FBG (Fiber Bragg Gratings) and LPG (Long Period Gratings) are both types of fiber optic sensors used for monitoring strain, temperature, and pressure, but they differ in their operating principles and spectral characteristics--FBGs reflect specific wavelengths while LPGs couple light to cladding modes, resulting in transmission dips. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right grating for your sensing application; explore the rest of the article to learn more about their unique features and advantages.
Table of Comparison
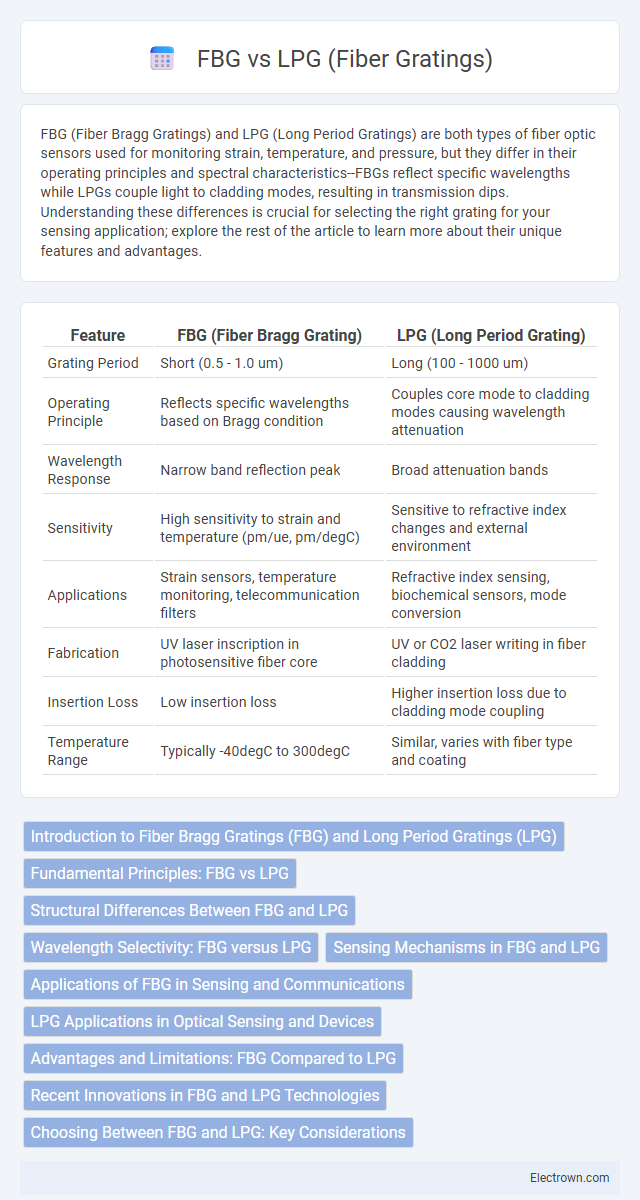
| Feature | FBG (Fiber Bragg Grating) | LPG (Long Period Grating) |
|---|---|---|
| Grating Period | Short (0.5 - 1.0 um) | Long (100 - 1000 um) |
| Operating Principle | Reflects specific wavelengths based on Bragg condition | Couples core mode to cladding modes causing wavelength attenuation |
| Wavelength Response | Narrow band reflection peak | Broad attenuation bands |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity to strain and temperature (pm/ue, pm/degC) | Sensitive to refractive index changes and external environment |
| Applications | Strain sensors, temperature monitoring, telecommunication filters | Refractive index sensing, biochemical sensors, mode conversion |
| Fabrication | UV laser inscription in photosensitive fiber core | UV or CO2 laser writing in fiber cladding |
| Insertion Loss | Low insertion loss | Higher insertion loss due to cladding mode coupling |
| Temperature Range | Typically -40degC to 300degC | Similar, varies with fiber type and coating |
Introduction to Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) and Long Period Gratings (LPG)
Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) and Long Period Gratings (LPG) are specialized optical fibers used for sensing and filtering applications, differing mainly in their grating structure and wavelength selectivity. FBGs reflect specific wavelengths of light while transmitting others, allowing precise measurement of strain and temperature by monitoring shifts in the reflected Bragg wavelength. LPGs couple light from the core mode to cladding modes over longer distances, producing attenuation bands that make them ideal for refractive index sensing and wavelength filtering in your photonic systems.
