Copper clad laminate offers superior electrical conductivity and excellent thermal performance, making it ideal for high-frequency circuit applications, while aluminum clad laminate provides better heat dissipation and cost efficiency, suited for power electronics and LED substrates. Discover how choosing between copper and aluminum clad laminates can impact your project's performance and budget by exploring the detailed comparison ahead.
Table of Comparison
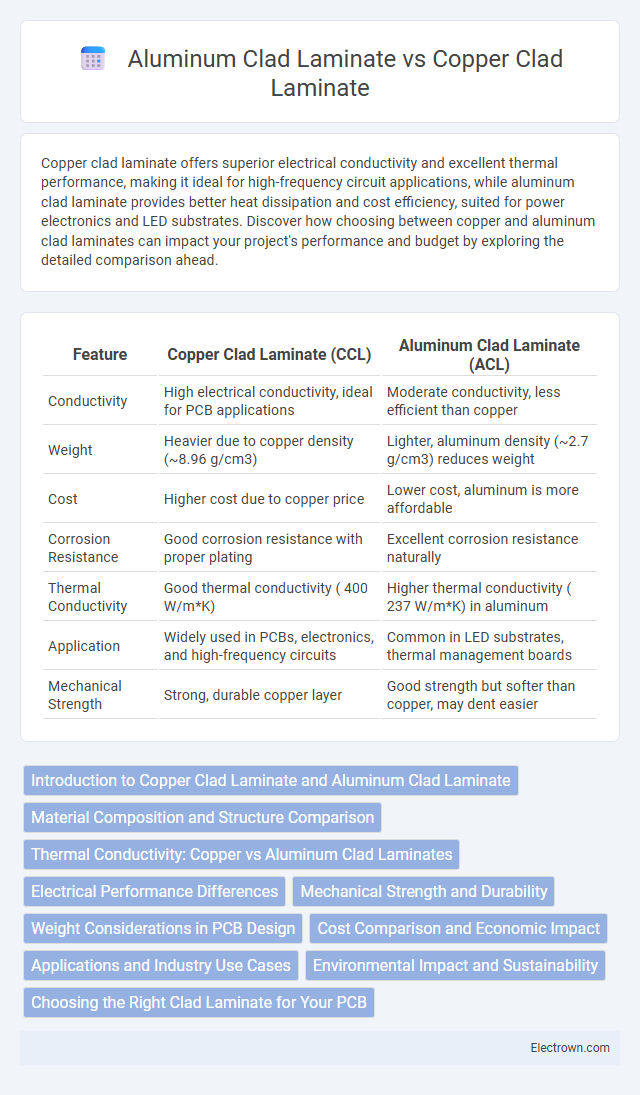
| Feature | Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) | Aluminum Clad Laminate (ACL) |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity, ideal for PCB applications | Moderate conductivity, less efficient than copper |
| Weight | Heavier due to copper density (~8.96 g/cm3) | Lighter, aluminum density (~2.7 g/cm3) reduces weight |
| Cost | Higher cost due to copper price | Lower cost, aluminum is more affordable |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good corrosion resistance with proper plating | Excellent corrosion resistance naturally |
| Thermal Conductivity | Good thermal conductivity ( 400 W/m*K) | Higher thermal conductivity ( 237 W/m*K) in aluminum |
| Application | Widely used in PCBs, electronics, and high-frequency circuits | Common in LED substrates, thermal management boards |
| Mechanical Strength | Strong, durable copper layer | Good strength but softer than copper, may dent easier |
Introduction to Copper Clad Laminate and Aluminum Clad Laminate
Copper clad laminate (CCL) consists of a non-conductive substrate laminated with copper foil, widely used in printed circuit boards (PCBs) due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal performance. Aluminum clad laminate (ACL) features a metal core of aluminum bonded to an insulating layer, offering superior heat dissipation and mechanical strength for high-power electronic applications. Both materials serve distinct roles in electronics manufacturing, with CCL preferred for fine circuit patterns and ACL chosen for thermal management in high-power devices.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Copper clad laminate consists of a fiberglass or resin substrate coated with a thin layer of copper foil, providing excellent electrical conductivity and thermal stability for printed circuit boards (PCBs). Aluminum clad laminate features a similar resin base but uses an aluminum foil layer, offering superior heat dissipation and mechanical strength while reducing overall weight. The choice between copper and aluminum clad laminates depends on the specific requirements for conductivity, thermal management, and structural durability in electronic applications.
