MOSFET drivers are specifically designed to efficiently switch MOSFET transistors by providing appropriate voltage and current levels to their gates, ensuring fast and reliable operation. Understanding the differences between MOSFET drivers and general gate drivers can help you choose the right component for optimizing your electronic circuit's performance; continue reading to explore detailed comparisons and applications.
Table of Comparison
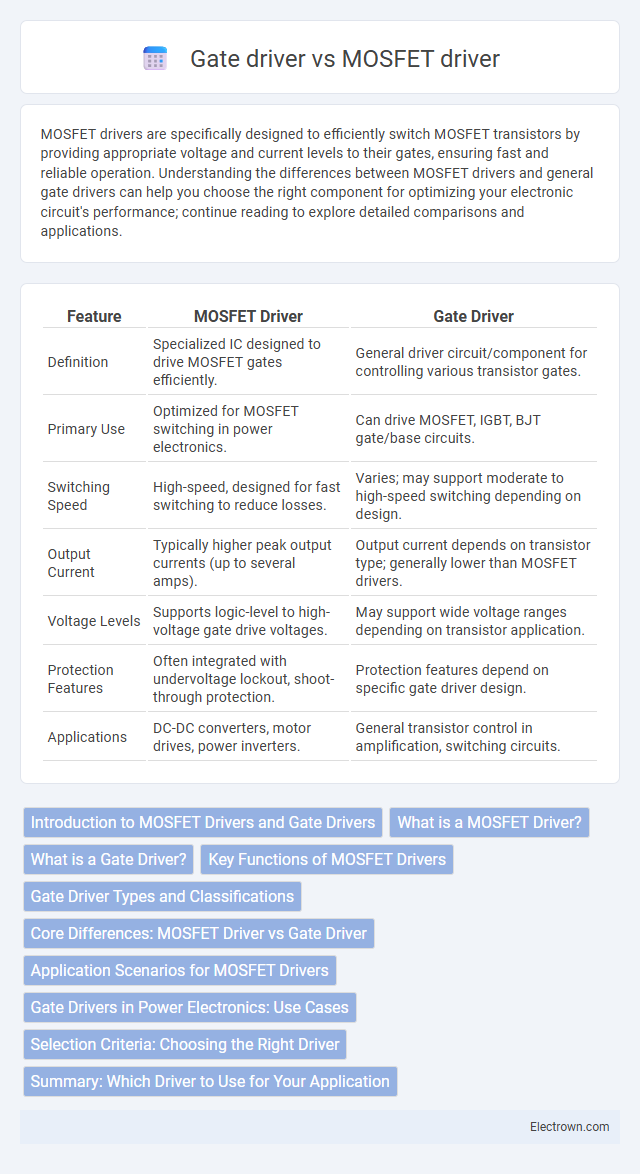
| Feature | MOSFET Driver | Gate Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialized IC designed to drive MOSFET gates efficiently. | General driver circuit/component for controlling various transistor gates. |
| Primary Use | Optimized for MOSFET switching in power electronics. | Can drive MOSFET, IGBT, BJT gate/base circuits. |
| Switching Speed | High-speed, designed for fast switching to reduce losses. | Varies; may support moderate to high-speed switching depending on design. |
| Output Current | Typically higher peak output currents (up to several amps). | Output current depends on transistor type; generally lower than MOSFET drivers. |
| Voltage Levels | Supports logic-level to high-voltage gate drive voltages. | May support wide voltage ranges depending on transistor application. |
| Protection Features | Often integrated with undervoltage lockout, shoot-through protection. | Protection features depend on specific gate driver design. |
| Applications | DC-DC converters, motor drives, power inverters. | General transistor control in amplification, switching circuits. |
Introduction to MOSFET Drivers and Gate Drivers
MOSFET drivers and gate drivers are essential components in power electronics, designed to efficiently control the switching of MOSFETs by providing the necessary voltage and current to the gate terminals. MOSFET drivers typically focus on enhancing the performance of MOSFET transistors in high-speed switching applications, ensuring faster switching times and reduced power losses. Your choice between a MOSFET driver and a general gate driver depends on the specific requirements of the circuit, including voltage levels, switching frequency, and load characteristics.
What is a MOSFET Driver?
