Anodized aluminum offers enhanced corrosion resistance, increased surface hardness, and improved aesthetic appeal compared to bare aluminum, making it ideal for applications where durability and appearance matter. Discover how choosing the right aluminum type can impact Your projects by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
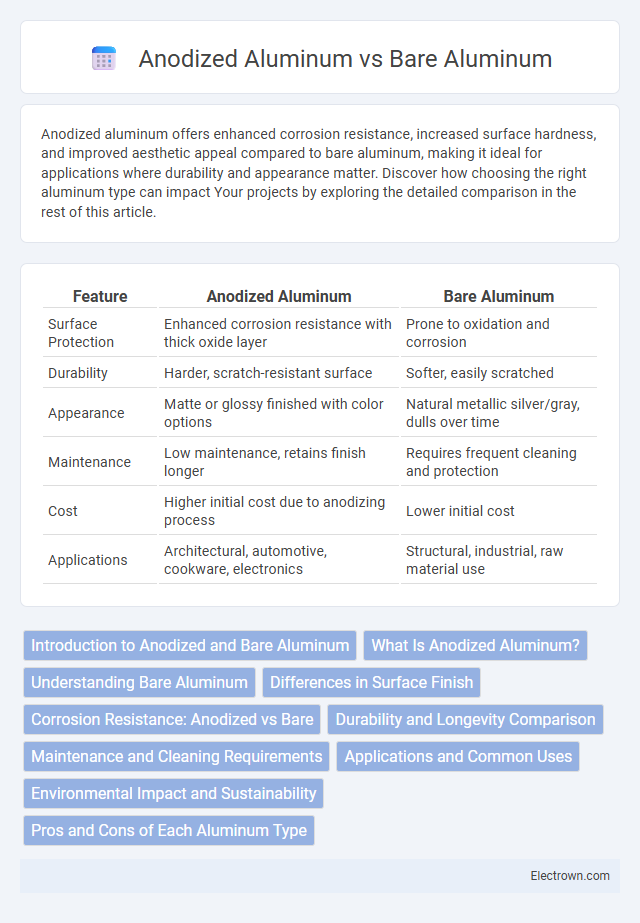
| Feature | Anodized Aluminum | Bare Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Protection | Enhanced corrosion resistance with thick oxide layer | Prone to oxidation and corrosion |
| Durability | Harder, scratch-resistant surface | Softer, easily scratched |
| Appearance | Matte or glossy finished with color options | Natural metallic silver/gray, dulls over time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, retains finish longer | Requires frequent cleaning and protection |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to anodizing process | Lower initial cost |
| Applications | Architectural, automotive, cookware, electronics | Structural, industrial, raw material use |
Introduction to Anodized and Bare Aluminum
Anodized aluminum features a protective oxide layer created through electrochemical treatment, enhancing corrosion resistance and surface hardness compared to bare aluminum. Bare aluminum is naturally prone to oxidation and scratches, making it less durable for harsh environments. Understanding these differences helps you select the right aluminum type for optimal performance and longevity in your applications.
What Is Anodized Aluminum?
Anodized aluminum is aluminum that has undergone an electrochemical process to form a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer on its surface. This oxide layer enhances the metal's resistance to wear, scratching, and environmental factors compared to bare aluminum, which remains susceptible to oxidation and surface damage. Anodizing also allows for improved adhesion of paints and dyes, making it ideal for applications requiring both protection and aesthetic customization.
Understanding Bare Aluminum
Bare aluminum offers a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity but lacks the protective oxide layer found in anodized aluminum. Without anodization, bare aluminum is more susceptible to surface scratches, wear, and environmental damage such as oxidation and pitting. Understanding bare aluminum helps you determine whether its natural finish meets your durability and maintenance requirements or if anodizing is essential for enhanced protection.
Differences in Surface Finish
Anodized aluminum features a durable, corrosion-resistant surface with a matte or glossy finish created through an electrochemical process, enhancing its hardness and color retention. Bare aluminum retains a natural, smooth metallic appearance but is more prone to oxidation, wear, and discoloration over time without protective coatings. Choosing anodized aluminum for your project ensures a longer-lasting, aesthetically versatile surface finish compared to the untreated, raw look of bare aluminum.
Corrosion Resistance: Anodized vs Bare
Anodized aluminum exhibits significantly enhanced corrosion resistance compared to bare aluminum due to its thick, protective oxide layer formed through the anodizing process. This oxide layer acts as a barrier against environmental elements such as moisture, salts, and chemicals, preventing the metal substrate from oxidizing and degrading. Bare aluminum, lacking this protective coating, is more susceptible to natural oxidation and corrosion, especially in harsh or marine environments.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Anodized aluminum offers superior durability compared to bare aluminum due to its enhanced resistance to corrosion, wear, and scratches from the protective oxide layer formed during the anodizing process. This layer significantly extends the longevity of the material, making it ideal for applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions or frequent handling. Choosing anodized aluminum ensures your product maintains structural integrity and aesthetic appeal for a much longer period than bare aluminum.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Anodized aluminum offers superior resistance to corrosion and surface wear, significantly reducing the frequency and intensity of maintenance compared to bare aluminum. Its protective oxide layer prevents oxidation and staining, making cleaning easier and less labor-intensive, often requiring only mild soap and water. Bare aluminum, lacking this protective coating, demands more frequent cleaning and the use of specialized cleaners to prevent tarnish and deterioration over time.
Applications and Common Uses
Anodized aluminum is widely used in architectural applications, consumer electronics, and automotive parts due to its enhanced corrosion resistance and decorative finish, making it ideal for outdoor and high-wear environments. Bare aluminum is often favored in aerospace, packaging, and electrical applications where lightweight properties and excellent thermal conductivity are prioritized without the need for additional surface treatment. Your choice depends on whether durability and aesthetics or raw performance and cost-efficiency are more critical for the intended use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Anodized aluminum offers enhanced corrosion resistance and durability, significantly extending the material's lifespan compared to bare aluminum, which reduces the frequency of replacement and raw material demand. The anodizing process is environmentally friendly, using non-toxic chemicals and producing a protective oxide layer without adding hazardous waste, unlike coatings that emit volatile organic compounds. Bare aluminum, while recyclable, lacks the protective barrier anodized aluminum has, making it more prone to degradation and increasing its overall environmental footprint through accelerated wear and higher maintenance.
Pros and Cons of Each Aluminum Type
Anodized aluminum offers superior corrosion resistance, enhanced surface hardness, and a decorative, colorful finish, making it ideal for outdoor and aesthetic applications, but it may be more expensive and prone to chipping over time. Bare aluminum is lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to machine or weld, but it lacks protective coating, making it susceptible to oxidation and surface damage without additional treatment. You should consider anodized aluminum for durability and appearance, while bare aluminum suits projects prioritizing affordability and ease of fabrication.
Anodized aluminum vs Bare aluminum Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com