Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to acrylic, making it ideal for applications requiring toughness and shatterproof qualities. Explore the rest of the article to understand which material best suits Your specific needs and projects.
Table of Comparison
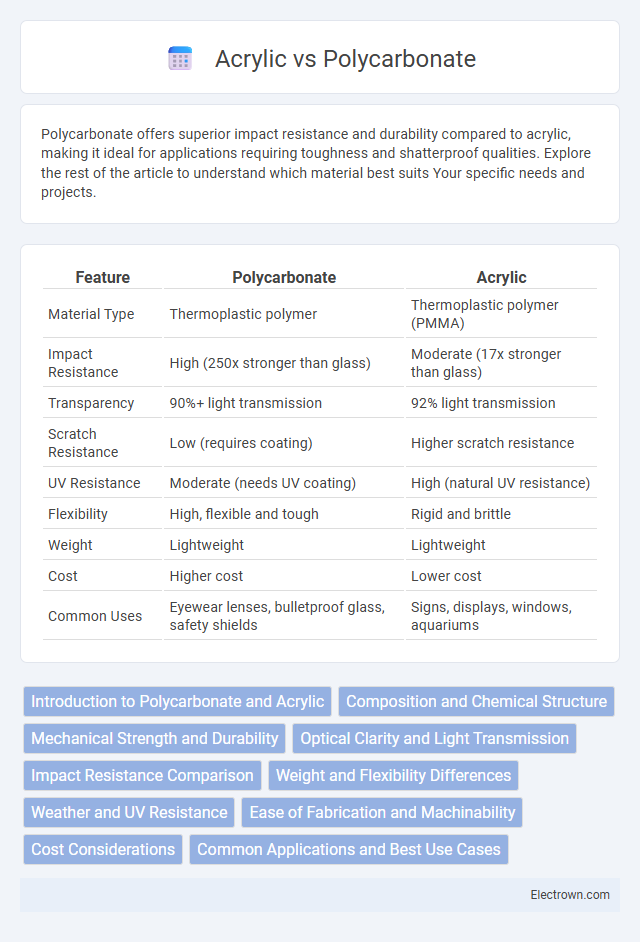
| Feature | Polycarbonate | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer (PMMA) |
| Impact Resistance | High (250x stronger than glass) | Moderate (17x stronger than glass) |
| Transparency | 90%+ light transmission | 92% light transmission |
| Scratch Resistance | Low (requires coating) | Higher scratch resistance |
| UV Resistance | Moderate (needs UV coating) | High (natural UV resistance) |
| Flexibility | High, flexible and tough | Rigid and brittle |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Common Uses | Eyewear lenses, bulletproof glass, safety shields | Signs, displays, windows, aquariums |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Acrylic
Polycarbonate is a highly durable thermoplastic known for its impact resistance, transparency, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for applications such as eyewear lenses, automotive parts, and protective gear. Acrylic, also called polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is a transparent plastic that offers excellent clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, commonly used in signage, aquariums, and lighting fixtures. Both materials serve as versatile alternatives to glass but differ significantly in strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Composition and Chemical Structure
Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic polymer composed of bisphenol A and phosgene, characterized by its carbonate groups in the polymer backbone, which provide high impact resistance and thermal stability. Acrylic, or polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), consists of methyl methacrylate monomers with ester functional groups, resulting in a rigid, transparent material with excellent UV resistance. The chemical structure of polycarbonate's carbonate linkages differs significantly from acrylic's ester groups, influencing their mechanical properties and applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polycarbonate exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to acrylic, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Acrylic offers good scratch resistance but is more prone to cracking and shattering upon impact. Polycarbonate's superior toughness and flexibility ensure longer-lasting performance in demanding environments.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polycarbonate offers excellent impact resistance but slightly lower optical clarity compared to acrylic, with a light transmission rate of around 88-90%. Acrylic provides superior optical clarity and higher light transmission, typically up to 92%, making it ideal for applications where clear, bright visibility is essential. Your choice depends on whether impact strength or maximum clarity and brightness are the priority for your project.
Impact Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance compared to acrylic, withstanding up to 250 times more force without cracking or breaking. Acrylic, while more scratch-resistant and clearer, is significantly more brittle and prone to shattering under high impact. If your project demands maximum durability and safety, polycarbonate is the optimal choice to protect your investment.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Polycarbonate is significantly lighter than acrylic, making it a preferred choice for applications where weight reduction is crucial. Its superior flexibility allows polycarbonate to withstand impacts and bending without cracking, unlike acrylic which is more rigid and prone to shattering under stress. Your selection between these materials should consider the balance between lightweight durability and the need for structural stiffness.
Weather and UV Resistance
Polycarbonate offers superior weather and UV resistance compared to acrylic, making it ideal for outdoor applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its inherent UV stabilizers prevent yellowing and degradation over time, ensuring long-lasting clarity and durability. Acrylic, while resistant to sunlight and weather to a certain extent, tends to become brittle and discolored more quickly when exposed to prolonged UV radiation.
Ease of Fabrication and Machinability
Polycarbonate offers superior ease of fabrication and machinability compared to acrylic due to its higher impact resistance and flexibility, making it less prone to cracking during cutting or drilling. Your projects benefit from polycarbonate's ability to be thermoformed and machined with standard tools, while acrylic requires more careful handling to avoid chipping or stress fractures. Both materials can be polished for clarity, but polycarbonate's durability makes it a more efficient choice for complex machining tasks.
Cost Considerations
Polycarbonate is generally more expensive than acrylic due to its superior impact resistance and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced safety and longevity. Acrylic offers a lower-cost alternative with excellent optical clarity, suitable for decorative or low-impact uses where budget constraints are critical. When choosing between polycarbonate and acrylic, consider the total cost of ownership, including potential replacement or maintenance expenses, which may offset the initial price difference.
Common Applications and Best Use Cases
Polycarbonate is commonly used for impact-resistant applications like safety goggles, machine guards, and bulletproof windows due to its high durability and toughness. Acrylic excels in optical clarity and weather resistance, making it ideal for display cases, signage, and skylights where light transmission and aesthetic appeal are essential. Your choice between polycarbonate and acrylic should depend on whether impact resistance or visual clarity is the priority for your project.
Polycarbonate vs Acrylic Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com