Glass epoxy PCBs offer superior mechanical strength and moisture resistance, making them ideal for high-performance and durable electronic applications, while phenolic PCBs are more cost-effective but less robust, suitable for low-cost, low-frequency devices. Explore this article to understand which PCB material best suits Your electronic project requirements.
Table of Comparison
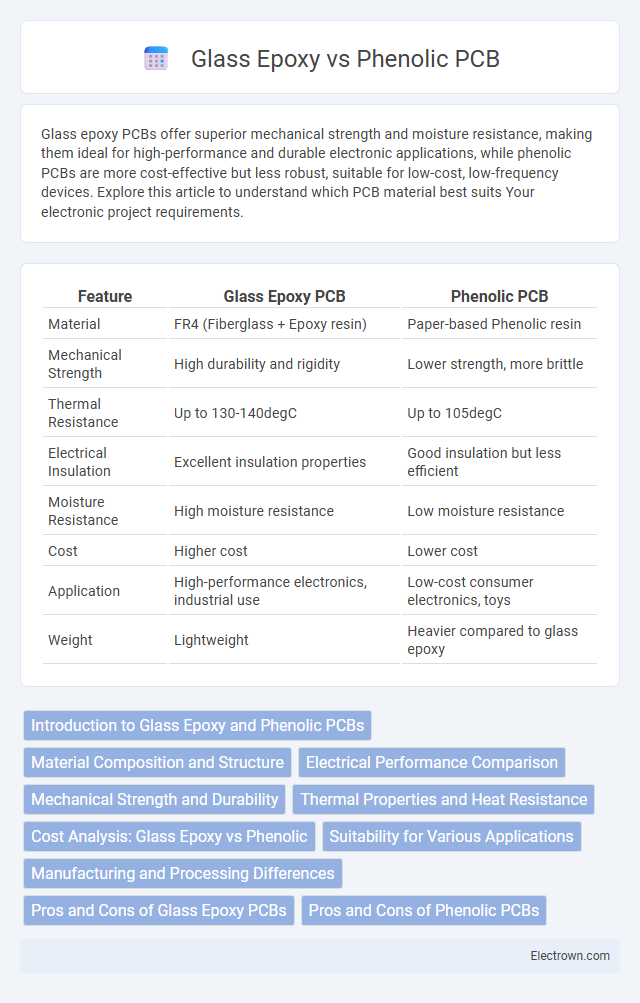
| Feature | Glass Epoxy PCB | Phenolic PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Material | FR4 (Fiberglass + Epoxy resin) | Paper-based Phenolic resin |
| Mechanical Strength | High durability and rigidity | Lower strength, more brittle |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 130-140degC | Up to 105degC |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent insulation properties | Good insulation but less efficient |
| Moisture Resistance | High moisture resistance | Low moisture resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Application | High-performance electronics, industrial use | Low-cost consumer electronics, toys |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier compared to glass epoxy |
Introduction to Glass Epoxy and Phenolic PCBs
Glass epoxy PCBs, commonly known as FR4, are made from woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder, offering superior mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation properties for high-performance electronics. Phenolic PCBs use phenol-formaldehyde resin, providing a cost-effective and lightweight option, but with lower durability and heat tolerance compared to glass epoxy boards. Choosing between these materials impacts the reliability, heat resistance, and overall lifespan of Your electronic assemblies.
Material Composition and Structure
Glass epoxy PCBs consist of woven fiberglass cloth bonded with epoxy resin, providing superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance compared to phenolic PCBs, which are made from paper-based laminate with phenolic resin. The glass fibers in epoxy boards create a rigid, durable structure ideal for high-frequency and high-temperature applications, while phenolic boards offer a more cost-effective solution with lower mechanical robustness and thermal stability. Choosing between these materials depends on your circuit's performance requirements, with glass epoxy being preferred for reliability and phenolic suited for budget-sensitive, low-stress environments.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Glass epoxy PCBs exhibit higher dielectric strength and lower dissipation factors compared to phenolic PCBs, resulting in superior insulation and reduced signal loss in high-frequency applications. Phenolic PCBs typically have greater dielectric constants, which can lead to increased signal delay and attenuation, limiting their use in precision electronic circuits. The thermal stability of glass epoxy substrates further enhances electrical performance, ensuring consistent conductivity and minimal impedance variation under varying operating conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Glass epoxy PCBs exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to phenolic PCBs due to their fiberglass reinforcement, providing enhanced resistance to wear, impact, and environmental stress. Phenolic PCBs tend to be more brittle and less resistant to heat and moisture, resulting in lower longevity in demanding applications. The enhanced thermal stability and rigidity of glass epoxy materials ensure consistent performance in high-stress mechanical environments.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Glass epoxy PCBs exhibit superior thermal properties with a higher glass transition temperature (Tg) typically around 130-180degC, ensuring excellent heat resistance and dimensional stability under thermal stress. Phenolic PCBs have a lower Tg, usually around 90-120degC, making them less suitable for high-temperature applications and prone to warping or degradation when exposed to intense heat. Your choice of PCB material should consider these thermal performance differences to ensure reliable operation in environments with significant heat exposure.
Cost Analysis: Glass Epoxy vs Phenolic
Glass epoxy PCBs generally incur higher material and manufacturing costs compared to phenolic PCBs due to superior thermal stability and electrical performance. Phenolic PCBs offer a cost-effective solution for low-end, less demanding applications but may suffer from lower durability and moisture resistance. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for reliability and long-term performance in the intended electronic device.
Suitability for Various Applications
Glass epoxy PCBs offer superior electrical insulation and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-frequency and high-performance electronic applications such as aerospace and telecommunications. Phenolic PCBs, being more cost-effective with moderate heat resistance, suit low-cost consumer electronics and simple circuit designs where extreme performance is not critical. You should choose glass epoxy for durability and reliability in demanding environments, while phenolic is suitable for budget-friendly projects with less stringent requirements.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Glass epoxy PCBs, made from fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin, offer superior mechanical strength and thermal stability due to their high-quality laminate materials, whereas phenolic PCBs use a cheaper cellulose-based resin that results in lower durability and heat resistance. Manufacturing processes for glass epoxy involve precision layering and curing under controlled temperatures to ensure reliability in high-frequency applications, while phenolic PCBs are processed with simpler molding techniques suited for cost-sensitive, low-performance uses. Your choice depends on the required PCB performance, as glass epoxy demands more complex fabrication but provides enhanced longevity and electrical insulation compared to the more easily produced and economical phenolic boards.
Pros and Cons of Glass Epoxy PCBs
Glass epoxy PCBs offer excellent electrical insulation, high mechanical strength, and good thermal resistance, making them suitable for most electronic applications requiring durability and stability. However, they are generally more expensive than phenolic PCBs and may be less environmentally friendly due to the use of epoxy resins. Their superior performance in moisture resistance and dimensional stability compensates for these drawbacks in high-reliability and high-frequency circuits.
Pros and Cons of Phenolic PCBs
Phenolic PCBs offer cost-effective manufacturing and good mechanical strength, making them suitable for budget-sensitive applications and simple electronic devices. However, their thermal resistance is lower than glass epoxy PCBs, leading to potential warping or degradation under high-temperature conditions. Electrical performance is also inferior, resulting in higher signal loss and reduced reliability for complex or high-frequency circuits.
glass epoxy vs phenolic PCB Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com