Electrolytic capacitors offer high capacitance values and are commonly used for power supply filtering, while film capacitors provide superior stability, low loss, and long lifespan, making them ideal for precision applications. To understand which capacitor best suits your needs, explore the detailed comparison in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
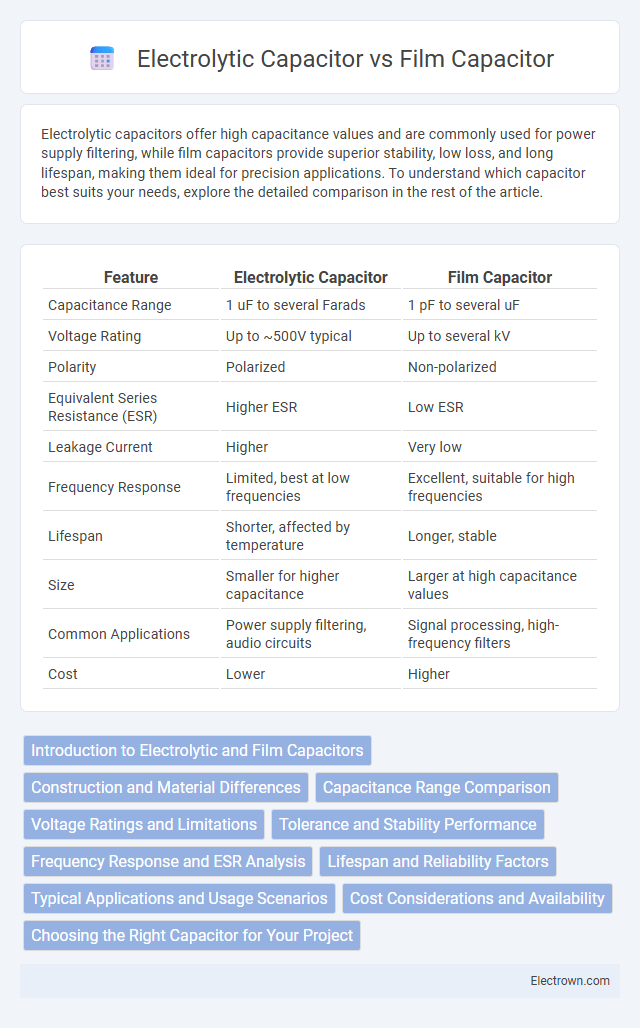
| Feature | Electrolytic Capacitor | Film Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance Range | 1 uF to several Farads | 1 pF to several uF |
| Voltage Rating | Up to ~500V typical | Up to several kV |
| Polarity | Polarized | Non-polarized |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Higher ESR | Low ESR |
| Leakage Current | Higher | Very low |
| Frequency Response | Limited, best at low frequencies | Excellent, suitable for high frequencies |
| Lifespan | Shorter, affected by temperature | Longer, stable |
| Size | Smaller for higher capacitance | Larger at high capacitance values |
| Common Applications | Power supply filtering, audio circuits | Signal processing, high-frequency filters |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Electrolytic and Film Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors utilize an electrolyte as one of their plates, offering high capacitance values suitable for power supply filtering and bulk energy storage. Film capacitors, constructed from thin plastic films, provide superior stability, low loss, and high voltage ratings, making them ideal for precision applications and signal processing. These capacitor types differ significantly in dielectric materials, performance characteristics, and typical usage scenarios.
Construction and Material Differences
Electrolytic capacitors utilize an aluminum or tantalum anode coated with an oxide layer as the dielectric, combined with a liquid or gel electrolyte that completes the circuit, enabling high capacitance in a compact size. Film capacitors consist of thin plastic films such as polyester, polypropylene, or polytetrafluoroethylene as the dielectric material, wound or stacked to offer superior stability, low losses, and longer lifespan. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize high capacitance with moderate tolerance or low loss with precise performance.
Capacitance Range Comparison
Electrolytic capacitors typically offer capacitance values ranging from 1 uF to several thousand uF, making them suitable for applications requiring high capacitance in a compact size. Film capacitors generally provide lower capacitance values, usually between 1 nF and 10 uF, but excel in stability and low loss characteristics. Choosing between the two depends on your need for capacitance magnitude versus performance attributes like tolerance and longevity.
Voltage Ratings and Limitations
Electrolytic capacitors typically offer higher capacitance values but have lower voltage ratings, usually ranging from 6.3V to 500V, and are prone to voltage derating under load conditions. Film capacitors provide superior voltage stability with ratings often exceeding 1000V, making them ideal for high-voltage applications due to their self-healing properties and low dielectric losses. The voltage limitations of electrolytic capacitors restrict their use in circuits demanding high voltage durability, whereas film capacitors excel in scenarios requiring long-term reliability and consistent voltage handling.
Tolerance and Stability Performance
Electrolytic capacitors typically exhibit wider tolerance ranges, often between +-20%, while film capacitors maintain tighter tolerances, commonly around +-1% to +-5%, ensuring more precise capacitance values. In terms of stability, film capacitors outperform electrolytic types by providing superior long-term reliability and minimal capacitance drift due to temperature and aging effects. Your choice should consider that film capacitors deliver consistent performance in demanding applications requiring high accuracy and stability, whereas electrolytic capacitors suit scenarios where higher capacitance is needed despite variability.
Frequency Response and ESR Analysis
Electrolytic capacitors typically exhibit higher Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and poorer frequency response compared to film capacitors, making them suitable for low-frequency applications and power smoothing. Film capacitors have low ESR and stable characteristics across a broad frequency range, which enhances their performance in high-frequency filtering and signal integrity tasks. Understanding these differences allows you to select the appropriate capacitor type for optimizing circuit efficiency and frequency behavior.
Lifespan and Reliability Factors
Electrolytic capacitors typically have a shorter lifespan, often ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 hours, due to electrolyte evaporation and degradation under high temperatures. Film capacitors offer superior reliability and longevity, frequently exceeding 100,000 hours, because their solid dielectric materials resist aging and environmental stress more effectively. When selecting a capacitor for your application, consider the demanding operating conditions since film capacitors generally provide better stability and reliability over time compared to electrolytic types.
Typical Applications and Usage Scenarios
Electrolytic capacitors are commonly used in power supply filtering, audio equipment, and energy storage due to their high capacitance and voltage ratings, making them ideal for smoothing and decoupling applications. Film capacitors excel in high-frequency, low-loss circuits such as RF circuits, audio signal processing, and precision timing because of their stability, low ESR, and long lifespan. Your choice between electrolytic and film capacitors depends on the required capacitance, frequency response, and reliability for the specific application.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Electrolytic capacitors offer a lower cost per microfarad, making them economically suitable for applications requiring high capacitance values, while film capacitors generally come at a higher price due to their superior stability and lower dielectric losses. Availability of electrolytic capacitors is widespread in various capacitance and voltage ratings, favored in mass production and bulk purchases, whereas film capacitors are available in more limited capacitance ranges and commonly used in niche applications needing precision and reliability. Choosing between the two often depends on balancing budget constraints against performance and availability requirements in specific electronic designs.
Choosing the Right Capacitor for Your Project
Electrolytic capacitors offer high capacitance values and are ideal for filtering and bulk energy storage in power supply circuits, while film capacitors excel in stability, low loss, and high voltage applications such as signal processing and precision circuits. Selecting between these capacitors depends on requirements like capacitance range, voltage rating, tolerance, and intended frequency response. Understanding these parameters ensures optimal performance and reliability in electronic projects.
electrolytic capacitor vs film capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com