Active components, such as transistors and integrated circuits, require power to operate and can amplify signals, while passive components like resistors and capacitors do not need power and only attenuate or store energy. Understanding the functions and applications of passive versus active components can help you optimize your electronic designs; explore the rest of this article to learn more.
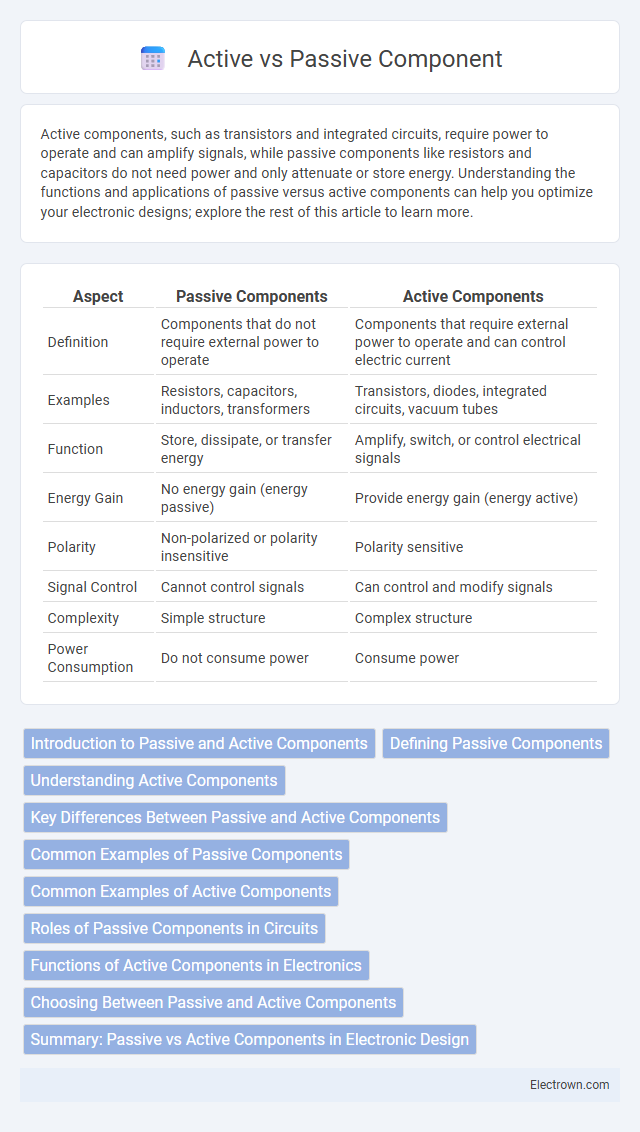
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Passive Components | Active Components |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Components that do not require external power to operate | Components that require external power to operate and can control electric current |
| Examples | Resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers | Transistors, diodes, integrated circuits, vacuum tubes |
| Function | Store, dissipate, or transfer energy | Amplify, switch, or control electrical signals |
| Energy Gain | No energy gain (energy passive) | Provide energy gain (energy active) |
| Polarity | Non-polarized or polarity insensitive | Polarity sensitive |
| Signal Control | Cannot control signals | Can control and modify signals |
| Complexity | Simple structure | Complex structure |
| Power Consumption | Do not consume power | Consume power |
Introduction to Passive and Active Components
Passive components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not generate energy but instead store or dissipate it within electrical circuits. Active components, including transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits, are capable of controlling electron flow and amplifying signals by supplying energy from an external power source. Understanding the distinct roles of passive and active elements is essential for designing and optimizing your electronic systems effectively.
Defining Passive Components
Passive components are electronic parts that do not require external power to operate and cannot amplify signals, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. These components primarily store or dissipate energy, providing essential functions like filtering, energy storage, and impedance matching in circuits. Understanding the role of passive components helps you design efficient and stable electronic systems by ensuring proper signal control and power management.
Understanding Active Components
Active components, such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits, are essential for controlling electric current and amplifying signals in electronic circuits. Unlike passive components, active components require an external power source to operate and can introduce gain or modulation to the signal. Their ability to control energy flow makes them fundamental in designing amplifiers, oscillators, and switching devices in modern electronics.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Components
Passive components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not require an external power source to operate and cannot amplify or generate energy. Active components, including transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits, rely on an external power supply to control the flow of electricity and amplify signals. Understanding these key differences helps you design efficient electronic circuits tailored to specific functions and performance requirements.
Common Examples of Passive Components
Common examples of passive components include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which do not require an external power source to operate. These components stabilize and regulate electrical signals by controlling current flow, storing energy, or filtering frequencies in circuits. Your electronic designs benefit from these passive components to ensure efficient performance and signal integrity.
Common Examples of Active Components
Active components are electronic devices that require an external power source to operate and can amplify or control electrical signals. Common examples of active components include transistors, integrated circuits (ICs), diodes, and operational amplifiers, which are fundamental in building amplifiers, switches, and signal processors. Understanding the function of these components is essential for designing and troubleshooting electronic circuits effectively, ensuring Your projects perform as intended.
Roles of Passive Components in Circuits
Passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors play crucial roles in circuits by controlling voltage, current, and signal flow without requiring external power. They provide essential functions including filtering noise, storing energy, and setting time constants to regulate circuit behavior. Your electronic designs rely on these components to ensure stability, protect active components, and maintain overall circuit performance.
Functions of Active Components in Electronics
Active components in electronics, such as transistors, integrated circuits, and diodes, are essential for amplification, switching, and signal modulation. These components can control electrical energy, thereby enabling the processing and manipulation of signals within electronic circuits. Their ability to inject power into a circuit distinguishes them from passive components, which only store or dissipate energy.
Choosing Between Passive and Active Components
Choosing between passive and active components depends on your circuit requirements and functionality. Passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors do not require power to operate and are essential for filtering, energy storage, and impedance matching. Active components such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits provide amplification, switching, and signal modulation capabilities, making them indispensable for complex electronic designs.
Summary: Passive vs Active Components in Electronic Design
Passive components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not require external power to operate and primarily store or dissipate energy. Active components, including transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits, require power supply and can amplify or switch electronic signals. Understanding the distinct roles of passive and active components is essential for optimizing your electronic circuit design and functionality.
passive vs active component Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com