Single loop control focuses on correcting errors without questioning underlying policies, while double loop control challenges and modifies the root causes of errors by re-evaluating goals and assumptions. Discover how understanding these control mechanisms can enhance Your decision-making and organizational learning by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
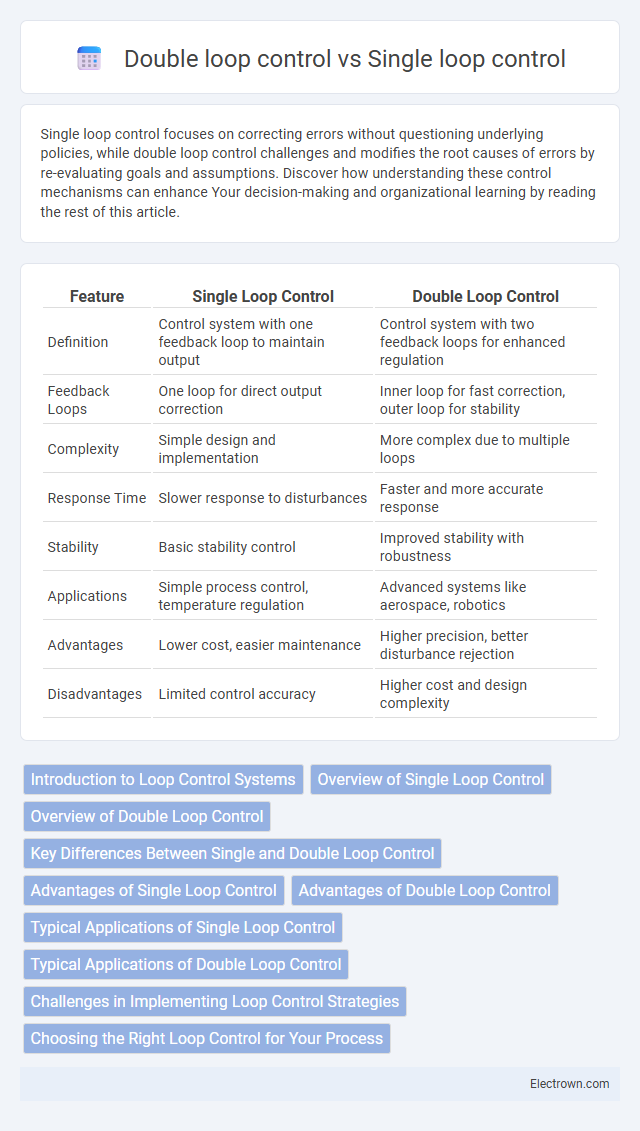
| Feature | Single Loop Control | Double Loop Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control system with one feedback loop to maintain output | Control system with two feedback loops for enhanced regulation |
| Feedback Loops | One loop for direct output correction | Inner loop for fast correction, outer loop for stability |
| Complexity | Simple design and implementation | More complex due to multiple loops |
| Response Time | Slower response to disturbances | Faster and more accurate response |
| Stability | Basic stability control | Improved stability with robustness |
| Applications | Simple process control, temperature regulation | Advanced systems like aerospace, robotics |
| Advantages | Lower cost, easier maintenance | Higher precision, better disturbance rejection |
| Disadvantages | Limited control accuracy | Higher cost and design complexity |
Introduction to Loop Control Systems
Single loop control systems regulate a process by comparing the output to a predefined setpoint and making adjustments based on this error signal. Double loop control systems enhance this approach by incorporating an additional feedback loop, which adjusts the setpoint or system parameters dynamically for improved stability and performance under varying conditions. These systems are widely used in industrial automation to optimize control accuracy and responsiveness.
Overview of Single Loop Control
Single loop control involves a feedback mechanism that adjusts system behavior based on deviations from a set point, ensuring stable and consistent performance. It primarily monitors outputs and makes corrections without questioning underlying assumptions or goals. Your process efficiency improves through straightforward error correction, making single loop control suitable for routine, predictable environments.
Overview of Double Loop Control
Double loop control enhances traditional single loop control by incorporating a secondary feedback loop that adjusts the control parameters based on system performance, allowing for adaptive correction beyond immediate outputs. This method improves system resilience and learning by continuously questioning and modifying the underlying assumptions and goals, leading to more robust and flexible control in complex environments. You benefit from double loop control when managing dynamic systems that require ongoing optimization and error correction at both the operational and strategic levels.
Key Differences Between Single and Double Loop Control
Single loop control primarily focuses on correcting errors by adjusting actions within a fixed set of rules or parameters, emphasizing immediate problem resolution. Double loop control goes deeper by questioning and modifying the underlying policies, objectives, and assumptions that guide actions, enabling adaptive learning and systemic change. This fundamental difference allows double loop control to address root causes rather than just symptoms, making it more effective for complex and evolving systems.
Advantages of Single Loop Control
Single loop control offers simplicity and faster response times by continuously correcting errors between the desired setpoint and the process variable using a single feedback loop. This approach reduces system complexity and minimizes computational load, making it ideal for straightforward processes where precise adjustments are not critical. You benefit from increased reliability and easier implementation in automation systems with single loop control.
Advantages of Double Loop Control
Double loop control enhances system adaptability by continuously evaluating and adjusting underlying goals and assumptions, leading to improved problem-solving in dynamic environments. Your processes become more resilient to disturbances and uncertainty, ensuring higher accuracy and long-term performance stability compared to single loop control. This method fosters deeper organizational learning by challenging existing strategies rather than merely correcting errors.
Typical Applications of Single Loop Control
Single loop control is commonly applied in temperature regulation systems, such as HVAC units, where maintaining a set temperature is critical for comfort and efficiency. It is also widely used in industrial processes like pressure control in boilers and flow control in chemical reactors, ensuring consistent operation within predefined parameters. These systems benefit from the simplicity and reliability of single loop control for maintaining steady-state conditions.
Typical Applications of Double Loop Control
Double loop control is typically applied in complex systems requiring adaptive and strategic decision-making, such as organizational management, robotics, and artificial intelligence. It allows systems to modify underlying goals and control parameters based on feedback, enhancing flexibility and learning in dynamic environments. Industries like manufacturing and autonomous vehicle navigation leverage double loop control to optimize performance and respond to unpredicted disturbances effectively.
Challenges in Implementing Loop Control Strategies
Implementing single loop control often faces challenges related to limited adaptability and slow response to dynamic system changes, restricting its effectiveness in complex environments. Double loop control strategies encounter difficulties in accurately diagnosing root causes due to the need for deeper system understanding and increased computational resources for feedback processing. Both approaches require careful tuning and integration with real-time system monitoring to avoid instability and performance degradation.
Choosing the Right Loop Control for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate loop control depends on process complexity and control objectives; single loop control efficiently manages straightforward, stable processes by maintaining a single variable within set parameters. Double loop control enhances adaptability by adjusting both the control variable and the setpoint based on feedback, making it ideal for dynamic or uncertain environments. Understanding the process dynamics and desired responsiveness ensures optimal performance and stability in automated systems.
single loop control vs double loop control Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com