Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance per volume and better stability under varying temperatures, while ceramic capacitors provide lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) and superior high-frequency performance. Discover which capacitor suits Your specific electronic applications by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
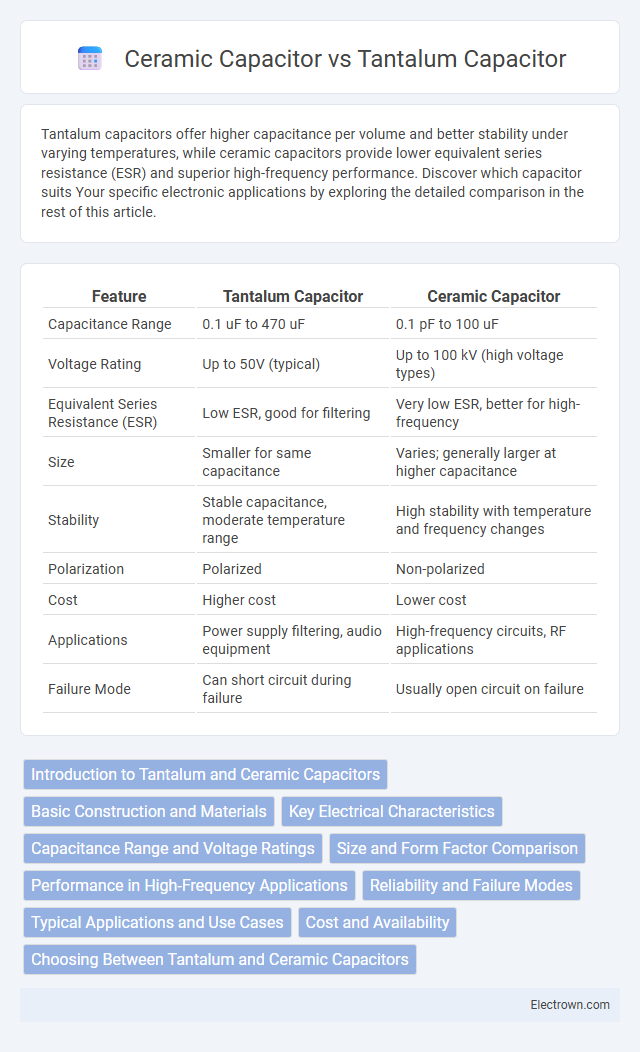
| Feature | Tantalum Capacitor | Ceramic Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance Range | 0.1 uF to 470 uF | 0.1 pF to 100 uF |
| Voltage Rating | Up to 50V (typical) | Up to 100 kV (high voltage types) |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Low ESR, good for filtering | Very low ESR, better for high-frequency |
| Size | Smaller for same capacitance | Varies; generally larger at higher capacitance |
| Stability | Stable capacitance, moderate temperature range | High stability with temperature and frequency changes |
| Polarization | Polarized | Non-polarized |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Applications | Power supply filtering, audio equipment | High-frequency circuits, RF applications |
| Failure Mode | Can short circuit during failure | Usually open circuit on failure |
Introduction to Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance per volume and stable electrical characteristics, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term reliability and low ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance). Ceramic capacitors are widely used for their low cost, high-frequency performance, and excellent temperature stability across various capacitance values. Both types serve distinct roles in electronic circuits, with tantalum capacitors favored for energy storage in power supply filtering and ceramic capacitors preferred for decoupling and signal filtering.
Basic Construction and Materials
Tantalum capacitors feature an anode made from sintered tantalum powder, a solid manganese dioxide or polymer cathode, and a tantalum pentoxide dielectric layer, offering stable capacitance with high volumetric efficiency. Ceramic capacitors consist of a ceramic dielectric material between multiple layers of metal electrodes, typically made of barium titanate or other ferroelectric ceramics, allowing for a wide range of capacitance values and high-frequency performance. Your choice between these depends on the trade-offs in dielectric type and material properties linked with stability, size, and application requirements.
Key Electrical Characteristics
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance values with stable electrical performance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR), making them ideal for filtering and timing applications in power-sensitive circuits. Ceramic capacitors provide excellent high-frequency performance, low dielectric losses, and a wide range of voltage ratings, suitable for decoupling and noise suppression. Choosing between the two depends on your circuit's specific requirements for tolerance, voltage stability, and operating frequency.
Capacitance Range and Voltage Ratings
Tantalum capacitors typically offer capacitance values ranging from 0.1 uF to 470 uF with voltage ratings between 4V and 50V, making them suitable for stable, high-capacitance applications. Ceramic capacitors provide a broader capacitance range from a few picofarads up to 100 uF and can withstand higher voltages, often exceeding 100V, ideal for high-frequency and high-voltage circuits. Your choice depends on the required capacitance stability and voltage handling, where tantalum excels in lower voltage, higher capacitance, and ceramic is preferred for higher voltage, smaller capacitance needs.
Size and Form Factor Comparison
Tantalum capacitors generally offer a smaller size and higher volumetric efficiency compared to ceramic capacitors, making them ideal for compact electronic designs. Ceramic capacitors come in a wider variety of form factors, including surface-mount and through-hole versions, providing versatility but often resulting in larger physical dimensions for equivalent capacitance values. Your choice depends on the space constraints and performance requirements of your application, with tantalum capacitors preferred for high-capacitance, space-saving solutions.
Performance in High-Frequency Applications
Tantalum capacitors offer stable capacitance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR), making them suitable for moderate frequency circuits, while ceramic capacitors excel in high-frequency applications due to their low losses and superior high-frequency performance. Ceramic capacitors provide better impedance characteristics and faster response times, enhancing signal integrity in RF and microwave circuits. For your high-frequency designs, ceramic capacitors typically deliver improved performance and reliability over tantalum capacitors.
Reliability and Failure Modes
Tantalum capacitors exhibit higher reliability in DC applications due to their stable capacitance and lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR), but they are prone to catastrophic failure from voltage spikes and reverse polarity, often leading to short circuits. Ceramic capacitors offer excellent reliability under high-frequency conditions with low failure rates caused by mechanical stress or cracking, but their capacitance can degrade over time with temperature fluctuations and applied voltage (DC bias effect). Designers often choose tantalum capacitors for bulk energy storage with consistent performance, while ceramic capacitors are preferred for decoupling and filtering where mechanical robustness and self-healing properties mitigate failure risks.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Tantalum capacitors are frequently used in military, aerospace, and medical devices due to their stable capacitance and reliability under high temperatures and voltages. Ceramic capacitors find widespread application in consumer electronics, such as smartphones and computing devices, because of their low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and excellent high-frequency performance. Both types serve critical roles in power supply filtering, decoupling, and timing circuits, with tantalum preferred for compact, high-capacitance needs and ceramics favored for cost-effective, high-frequency applications.
Cost and Availability
Tantalum capacitors generally have higher costs due to their complex manufacturing process and reliance on scarce tantalum metal, affecting their availability in large volumes. Ceramic capacitors are more cost-effective and widely available, benefiting from abundant raw materials and automated mass production. This makes ceramic capacitors preferable for high-volume, cost-sensitive applications, while tantalum capacitors are reserved for specialized uses requiring stable capacitance and reliability.
Choosing Between Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance per volume and stable electrical characteristics, making them ideal for applications requiring reliable, long-term performance at low frequencies. Ceramic capacitors, known for their low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and high-frequency operation, excel in filtering and decoupling tasks in compact electronic circuits. Selecting between these capacitors depends on factors such as voltage rating, capacitance value, operating frequency, and environmental durability requirements.
tantalum capacitor vs ceramic capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com