unwanted high-frequency noise in power electronics. The inductor blocks rapid current changes while the capacitor shunts high-frequency harmonics to ground, effectively smoothing voltage and current waveforms. This working principle makes LC filters essential in reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improving power quality in inverters and converters.
Working Principle: LCL Filter
The LCL filter operates by combining inductors and capacitors in a three-component structure to effectively attenuate high-frequency harmonic currents in power converters. Its working principle relies on the resonance between the two inductors and the capacitor to enhance the filtering of switching harmonics, resulting in improved power quality and reduced electromagnetic interference. Compared to the traditional LC filter, the LCL filter offers superior performance in mitigating high-frequency noise while maintaining lower overall inductance and cost.
Key Differences Between LCL and LC Filters
LCL filters feature an additional inductor compared to LC filters, significantly enhancing harmonic attenuation and reducing switching ripple in power electronics systems. LC filters consist of a single inductor and capacitor, providing basic filtering but less effective in suppressing high-frequency noise. You can achieve improved grid compatibility and reduced electromagnetic interference with LCL filters, making them ideal for applications requiring stringent power quality standards.
Efficiency Comparison
LCL filters provide higher efficiency in power conversion by offering better harmonic attenuation and reduced switching losses compared to traditional LC filters. Your system benefits from improved grid compliance and lower total harmonic distortion, enhancing overall performance in renewable energy applications. LC filters typically result in higher losses due to less effective damping and larger component sizes, making LCL filters the preferred choice for efficient power electronics.
Harmonic Attenuation Capabilities
LCL filters provide superior harmonic attenuation compared to LC filters due to their three-component design, which effectively reduces high-frequency harmonics in power systems. The inclusion of an additional inductor in LCL filters enhances the filter's ability to dampen harmonic distortion, improving overall power quality and reducing electromagnetic interference. You can achieve more efficient harmonic suppression with LCL filters, making them ideal for applications requiring stringent harmonic standards.
Applications in Power Electronics
LCL filters offer superior harmonic attenuation and are widely used in grid-connected inverters for renewable energy systems, enhancing power quality by reducing high-frequency switching noise. LC filters, simpler and cost-effective, are commonly applied in basic power converter circuits to smooth output voltage and minimize current ripple. Choosing the right filter depends on your system's harmonic reduction needs and design complexity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Filter
LCL filters offer superior harmonic attenuation and reduced size compared to LC filters, making them ideal for high-frequency applications in power converters. However, LCL filters tend to be more complex to design and may introduce resonance issues that require damping techniques. LC filters are simpler and more cost-effective but provide less effective harmonic suppression, often resulting in larger components and increased losses.
How to Choose Between LCL and LC Filters
Choosing between LCL and LC filters depends on the specific harmonic attenuation and system stability requirements of your application. LCL filters offer superior high-frequency harmonic suppression and better damping characteristics, making them ideal for grid-connected inverters, while LC filters provide simpler design and lower cost suitable for less demanding scenarios. Evaluate factors such as switching frequency, allowed total harmonic distortion (THD), and system resonance to determine the optimal filter type for your power electronics setup.
LCL filter vs LC filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com