Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and Printed Wiring Boards (PWBs) are often used interchangeably, but PCBs typically include added components like conductive pathways, pads, and more complex features for electronic circuits, while PWBs are simpler boards focused primarily on wiring connections. If you want to understand the key differences and choose the best option for your electronics project, continue reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
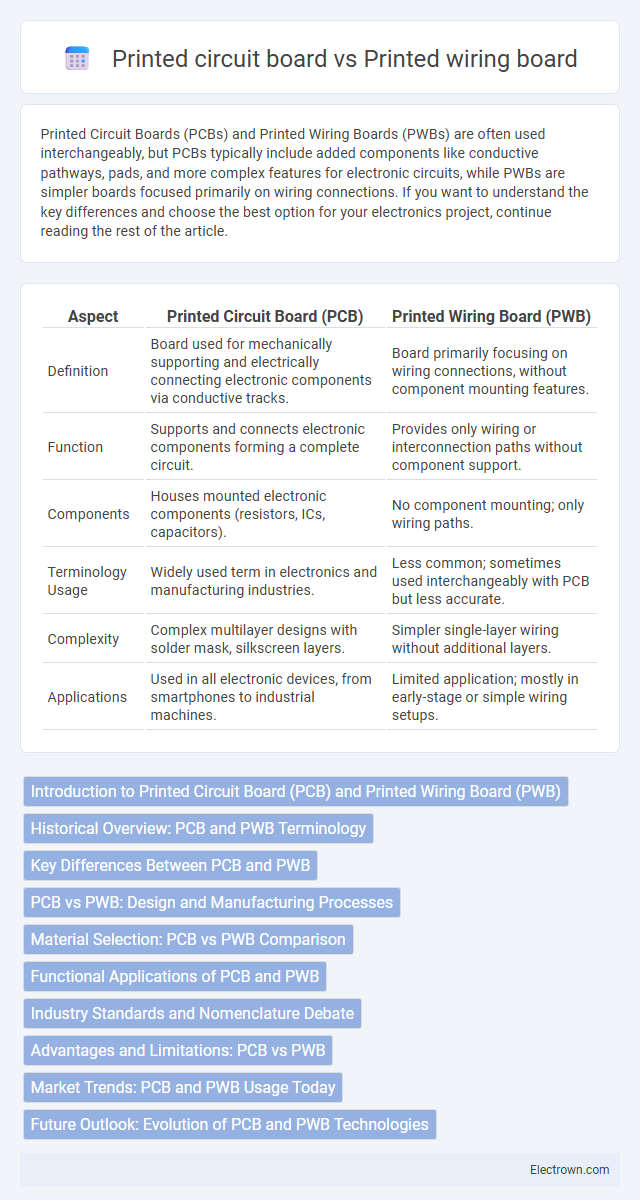
| Aspect | Printed Circuit Board (PCB) | Printed Wiring Board (PWB) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Board used for mechanically supporting and electrically connecting electronic components via conductive tracks. | Board primarily focusing on wiring connections, without component mounting features. |
| Function | Supports and connects electronic components forming a complete circuit. | Provides only wiring or interconnection paths without component support. |
| Components | Houses mounted electronic components (resistors, ICs, capacitors). | No component mounting; only wiring paths. |
| Terminology Usage | Widely used term in electronics and manufacturing industries. | Less common; sometimes used interchangeably with PCB but less accurate. |
| Complexity | Complex multilayer designs with solder mask, silkscreen layers. | Simpler single-layer wiring without additional layers. |
| Applications | Used in all electronic devices, from smartphones to industrial machines. | Limited application; mostly in early-stage or simple wiring setups. |
Introduction to Printed Circuit Board (PCB) and Printed Wiring Board (PWB)
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and Printed Wiring Boards (PWBs) are foundational components in electronic device assembly, serving as the platform for mounting and connecting electronic components. PCBs integrate conductive pathways etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate, enabling complex circuit designs, while PWBs primarily refer to the bare boards without component mounting, focusing on the physical wiring layout. Understanding the distinction between PCBs and PWBs helps optimize your electronic design process, ensuring appropriate selection based on circuit complexity and manufacturing needs.
