Zener diodes regulate voltage by maintaining a stable reference voltage during reverse breakdown, while varistors protect circuits by clamping high voltage spikes through nonlinear resistance. To learn how these components can safeguard Your electronics, continue reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
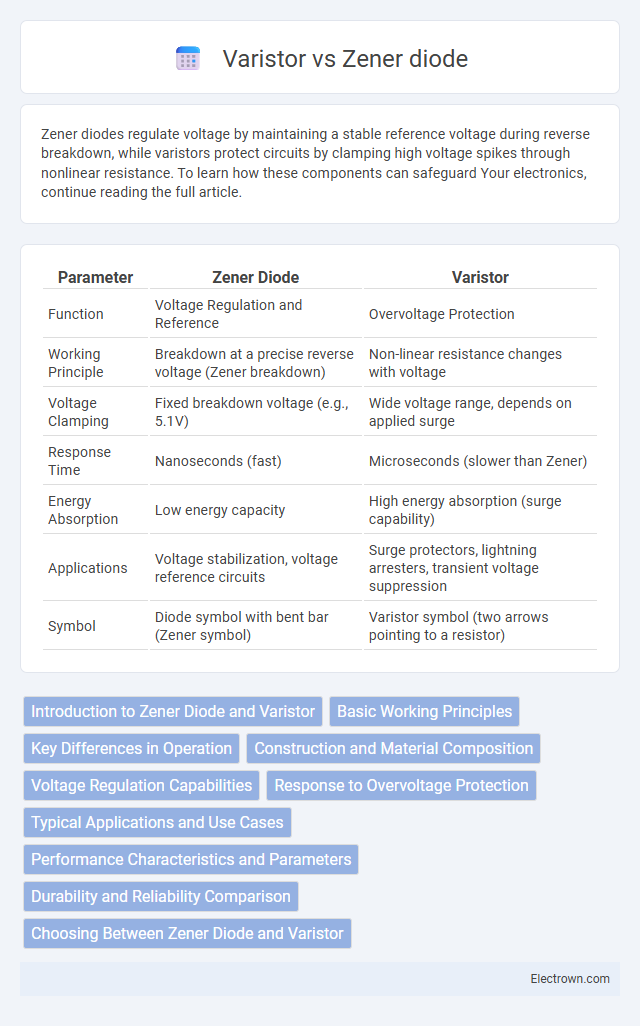
| Parameter | Zener Diode | Varistor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Voltage Regulation and Reference | Overvoltage Protection |
| Working Principle | Breakdown at a precise reverse voltage (Zener breakdown) | Non-linear resistance changes with voltage |
| Voltage Clamping | Fixed breakdown voltage (e.g., 5.1V) | Wide voltage range, depends on applied surge |
| Response Time | Nanoseconds (fast) | Microseconds (slower than Zener) |
| Energy Absorption | Low energy capacity | High energy absorption (surge capability) |
| Applications | Voltage stabilization, voltage reference circuits | Surge protectors, lightning arresters, transient voltage suppression |
| Symbol | Diode symbol with bent bar (Zener symbol) | Varistor symbol (two arrows pointing to a resistor) |
Introduction to Zener Diode and Varistor
Zener diodes are semiconductor devices designed to regulate voltage by allowing current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific breakdown voltage is reached, making them ideal for voltage stabilization and reference applications. Varistors, typically made from metal oxide, provide protection against voltage surges by changing resistance at high voltage levels, thus absorbing excess energy to shield electronic circuits. Both components play crucial roles in overvoltage protection but operate based on different principles and are selected according to the specific protection needs in electrical and electronic systems.
Basic Working Principles
Zener diodes operate by allowing current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage exceeds the breakdown voltage, maintaining a stable voltage across sensitive electronic circuits. Varistors, also known as voltage-dependent resistors, change their resistance significantly when the voltage across them surpasses a certain threshold, effectively clamping voltage spikes to protect devices. Understanding the basic working principles of these components helps you select the right device for voltage regulation or surge protection in your electronic applications.
Key Differences in Operation
Zener diodes regulate voltage by maintaining a constant voltage output through reverse breakdown at a precise voltage level, making them ideal for voltage reference and stabilization. Varistors, typically made from metal oxide, provide surge protection by changing resistance with voltage, clamping transient voltage spikes and dissipating energy to protect circuits. The key operational difference lies in Zener diodes offering voltage regulation with a sharp breakdown threshold, while varistors respond non-linearly to voltage surges without a defined breakdown voltage.
Construction and Material Composition
Zener diodes consist of heavily doped p-n junctions made from silicon semiconductor material, allowing precise voltage regulation through controlled breakdown. Varistors, typically made from metal oxide semiconductor materials like zinc oxide, have a ceramic-like structure with grain boundaries that change conductivity under high voltage stress. Your choice between these components depends on their distinct construction and material properties, which influence their voltage clamping and transient energy absorption capabilities.
Voltage Regulation Capabilities
Zener diodes provide precise voltage regulation by maintaining a stable reference voltage during reverse breakdown, ensuring your electronic circuits receive consistent voltage. Varistors protect against voltage spikes by clamping high-voltage surges but do not offer steady voltage regulation for normal operation. Choosing a Zener diode is ideal when accurate voltage control is essential, while varistors are suited for transient voltage suppression.
Response to Overvoltage Protection
Zener diodes provide precise voltage regulation by clamping voltage at a specific breakdown level, making them ideal for stable overvoltage protection in low-power circuits. Varistors, composed of metal oxide materials, offer non-linear resistance that rapidly decreases during high voltage spikes, absorbing large transient surges effectively. Your choice depends on whether you need controlled voltage clipping with fast response (Zener diode) or robust energy absorption for high-energy transients (varistor).
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Zener diodes are commonly used for voltage regulation and voltage reference in power supplies, ensuring stable output voltage despite input fluctuations. Varistors excel in transient voltage suppression, protecting circuits from voltage spikes caused by lightning or switching surges. Your choice between the two will depend on whether you need precise voltage control or robust surge protection in your electronic design.
Performance Characteristics and Parameters
Zener diodes exhibit precise voltage regulation with sharp breakdown voltage and low dynamic resistance, making them ideal for voltage reference and clamping applications. Varistors, typically metal oxide varistors (MOVs), offer nonlinear resistance that sharply decreases with increasing voltage, providing superior transient voltage suppression but less precision. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize stable voltage regulation (Zener diode) or high-energy surge absorption (varistor).
Durability and Reliability Comparison
Zener diodes exhibit high durability in low-voltage, precise voltage regulation applications due to their stable breakdown voltage and predictable performance under specified conditions. Varistors offer superior reliability in transient voltage suppression with their ability to absorb high-energy surges and repetitive spike events without significant degradation. Both components provide robust protection but varistors generally demonstrate enhanced longevity in environments with frequent high-energy transients.
Choosing Between Zener Diode and Varistor
Choosing between a Zener diode and a varistor depends on the specific voltage regulation and transient suppression needs. Zener diodes provide precise voltage clamping with a stable breakdown voltage ideal for voltage reference and regulation circuits. Varistors excel in absorbing high-energy surges and protecting against transient voltage spikes with a nonlinear resistance characteristic, making them suitable for surge protection in power lines.
Zener diode vs varistor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com