Conformal coating provides a thin protective layer that guards electronics against moisture, dust, and contaminants while maintaining component accessibility, whereas potting involves encapsulating the entire assembly in a thick compound for robust mechanical and environmental protection. Explore the article to understand which method best suits your project's specific needs and performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
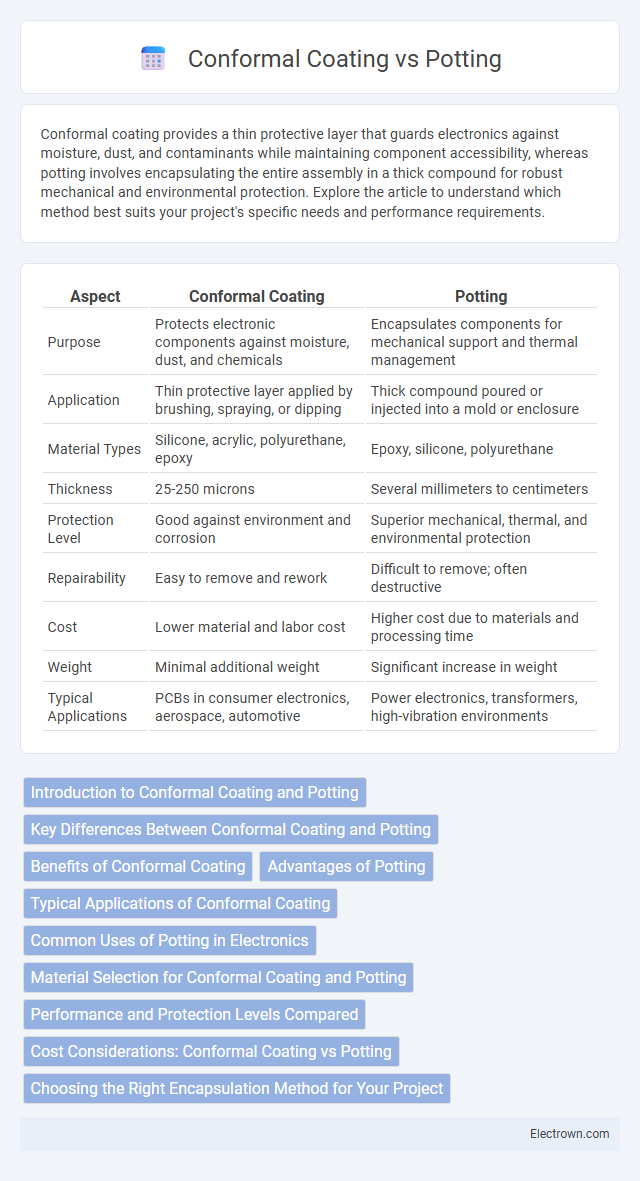
| Aspect | Conformal Coating | Potting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects electronic components against moisture, dust, and chemicals | Encapsulates components for mechanical support and thermal management |
| Application | Thin protective layer applied by brushing, spraying, or dipping | Thick compound poured or injected into a mold or enclosure |
| Material Types | Silicone, acrylic, polyurethane, epoxy | Epoxy, silicone, polyurethane |
| Thickness | 25-250 microns | Several millimeters to centimeters |
| Protection Level | Good against environment and corrosion | Superior mechanical, thermal, and environmental protection |
| Repairability | Easy to remove and rework | Difficult to remove; often destructive |
| Cost | Lower material and labor cost | Higher cost due to materials and processing time |
| Weight | Minimal additional weight | Significant increase in weight |
| Typical Applications | PCBs in consumer electronics, aerospace, automotive | Power electronics, transformers, high-vibration environments |
Introduction to Conformal Coating and Potting
Conformal coating is a thin, protective polymeric film applied to electronic assemblies to guard against moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature extremes while maintaining component accessibility. Potting involves encapsulating electronic components in a rigid or gel-like resin, providing superior mechanical support and environmental protection but limiting accessibility for repairs. Both techniques enhance reliability and longevity of electronics in harsh environments, with conformal coating favored for lightweight protection and potting chosen for robust defense.