A MOSFET driver is an integrated circuit specifically designed to efficiently switch MOSFETs by providing proper voltage and current levels to the gate terminal, enabling fast and reliable transistor switching. It optimizes switching speed and reduces power loss by delivering precise gate drive signals that overcome MOSFET gate capacitance. Compared to general gate drivers, MOSFET drivers are tailored for high-speed switching applications in power electronics, such as DC-DC converters and motor controllers.
What is a Gate Driver?
A Gate Driver is an essential electronic component designed to control the gate of power transistors like MOSFETs and IGBTs, providing the required voltage and current to switch them efficiently. It ensures fast switching speeds and reduces power loss during operation by delivering precise drive signals tailored to the transistor's specifications. Your choice of a Gate Driver impacts overall circuit performance, reliability, and efficiency in power electronics applications.
Key Functions of MOSFET Drivers
MOSFET drivers play a crucial role in power electronics by efficiently switching MOSFET transistors on and off, ensuring rapid charging and discharging of the gate capacitance to minimize switching losses and electromagnetic interference (EMI). These drivers provide level shifting, voltage amplification, and isolation to match low voltage microcontroller outputs with high voltage MOSFET gates, enhancing overall circuit performance and reliability. Key features include high peak current capability, fast switching speed, and protection mechanisms such as under-voltage lockout (UVLO) to safeguard semiconductor devices during operation.
Gate Driver Types and Classifications
Gate drivers are specialized circuits designed to efficiently switch MOSFETs by providing the correct voltage and current levels to the gate terminal. They are classified into low-side, high-side, and half-bridge drivers based on their connection relative to the MOSFET and load, with further types including isolated, bootstrap, and integrated drivers tailored for specific applications. Understanding your gate driver type is crucial for optimizing switching speed, reducing power loss, and ensuring reliable operation in power electronics systems.
Core Differences: MOSFET Driver vs Gate Driver
MOSFET drivers are specialized gate drivers designed specifically to optimize the switching performance of MOSFETs by providing appropriate voltage and current levels to quickly charge and discharge the MOSFET gate capacitance. Gate drivers serve as interface circuits that control the voltage applied to the gate terminal of power transistors, including MOSFETs, IGBTs, and others, ensuring proper switching and reducing power losses. The core difference lies in MOSFET drivers being tailored for high-speed, efficient MOSFET operation, whereas gate drivers encompass a broader range of transistor types and switching requirements.
Application Scenarios for MOSFET Drivers
MOSFET drivers are specifically designed to efficiently switch MOSFET transistors in high-speed applications such as motor control, DC-DC converters, and power inverters, where rapid gate charging and discharging is critical. These drivers provide the necessary voltage and current to drive the MOSFET gates, improving switching performance and reducing power losses. Your choice of a MOSFET driver directly impacts the reliability and efficiency of power electronics in automotive, industrial, and renewable energy systems.
Gate Drivers in Power Electronics: Use Cases
Gate drivers are essential in power electronics for efficiently controlling MOSFETs and IGBTs in high-speed switching applications, such as DC-DC converters, motor drives, and inverters. These drivers provide the necessary voltage and current to rapidly switch the transistor gate, minimizing switching losses and improving overall system performance. Your choice of gate driver impacts power efficiency, thermal management, and the reliability of power electronic systems in industrial and automotive environments.
Selection Criteria: Choosing the Right Driver
Selecting the right driver involves evaluating key factors such as voltage and current requirements, switching frequency, and compatibility with the MOSFET or gate device. MOSFET drivers are optimized for high-speed switching with precise gate charge control, ideal for power management and motor control. Gate drivers offer broader application flexibility, supporting various transistor types and configurations, making them suitable for diverse analog and digital circuits.
Summary: Which Driver to Use for Your Application
MOSFET drivers specifically optimize the switching performance of MOSFET transistors by providing precise gate voltage control and fast switching speeds, ideal for high-frequency applications such as power supplies and motor controllers. Gate drivers, a broader category, support various transistor types including MOSFETs and IGBTs, offering flexibility in diverse circuit configurations and enabling efficient power management across different semiconductor devices. Choose a MOSFET driver when your application demands rapid switching and low gate charge control for MOSFETs, whereas a generic gate driver suits mixed-transistor environments requiring versatile gate drive solutions.
MOSFET driver vs Gate driver Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com