Thermal Conductivity: Copper vs Aluminum Clad Laminates
Copper clad laminates exhibit superior thermal conductivity, typically around 400 W/mK, enabling efficient heat dissipation in high-performance electronic applications. Aluminum clad laminates, with thermal conductivity near 235 W/mK, provide a lightweight and cost-effective alternative but deliver lower heat transfer capabilities compared to copper. The enhanced thermal management of copper clad laminates is critical for minimizing thermal resistance and maintaining device reliability in demanding thermal environments.
Electrical Performance Differences
Copper clad laminates exhibit superior electrical conductivity compared to aluminum clad laminates, resulting in lower signal loss and enhanced performance in high-frequency applications. The electrical resistivity of copper (1.68 uO*cm) is significantly lower than that of aluminum (2.65 uO*cm), which improves current carrying capacity and reduces heat generation. This makes copper clad laminates the preferred choice for printed circuit boards (PCBs) requiring high efficiency and reliability in demanding electronic environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Copper clad laminates exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to aluminum clad laminates due to copper's higher tensile strength and better resistance to wear and corrosion. The enhanced toughness of copper clad laminates ensures longer operational life in demanding electrical and electronic applications. Aluminum clad laminates, while lighter and cost-effective, tend to have lower resistance to mechanical stress and environmental degradation.
Weight Considerations in PCB Design
Copper clad laminate (CCL) typically offers higher conductivity and durability but adds more weight compared to aluminum clad laminate (ACL), which is favored in PCB designs where weight reduction is critical. ACL provides enhanced thermal management with significantly lower density, making it suitable for lightweight and high-performance applications such as aerospace and portable electronics. Engineers must balance weight constraints with electrical and thermal requirements when selecting between CCL and ACL materials for optimal PCB performance.
Cost Comparison and Economic Impact
Copper clad laminate (CCL) typically has a higher initial cost than aluminum clad laminate (ACL) due to copper's superior electrical conductivity and durability. Your choice impacts long-term economic efficiency; CCL offers better signal integrity and corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses. ACL presents cost savings upfront but may incur higher lifecycle costs due to lower performance and shorter lifespan in demanding applications.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Copper clad laminate (CCL) is widely used in printed circuit boards (PCBs) for electronics, telecommunications, and automotive industries due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal management. Aluminum clad laminate (ACL) is preferred in LED lighting, power electronics, and high-power modules where enhanced heat dissipation and mechanical durability are critical. Your choice depends on whether the application prioritizes electrical performance with CCL or thermal management with ACL in industrial manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper clad laminates generally have a higher environmental impact due to the mining and refining processes of copper, which consume significant energy and generate waste. Aluminum clad laminates are often considered more sustainable because aluminum is highly recyclable and requires less energy to produce in recycled form. Choosing aluminum clad laminates can help reduce your project's carbon footprint and support circular economy initiatives.
Choosing the Right Clad Laminate for Your PCB
Copper clad laminate offers superior electrical conductivity and thermal performance, making it ideal for high-frequency and high-power PCB applications. Aluminum clad laminate provides enhanced heat dissipation and mechanical strength, suitable for LED lighting and power electronics requiring efficient thermal management. Selecting the right clad laminate depends on balancing factors like electrical requirements, thermal management needs, and mechanical durability for optimal PCB performance.
copper clad laminate vs aluminum clad laminate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com