Fundamental Principles: FBG vs LPG
Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) operate by reflecting specific wavelengths of light based on periodic variations in the refractive index within the fiber core, creating a narrowband wavelength filter. Long Period Gratings (LPG) couple core modes to cladding modes through long periodic index modulations, resulting in multiple resonance bands and broadband attenuation. Understanding your application's wavelength selectivity and sensitivity needs helps determine whether FBGs' precise reflection or LPGs' broad mode coupling is more appropriate.
Structural Differences Between FBG and LPG
Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) feature periodic variations in the core's refractive index, creating a narrowband reflector that selectively reflects specific wavelengths of light. Long Period Gratings (LPG) consist of periodic modulations in the core-cladding boundary refractive index, coupling core modes to cladding modes and resulting in broadband attenuation bands. The key structural difference lies in the modulation period and location: FBGs have short periods (sub-millimeter scale) within the core, while LPGs have longer periods (hundreds of micrometers to millimeters) affecting the core-cladding interface.
Wavelength Selectivity: FBG versus LPG
Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) exhibit high wavelength selectivity by reflecting specific narrowband wavelengths, making them ideal for precise wavelength filtering in optical communication. Long Period Gratings (LPG) couple core modes to cladding modes, resulting in broader resonance bands suitable for sensing applications that require sensitivity over a range of wavelengths. Understanding these differences allows you to select the appropriate grating type based on the required spectral resolution and sensing or filtering application.
Sensing Mechanisms in FBG and LPG
Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) utilize periodic variations in the core's refractive index to reflect specific wavelengths, enabling strain and temperature sensing through shifts in the reflected Bragg wavelength. Long Period Gratings (LPG) induce coupling between core and cladding modes via longer periodic refractive index modulations, resulting in attenuation bands sensitive to external refractive index changes and mechanical perturbations. The distinct sensing mechanisms allow FBGs to excel in accurate strain and temperature measurement, while LPGs offer enhanced sensitivity to environmental parameters such as refractive index and surrounding chemical composition.
Applications of FBG in Sensing and Communications
Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBGs) are extensively utilized in sensing applications for precise strain, temperature, and pressure measurements due to their wavelength-specific reflection properties, enabling real-time monitoring in structural health and aerospace industries. In optical communications, FBGs serve as critical components for wavelength filtering, multiplexing, and dispersion compensation, improving signal integrity and network performance. Their robustness, compact size, and ability to operate in harsh environments make FBGs indispensable in both sensing and telecommunication systems.
LPG Applications in Optical Sensing and Devices
Long Period Gratings (LPGs) are extensively used in optical sensing due to their high sensitivity to changes in refractive index, temperature, and strain, making them ideal for environmental monitoring, biochemical sensing, and structural health assessment. LPGs enable selective wavelength filtering and refractive index modulation, enhancing the performance of fiber optic sensors and devices in real-time applications. Their capability to achieve mode coupling and attenuation bands allows for precise detection of physical and chemical parameters in complex systems.
Advantages and Limitations: FBG Compared to LPG
Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBGs) offer high wavelength selectivity and stability, making them ideal for precise strain and temperature sensing in telecommunications and structural health monitoring. Long Period Gratings (LPGs) exhibit higher sensitivity to changes in refractive index, suited for biochemical sensing, but have broader spectral responses and more temperature cross-sensitivity. FBGs demonstrate easier multiplexing and stronger signal reflection, while LPGs require longer grating lengths and are more affected by environmental variations, limiting their use in certain high-precision applications.
Recent Innovations in FBG and LPG Technologies
Recent innovations in Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) and Long Period Gratings (LPG) have significantly enhanced sensor sensitivity and multiplexing capabilities for structural health monitoring and telecommunications. Advances in fabrication techniques, such as femtosecond laser inscription and plasma etching, allow for precise control of grating parameters, improving wavelength selectivity and environmental stability. Your choice between FBG and LPG sensors can now leverage these cutting-edge developments to achieve higher accuracy and durability in diverse industrial applications.
Choosing Between FBG and LPG: Key Considerations
When choosing between Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG) and Long Period Gratings (LPG), consider factors such as sensitivity, spectral response, and application requirements. FBGs offer sharp reflection peaks suitable for precise wavelength filtering and sensing, while LPGs provide broader attenuation bands ideal for refractive index sensing and strain measurement. Your decision should align with the desired measurement parameters and the operational environment of the fiber optic system.
FBG vs LPG (fiber gratings) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com