Historical Overview: PCB and PWB Terminology
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) and Printed Wiring Board (PWB) terminology originated in the mid-20th century, where PWB was initially used to describe the mechanical support for wiring, while PCB evolved to include the conductive pathways etched onto an insulating substrate. The transition from PWB to PCB reflects advancements in electronics manufacturing, emphasizing integrated circuits and complex circuitry designs over simple wiring. Understanding this historical distinction helps clarify the evolution of your electronic assembly processes and the terminology used in modern manufacturing contexts.
Key Differences Between PCB and PWB
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) features a complete assembly of electronic components soldered onto a board with etched conductive pathways, serving as an integrated platform for electrical connections. Printed Wiring Board (PWB) refers specifically to the bare board containing only the conductive wiring patterns without any mounted components, essentially acting as the foundation for a PCB. The key differences lie in the PWB's role as an unpopulated substrate used for wire routing, whereas the PCB represents the fully assembled and functional electronic circuit.
PCB vs PWB: Design and Manufacturing Processes
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and Printed Wiring Boards (PWBs) differ primarily in complexity, with PCBs incorporating layered components and integrated circuits, while PWBs mostly involve simple wiring layouts. Your design process for PCBs requires advanced photolithography, solder mask application, and multilayer etching, whereas PWBs often use basic etching and single-layer fabrication techniques. Manufacturing PCBs demands higher precision and quality control due to their complexity, while PWBs offer cost-effective solutions for straightforward electrical connections.
Material Selection: PCB vs PWB Comparison
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) primarily use fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin (FR-4) or composite materials for enhanced durability and electrical insulation, whereas Printed Wiring Boards (PWBs) often feature simpler materials like phenolic or paper-based substrates for cost efficiency. PCBs demand high dielectric strength and thermal stability to support complex multi-layer circuits, making material selection critical to performance and reliability. In contrast, PWBs are suited for less complex applications where material properties can be more basic, focusing on mechanical support rather than advanced electrical characteristics.
Functional Applications of PCB and PWB
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are primarily used for supporting and electrically connecting electronic components in devices like computers, smartphones, and automotive systems, integrating complex circuits for signal processing and power management. Printed Wiring Boards (PWBs), on the other hand, mainly provide a physical platform with conductive pathways for simpler electronic assemblies, often used in basic or lower-density circuit designs. Your choice between PCB and PWB will depend on the complexity and functionality required in your electronic application.
Industry Standards and Nomenclature Debate
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and Printed Wiring Boards (PWBs) are often used interchangeably in the electronics industry, but industry standards like IPC-6012 clearly define PCBs to include conductive patterns and associated electronic components. The nomenclature debate arises primarily because PWBs technically refer only to the bare conductive patterns without components, while PCBs imply a fully assembled board. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate technical documentation and supplier specifications with greater accuracy.
Advantages and Limitations: PCB vs PWB
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) offer high-density component placement and superior electrical performance due to their layered structure and integrated conductive pathways, making them ideal for complex electronic assemblies. Printed Wiring Boards (PWBs), which primarily provide mechanical support and basic wiring, are simpler and cost-effective but lack the enhanced signal integrity and compact design capabilities of PCBs. Limitations of PWBs include less flexibility for multi-layer designs and reduced ability to handle high-speed signals compared to PCBs, which can incorporate various substrate materials and advanced manufacturing techniques for enhanced durability and functionality.
Market Trends: PCB and PWB Usage Today
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) dominate the electronics market due to their integrated design, providing reliable connections for complex devices like smartphones and computers, while printed wiring boards (PWBs) are primarily used in simpler, cost-sensitive applications. The global PCB market is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 5-6% from 2023 to 2028, driven by increased demand in automotive, consumer electronics, and telecommunications sectors. You should consider PCBs for modern, high-performance electronics due to their versatility and advanced manufacturing processes compared to PWBs.
Future Outlook: Evolution of PCB and PWB Technologies
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) and Printed Wiring Board (PWB) technologies are advancing towards higher density interconnects and flexible substrates to meet the demands of compact and high-performance electronic devices. Emerging trends include the integration of advanced materials such as graphene and the adoption of additive manufacturing techniques, which enhance conductivity and enable rapid prototyping. The evolution of PCB and PWB technologies is shaping the future of electronics by supporting increased miniaturization, improved thermal management, and enhanced signal integrity.
Printed circuit board vs Printed wiring board Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com