Polyphase power conversion offers higher efficiency and smoother power delivery by distributing electrical loads across multiple phases, reducing vibrations and improving motor performance compared to single-phase systems. Explore this article to understand how your choice between polyphase and single-phase power can impact energy efficiency and system reliability.
Table of Comparison
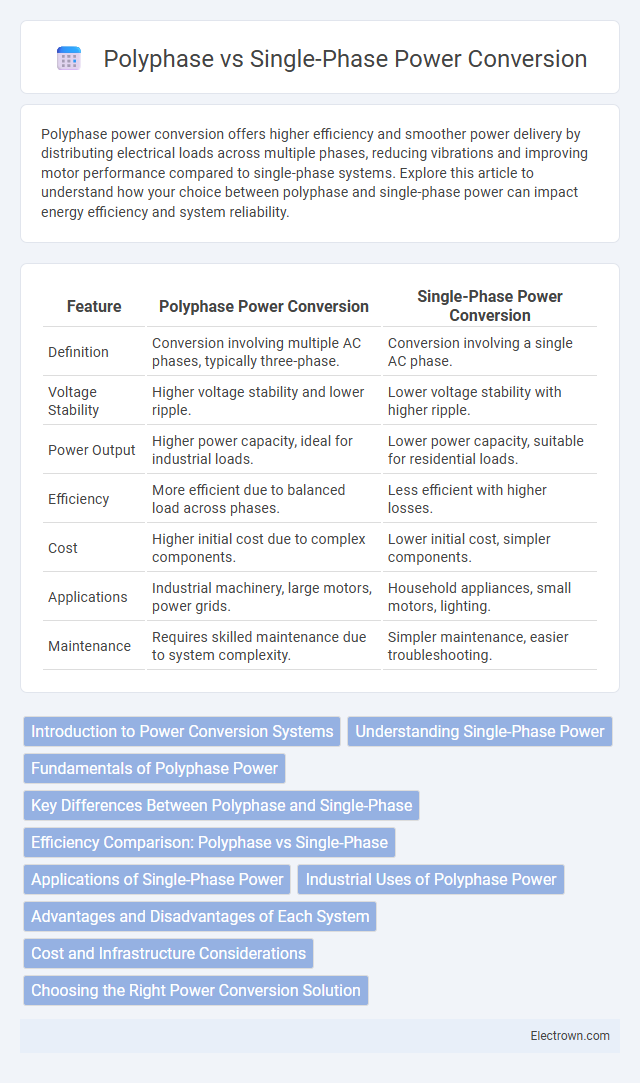
| Feature | Polyphase Power Conversion | Single-Phase Power Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conversion involving multiple AC phases, typically three-phase. | Conversion involving a single AC phase. |
| Voltage Stability | Higher voltage stability and lower ripple. | Lower voltage stability with higher ripple. |
| Power Output | Higher power capacity, ideal for industrial loads. | Lower power capacity, suitable for residential loads. |
| Efficiency | More efficient due to balanced load across phases. | Less efficient with higher losses. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to complex components. | Lower initial cost, simpler components. |
| Applications | Industrial machinery, large motors, power grids. | Household appliances, small motors, lighting. |
| Maintenance | Requires skilled maintenance due to system complexity. | Simpler maintenance, easier troubleshooting. |
Introduction to Power Conversion Systems
Power conversion systems transform electrical energy from one form to another to meet specific application needs, with polyphase and single-phase being two primary types. Polyphase systems, often three-phase, provide more efficient power delivery with smoother voltage and current flow, ideal for industrial and high-load scenarios. Your choice between single-phase and polyphase power conversion depends on the required efficiency, load capacity, and application environment.
Understanding Single-Phase Power
Single-phase power conversion delivers electricity through a single alternating current (AC) waveform, typically used in residential and light commercial applications. It provides a simpler, less costly power setup but is limited in capacity and efficiency compared to polyphase systems. Single-phase systems commonly operate at voltages of 120V or 240V, suitable for powering household appliances and small motors.
Fundamentals of Polyphase Power
Polyphase power systems use multiple alternating currents, each set 120 degrees out of phase, to deliver constant power flow and minimize pulsations compared to single-phase systems. The three-phase power setup enhances efficiency, reduces conductor material, and provides smoother operation for motors and industrial equipment. Your electrical designs benefit from improved performance and reliability when utilizing polyphase power fundamentals.
Key Differences Between Polyphase and Single-Phase
Polyphase power conversion uses multiple alternating currents, typically three, to deliver smoother and more efficient power transfer compared to single-phase systems, which rely on a single alternating current. Key differences include the ability of polyphase systems to provide constant power, reducing torque pulsations in motors, and enhancing energy efficiency, while single-phase systems often experience power fluctuations and are less efficient for heavy loads. Your choice between polyphase and single-phase power conversion depends on application requirements, with polyphase preferred for industrial and high-power uses and single-phase suited for residential and light-duty applications.
Efficiency Comparison: Polyphase vs Single-Phase
Polyphase power conversion systems typically achieve higher efficiency than single-phase systems due to balanced load distribution and reduced current ripple, which minimizes losses in electrical components. Polyphase converters also offer improved voltage stability and lower harmonic distortion, enhancing overall performance in industrial and high-power applications. Single-phase systems, while simpler and less costly, often experience higher energy losses and decreased efficiency under comparable load conditions.
Applications of Single-Phase Power
Single-phase power conversion is widely used in residential and small commercial applications, providing efficient energy for lighting, heating, and small appliances. Your home's electrical system typically relies on single-phase power due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness in transmitting electricity over short distances. This type of power is ideal for low to moderate energy demands, ensuring reliable operation of everyday devices without the need for complex infrastructure.
Industrial Uses of Polyphase Power
Polyphase power systems, particularly three-phase power, are extensively utilized in industrial applications due to their efficiency in delivering consistent and balanced power loads to heavy machinery and large motors. Industrial facilities benefit from polyphase power's ability to reduce power pulsations and improve the performance of electric motors, resulting in increased operational reliability and reduced maintenance costs. The scalability of polyphase systems also supports high-demand manufacturing processes by providing enhanced power capacity and improved energy distribution.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each System
Polyphase power conversion offers higher efficiency, better voltage regulation, and smoother power delivery, making it ideal for industrial and large-scale applications, but it requires more complex wiring and equipment, increasing installation and maintenance costs. Single-phase power conversion is simpler, less expensive, and sufficient for residential and light commercial use, but it delivers less power, experiences greater voltage drops, and suffers from fluctuating power quality under heavy loads. Choosing between polyphase and single-phase systems depends on load demands, cost constraints, and the need for power stability.
Cost and Infrastructure Considerations
Polyphase power conversion systems generally require higher initial infrastructure investment due to the complexity of transformers, wiring, and switchgear compared to single-phase systems. Single-phase power setups involve simpler and less costly components, making them more suitable for residential and small-scale applications with limited budgets. Your choice between polyphase and single-phase should factor in the long-term cost efficiency of polyphase power for industrial loads versus the more manageable upfront expenses of single-phase systems.
Choosing the Right Power Conversion Solution
Selecting between polyphase and single-phase power conversion depends on the application's load demand and efficiency requirements. Polyphase systems, typically three-phase, offer higher power density, improved efficiency, and smoother power delivery, making them ideal for industrial machinery and large motors. Single-phase power conversion suits residential and light commercial use due to simpler design and lower installation costs, but may face limitations under heavy loads compared to polyphase alternatives.
Polyphase vs Single-phase power conversion Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com