Niobium and tantalum capacitors both offer high capacitance and reliability, but niobium capacitors are often more cost-effective and have better frequency characteristics, while tantalum capacitors excel in stability and tolerance under high temperature conditions. Explore the rest of the article to understand which capacitor best suits Your electronic designs.
Table of Comparison
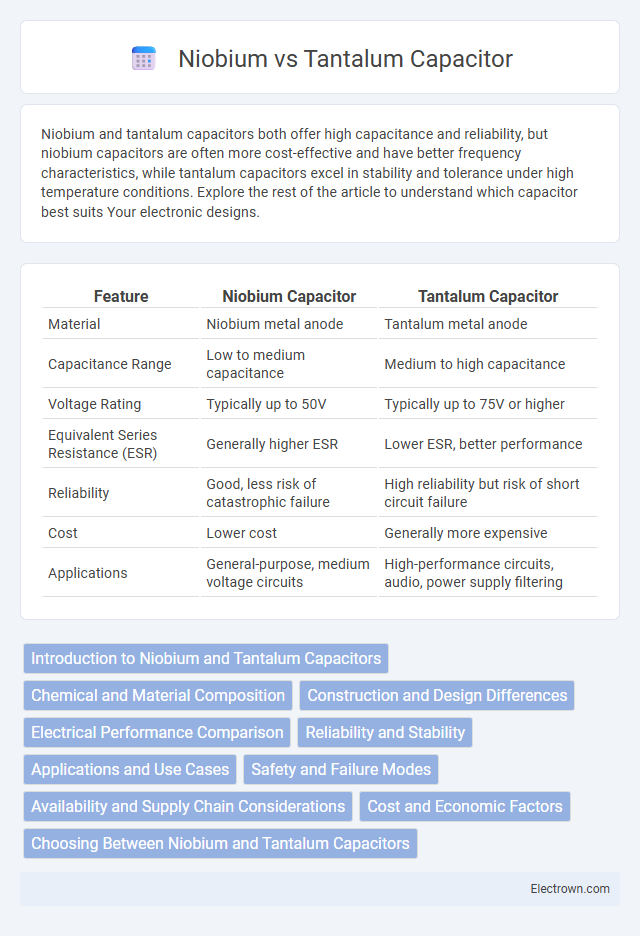
| Feature | Niobium Capacitor | Tantalum Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Niobium metal anode | Tantalum metal anode |
| Capacitance Range | Low to medium capacitance | Medium to high capacitance |
| Voltage Rating | Typically up to 50V | Typically up to 75V or higher |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Generally higher ESR | Lower ESR, better performance |
| Reliability | Good, less risk of catastrophic failure | High reliability but risk of short circuit failure |
| Cost | Lower cost | Generally more expensive |
| Applications | General-purpose, medium voltage circuits | High-performance circuits, audio, power supply filtering |
Introduction to Niobium and Tantalum Capacitors
Niobium capacitors offer an alternative to tantalum capacitors with similar high capacitance and stability but feature improved safety and lower cost due to niobium's abundance. Tantalum capacitors are widely used in electronics for their high volumetric efficiency, reliability, and excellent performance in filtering and energy storage applications. Both capacitor types utilize oxide layers as dielectric materials, but niobium capacitors often provide enhanced surge resistance and longer lifespan in demanding environments.
Chemical and Material Composition
Niobium capacitors utilize niobium metal or niobium oxide (Nb2O5) as the dielectric material, offering a stable dielectric layer with superior corrosion resistance. Tantalum capacitors are composed primarily of tantalum metal and tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5), providing high capacitance per volume due to its excellent dielectric properties. The distinct chemical composition influences their performance, with niobium capacitors being more environmentally friendly and less prone to failure compared to the higher capacitance but more sensitive tantalum counterparts.
Construction and Design Differences
Niobium capacitors utilize a niobium anode coated with an insulating layer of niobium pentoxide, offering stable capacitance and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) compared to tantalum capacitors that use a tantalum anode with tantalum pentoxide dielectric. The design of niobium capacitors often enables better surge current tolerance and improved self-healing characteristics, while tantalum capacitors are typically favored for their higher volumetric efficiency and longer established reliability in electronic circuits. Construction-wise, niobium capacitors tend to have a thicker dielectric layer, which contributes to enhanced stability and durability under harsh conditions, distinguishing them from traditional tantalum designs.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Niobium capacitors exhibit lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and better temperature stability compared to tantalum capacitors, making them suitable for high-frequency applications. Tantalum capacitors provide higher volumetric efficiency with greater capacitance density but often have higher leakage current and are more prone to catastrophic failure under surge conditions. Electrical performance choice depends on balancing reliability, frequency response, and capacitance requirements specific to the application.
Reliability and Stability
Niobium capacitors offer excellent reliability and stability due to their self-healing properties and resistance to voltage spikes, making them suitable for applications requiring consistent performance under stress. Tantalum capacitors provide higher capacitance per volume and superior long-term stability, but they are more sensitive to voltage derating and can fail catastrophically if improperly used. Choosing between niobium and tantalum capacitors depends on your application's tolerance for risk and the required balance between durability and electrical performance.
Applications and Use Cases
Niobium capacitors are widely used in applications requiring high capacitance and moderate voltage, such as power supply filtering in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial equipment. Tantalum capacitors excel in space-constrained devices like smartphones, medical implants, and aerospace technology due to their stable capacitance and high reliability under extreme conditions. Your choice between niobium and tantalum capacitors depends on the specific voltage, size, and durability requirements of the application.
Safety and Failure Modes
Niobium capacitors exhibit safer failure modes by typically failing open-circuit, reducing the risk of short circuits and potential fire hazards compared to tantalum capacitors, which are prone to catastrophic failures such as venting or burning when exposed to voltage spikes or manufacturing defects. The inherent stability of niobium oxide dielectric allows niobium capacitors to withstand higher current surges without degradation, enhancing overall reliability and safety in your electronic designs. Choosing niobium capacitors can significantly mitigate failure risks and improve safety margins in critical applications where capacitor failure could lead to severe consequences.
Availability and Supply Chain Considerations
Niobium capacitors generally benefit from more stable availability due to a diversified supply chain and less geopolitical risk compared to tantalum capacitors, which rely heavily on tantalum sourced from conflict-prone regions like the Democratic Republic of Congo. Tantalum faces stricter regulations and ethical sourcing challenges, impacting lead times and costs, while niobium's supply is more predictable and less subject to sudden shortages. For your designs, choosing niobium capacitors can reduce supply chain disruptions and ensure more reliable procurement.
Cost and Economic Factors
Niobium capacitors generally offer a lower cost compared to tantalum capacitors due to more abundant raw material availability and simpler manufacturing processes, making them economically favorable for budget-sensitive projects. Tantalum capacitors, while typically more expensive, provide superior performance characteristics such as higher capacitance and stability, justifying their cost in high-reliability applications. Your choice depends on balancing initial expenses with performance needs and long-term reliability considerations.
Choosing Between Niobium and Tantalum Capacitors
Niobium capacitors offer higher volumetric efficiency and are more cost-effective compared to tantalum capacitors, making them suitable for applications requiring compact size and budget constraints. Tantalum capacitors provide superior electrical performance with higher capacitance stability and better reliability under high-temperature conditions, ideal for demanding aerospace and military electronics. Selecting between niobium and tantalum capacitors depends on balancing performance requirements, cost considerations, and environmental operating conditions.
niobium vs tantalum capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com