Key Differences Between Conformal Coating and Potting
Conformal coating provides a thin protective film that shields electronic circuits from moisture, dust, and chemicals without hiding component details, whereas potting involves encapsulating the entire assembly in a thick resin for robust mechanical protection and enhanced thermal dissipation. Conformal coatings are typically measured in microns and allow for easier inspection and repair, while potting compounds create a solid barrier making rework difficult but offering superior vibration and shock resistance. The choice between conformal coating and potting depends on the application's environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and required maintenance accessibility.
Benefits of Conformal Coating
Conformal coating provides a thin, protective layer that shields electronic circuits from moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature variations, enhancing device reliability and lifespan without adding significant weight or bulk. It allows for easy inspection and rework of components since the coating is transparent and removable, unlike potting compounds which encapsulate devices more rigidly. This makes conformal coating ideal for applications requiring electrical insulation and environmental protection while maintaining flexibility in manufacturing and maintenance.
Advantages of Potting
Potting offers superior protection against moisture, vibration, and mechanical damage by fully encapsulating electronic components in a durable compound, enhancing long-term reliability. It provides excellent thermal dissipation, reducing the risk of overheating in high-power applications. Your electronics benefit from increased resistance to harsh environmental conditions, making potting ideal for rugged or outdoor use.
Typical Applications of Conformal Coating
Conformal coating is typically used in electronics where protection from moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature extremes is essential without adding significant bulk, such as in circuit boards for aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics. It preserves electrical insulation and reliability in compact devices like smartphones, medical equipment, and LED lighting. Your devices benefit from conformal coatings when lightweight, flexible, and thin protective layers are necessary to maintain performance and durability.
Common Uses of Potting in Electronics
Potting is commonly used in electronics to provide robust protection against moisture, vibration, and mechanical shock, making it ideal for sealed enclosures in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. It enhances electrical insulation and thermal management by encapsulating components in a durable resin that improves reliability and lifespan. Your sensitive electronic assemblies benefit from potting when exposed to harsh environments requiring superior protection beyond what conformal coating can offer.
Material Selection for Conformal Coating and Potting
Material selection for conformal coating typically involves thin, flexible polymers like acrylics, silicones, or urethanes that provide moisture resistance and dielectric protection without adding significant weight. Potting materials often include epoxies, polyurethanes, or silicone compounds designed for robust mechanical protection, thermal management, and environmental sealing by encapsulating entire electronic assemblies. Choosing between conformal coating and potting materials depends on specific application needs such as flexibility, thermal conductivity, insulation, and exposure to harsh environments.
Performance and Protection Levels Compared
Conformal coating provides a thin, protective layer that safeguards electronic components against moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants while maintaining flexibility and ease of inspection or repair. Potting encapsulates entire assemblies in a solid mass, offering superior mechanical strength, shock resistance, and environmental sealing, making it ideal for harsh conditions. Performance-wise, conformal coating excels in lightweight protection and heat dissipation, whereas potting delivers enhanced durability and protection in extreme environments.
Cost Considerations: Conformal Coating vs Potting
Conformal coating generally offers lower material and application costs compared to potting, making it a cost-effective solution for protecting electronic components with minimal added weight and bulk. Potting involves higher expenses due to the larger volume of encapsulant material and more labor-intensive processes required for complete encapsulation and curing. Your choice between conformal coating and potting should consider these cost differences alongside protection requirements and production volume to optimize budget and performance.
Choosing the Right Encapsulation Method for Your Project
Selecting between conformal coating and potting depends on the environmental protection requirements and mechanical stress of your project. Conformal coating offers a thin, lightweight layer that shields electronic components from moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants while maintaining component accessibility and heat dissipation. Potting provides robust protection by fully encapsulating components in a solid or gel compound, ideal for harsh environments requiring high impact resistance and vibration damping.
conformal coating vs potting Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com