Alumina substrates offer excellent electrical insulation and high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for a wide range of electronic applications, while aluminum nitride substrates provide superior thermal conductivity and better mechanical strength for high-performance devices. Discover how these differences impact your choice of substrate in various industries by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
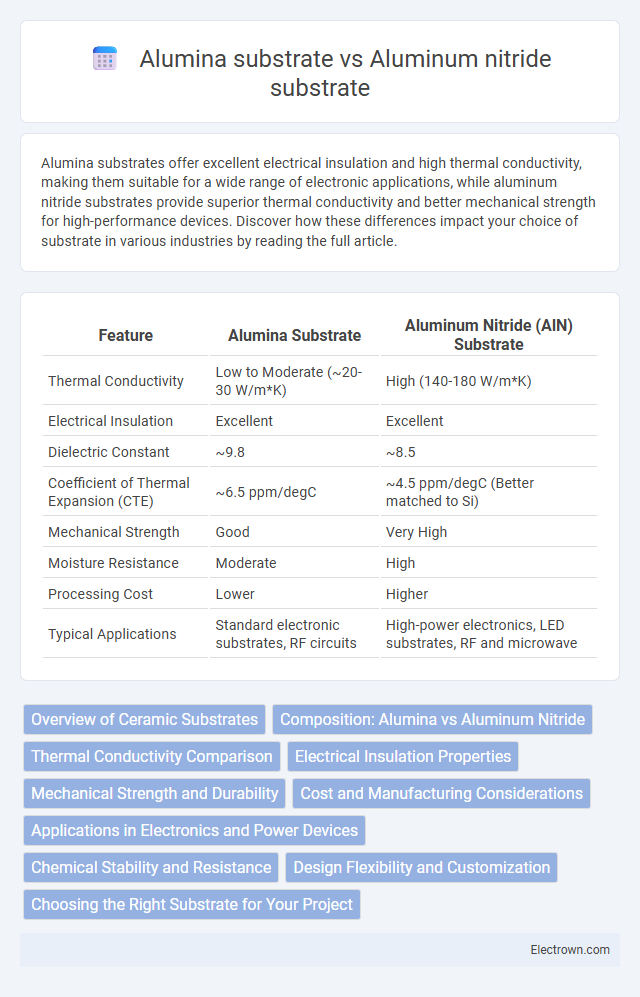
| Feature | Alumina Substrate | Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Substrate |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to Moderate (~20-30 W/m*K) | High (140-180 W/m*K) |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Excellent |
| Dielectric Constant | ~9.8 | ~8.5 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) | ~6.5 ppm/degC | ~4.5 ppm/degC (Better matched to Si) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | Very High |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Processing Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Standard electronic substrates, RF circuits | High-power electronics, LED substrates, RF and microwave |
Overview of Ceramic Substrates
Ceramic substrates like alumina and aluminum nitride offer exceptional thermal conductivity and electrical insulation for electronic applications. Alumina substrates provide excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness with thermal conductivities around 20-30 W/mK, while aluminum nitride substrates excel in superior thermal conductivity exceeding 170 W/mK, making them ideal for high-power devices. Both materials support high dielectric strength and chemical stability, but aluminum nitride's enhanced heat dissipation significantly improves device performance and reliability in demanding environments.
Composition: Alumina vs Aluminum Nitride
Alumina substrate consists primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), known for its excellent electrical insulation and thermal conductivity properties, while Aluminum Nitride (AlN) substrate is composed of aluminum and nitrogen atoms, offering significantly higher thermal conductivity and superior electrical insulation. Alumina's ceramic nature provides durability and cost-effectiveness, whereas Aluminum Nitride's unique crystal structure delivers enhanced performance in high-power electronic applications due to its superior heat dissipation capabilities. The choice between Alumina and Aluminum Nitride substrates depends on the specific thermal and electrical requirements of the device manufacturing process.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Aluminum nitride (AlN) substrates offer significantly higher thermal conductivity, typically around 170-230 W/mK, compared to alumina (Al2O3) substrates, which generally range from 20-30 W/mK. This makes aluminum nitride ideal for high-power electronic applications where efficient heat dissipation is critical. Choosing aluminum nitride over alumina substrate enhances your device's thermal management and reliability under demanding operational conditions.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Alumina substrates offer excellent electrical insulation with high dielectric strength and a stable dielectric constant, making them suitable for various electronic applications. Aluminum nitride substrates provide superior thermal conductivity while maintaining strong electrical insulation, ideal for high-power and high-frequency devices where efficient heat dissipation is critical. Your choice depends on balancing insulation performance with thermal management needs in your specific electronic design.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Aluminum nitride substrate offers superior mechanical strength and durability compared to alumina substrate due to its higher fracture toughness and resistance to thermal shock. Your electronics benefit from enhanced reliability and longevity when using aluminum nitride in demanding thermal and mechanical environments. Alumina substrates, while cost-effective, are more brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical stress over time.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Alumina substrates are generally more cost-effective due to their widespread availability and established manufacturing processes, making them suitable for budget-sensitive applications. Aluminum nitride substrates, while more expensive, offer superior thermal conductivity and require more specialized production techniques, which can increase overall manufacturing complexity and cost. Your choice between the two should balance the trade-off between cost efficiency and performance requirements in high thermal management scenarios.
Applications in Electronics and Power Devices
Alumina substrates are widely used in electronic applications such as circuit boards, LED lighting, and telecommunications due to their excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties. Aluminum nitride substrates outperform alumina in high-power electronic devices, offering superior thermal management and reliability in applications like power modules, radio frequency devices, and automotive electronics. Both materials play crucial roles in enhancing device performance, but aluminum nitride is preferred for demanding thermal environments in advanced power electronics.
Chemical Stability and Resistance
Alumina substrate exhibits excellent chemical stability and resistance to acids, alkalis, and high temperatures, making it suitable for harsh environments. Aluminum nitride substrate offers superior chemical inertness and enhanced resistance to oxidation compared to alumina, ensuring long-term durability in corrosive or high-temperature applications. Your choice depends on the specific chemical exposure and thermal requirements of your project.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Alumina substrates offer moderate design flexibility with cost-effective customization options suitable for standard electronic applications, while aluminum nitride substrates provide superior thermal conductivity and enhanced mechanical strength, enabling advanced design possibilities for high-performance devices. Your choice between alumina and aluminum nitride substrates depends on the specific thermal management requirements and the complexity of the circuit design. Customization in aluminum nitride supports intricate patterns and multilayer configurations, making it ideal for applications demanding precise thermal control and miniaturization.
Choosing the Right Substrate for Your Project
Alumina substrates offer excellent thermal conductivity around 20-30 W/mK and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for general electronic circuits and high-density multilayer applications. Aluminum nitride substrates provide superior thermal conductivity, typically above 170 W/mK, and excellent electrical insulation, suited for high-power, high-frequency devices requiring efficient heat dissipation. Selecting between alumina and aluminum nitride depends on the project's thermal management requirements, electrical performance needs, and budget constraints.
Alumina substrate vs Aluminum nitride substrate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com