Copper wire offers superior electrical conductivity and durability compared to aluminum wire, making it ideal for applications demanding high performance and longevity. Understanding the key differences between copper and aluminum wire can help you choose the best material for your electrical needs; continue reading to explore their advantages and drawbacks.
Table of Comparison
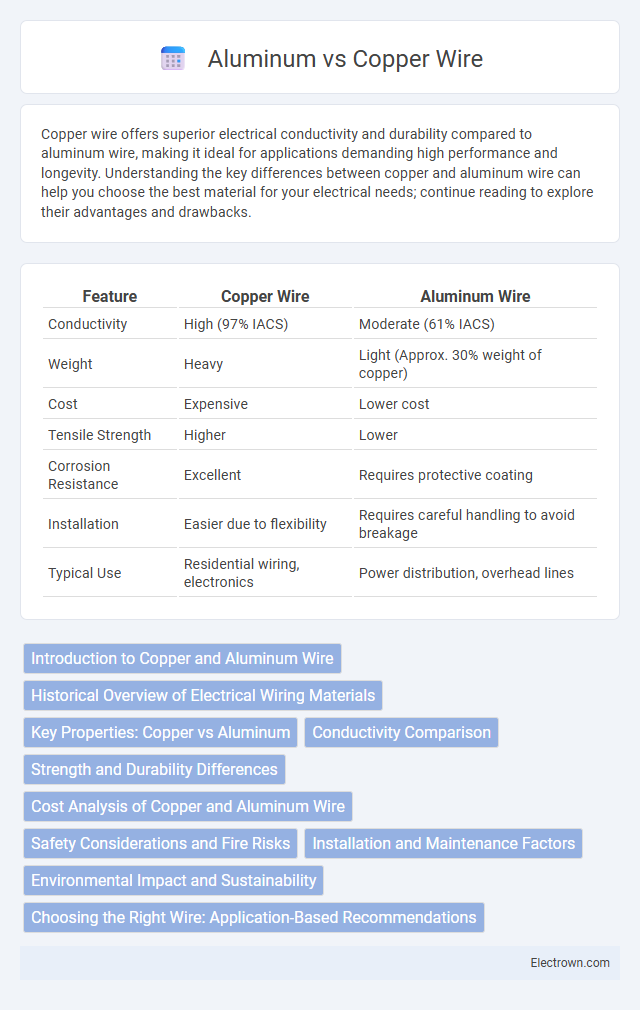
| Feature | Copper Wire | Aluminum Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High (97% IACS) | Moderate (61% IACS) |
| Weight | Heavy | Light (Approx. 30% weight of copper) |
| Cost | Expensive | Lower cost |
| Tensile Strength | Higher | Lower |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Requires protective coating |
| Installation | Easier due to flexibility | Requires careful handling to avoid breakage |
| Typical Use | Residential wiring, electronics | Power distribution, overhead lines |
Introduction to Copper and Aluminum Wire
Copper wire offers superior electrical conductivity and durability, making it ideal for high-performance electrical applications. Aluminum wire is lighter and more cost-effective, often used in overhead power lines and large-scale wiring projects where weight and cost savings are crucial. Your choice between copper and aluminum wire should consider conductivity, weight, cost, and specific application requirements.
Historical Overview of Electrical Wiring Materials
Copper and aluminum have been primary materials for electrical wiring since the early 20th century, with copper dominating due to its superior conductivity and durability. Aluminum wiring gained popularity in the 1960s and 1970s as a cost-effective alternative during copper shortages, despite concerns over expansion and oxidation affecting safety. Modern advancements include improved aluminum alloys and connection techniques to address historical issues, maintaining copper's preference in residential and commercial electrical installations.
Key Properties: Copper vs Aluminum
Copper wire offers superior electrical conductivity, better tensile strength, and greater corrosion resistance compared to aluminum wire. Aluminum wire, while lighter and more cost-effective, has higher electrical resistance and requires special connectors to prevent oxidation-related failures. Choosing the right wiring depends on your project's budget, electrical load, and durability requirements.
Conductivity Comparison
Copper wire exhibits superior electrical conductivity, measuring approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, compared to aluminum's 3.5 x 10^7 S/m. This means copper can transmit electrical current more efficiently with less resistance and power loss. As a result, copper is preferred in applications requiring optimal conductivity and minimal energy dissipation.
Strength and Durability Differences
Copper wire demonstrates superior tensile strength and resistance to metal fatigue compared to aluminum wire, enhancing its durability in various electrical applications. Copper's lower coefficient of thermal expansion minimizes the risk of loosening connections under temperature fluctuations, which is a common issue with aluminum wiring. These properties make copper a preferred choice for long-term reliability in wiring systems exposed to mechanical stress and environmental changes.
Cost Analysis of Copper and Aluminum Wire
Copper wire generally has higher initial costs due to its superior conductivity and durability, making it a preferred choice for long-term investments in electrical wiring. Aluminum wire costs less upfront and is lighter, which reduces labor expenses during installation but may incur higher maintenance or replacement costs over time because of its susceptibility to oxidation and thermal expansion. Your choice between copper and aluminum wiring should balance upfront budget constraints against potential long-term savings and performance reliability.
Safety Considerations and Fire Risks
Copper wire offers superior conductivity and greater resistance to overheating compared to aluminum wire, significantly reducing fire hazards in electrical systems. Aluminum wire's higher thermal expansion can cause loose connections over time, increasing the risk of arcing and electrical fires if not properly installed with compatible connectors. Utilizing copper wiring in residential and commercial applications enhances electrical safety by minimizing risks related to heat buildup and fire incidents.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Copper wire offers superior conductivity and tensile strength, resulting in easier handling and fewer connections during installation, which reduces the risk of electrical faults. Aluminum wire, being lighter and more flexible, simplifies installation in large-scale projects but requires specialized connectors and anti-oxidant compounds to prevent corrosion and maintain secure connections. Maintenance of aluminum wiring demands regular inspections to detect potential oxidation and thermal expansion issues, whereas copper wiring generally requires less frequent upkeep due to its durability and stable performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper wire demonstrates higher recyclability rates and lower environmental degradation during extraction compared to aluminum wire. Its superior conductivity reduces energy consumption in electrical systems, enhancing overall sustainability. Although aluminum is lighter and abundant, its production involves higher greenhouse gas emissions and energy-intensive refining processes.
Choosing the Right Wire: Application-Based Recommendations
Copper wire offers superior electrical conductivity and durability, making it ideal for high-performance applications like residential wiring and electric motor windings. Aluminum wire provides a lightweight and cost-effective alternative suited for overhead power lines and large-scale utility installations where weight reduction is critical. Selecting the right wire depends on factors such as current capacity, environmental conditions, budget constraints, and mechanical strength requirements.
copper vs aluminum wire Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com