NiMH batteries offer reliable performance with a lower risk of overheating and are often more affordable, while Li-ion batteries provide higher energy density, longer lifespan, and faster charging capabilities. To make an informed choice between NiMH vs Li-ion for your needs, explore the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
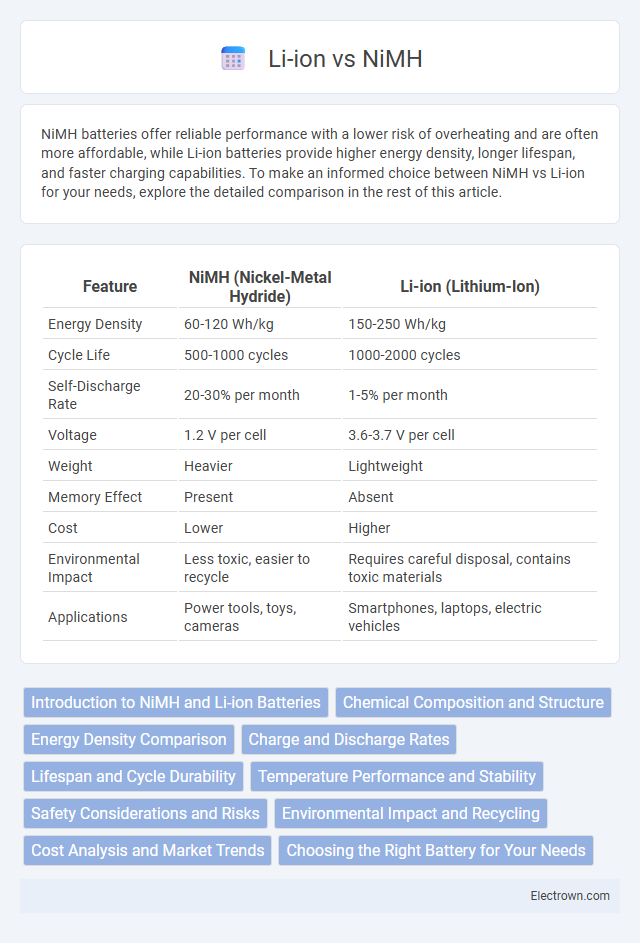
| Feature | NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) | Li-ion (Lithium-Ion) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 60-120 Wh/kg | 150-250 Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life | 500-1000 cycles | 1000-2000 cycles |
| Self-Discharge Rate | 20-30% per month | 1-5% per month |
| Voltage | 1.2 V per cell | 3.6-3.7 V per cell |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Memory Effect | Present | Absent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Environmental Impact | Less toxic, easier to recycle | Requires careful disposal, contains toxic materials |
| Applications | Power tools, toys, cameras | Smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles |
Introduction to NiMH and Li-ion Batteries
NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) and Li-ion (Lithium-ion) batteries are two widely used rechargeable battery types offering different performance characteristics. NiMH batteries provide a reliable energy density suitable for consumer electronics and hybrid vehicles, while Li-ion batteries deliver higher energy density, longer cycle life, and faster charging, making them dominant in portable devices and electric vehicles. Understanding the differences in chemistry, charge retention, and energy output helps you choose the optimal power source for your specific application.
Chemical Composition and Structure
NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) batteries consist of a nickel oxide hydroxide cathode and a hydrogen-absorbing alloy anode, relying on metal hydride electrochemistry for energy storage. Li-ion (Lithium-ion) batteries feature a lithium cobalt oxide or other lithium metal oxide cathode and a graphite anode, utilizing the intercalation of lithium ions to store and release energy efficiently. Understanding the chemical composition and internal structure of these batteries helps you determine their energy density, charge cycles, and overall performance characteristics.
Energy Density Comparison
Li-ion batteries typically offer an energy density ranging from 150 to 250 Wh/kg, significantly surpassing NiMH batteries, which generally provide around 60 to 120 Wh/kg. This higher energy density in Li-ion cells enables longer usage times and more compact battery designs in electronics and electric vehicles. Due to their lower energy density, NiMH batteries are bulkier and heavier for the same capacity, limiting their application where weight and size are critical factors.
Charge and Discharge Rates
NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) batteries typically exhibit lower charge and discharge rates compared to Li-ion (Lithium-ion) batteries, making them less suitable for applications requiring rapid energy replenishment or high power output. Li-ion chemistries can sustain higher charge currents and deliver more consistent discharge rates, enhancing performance in devices such as smartphones, electric vehicles, and power tools. The superior charge and discharge efficiency of Li-ion batteries contributes to faster charging times and prolonged battery life under intensive usage cycles.
Lifespan and Cycle Durability
NiMH batteries typically offer around 500 to 1,000 charge cycles with a lifespan of 3 to 5 years, while Li-ion batteries provide between 1,000 to 2,000 cycles and last approximately 5 to 10 years. Li-ion chemistry enables higher cycle durability due to lower self-discharge rates and better charge retention under varying temperatures. Battery management systems in Li-ion packs further enhance lifespan by preventing overcharging and deep discharges.
Temperature Performance and Stability
NiMH batteries maintain stable performance across moderate temperature ranges but suffer capacity loss and increased self-discharge in extreme heat or cold. Li-ion batteries offer superior temperature tolerance and consistent output, with advanced thermal management reducing risks of overheating and instability. Your device's efficiency and safety improve significantly with Li-ion cells due to their better temperature performance and enhanced chemical stability.
Safety Considerations and Risks
NiMH batteries offer enhanced safety due to their lower risk of overheating and thermal runaway compared to Li-ion cells, making them less prone to fire hazards. Li-ion batteries, while providing higher energy density, require strict management systems to prevent risks such as short circuits, overcharging, and potential explosions. Understanding these safety considerations helps you make informed decisions for applications where battery reliability and risk mitigation are critical.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
NiMH batteries contain fewer toxic metals compared to Li-ion, making them less harmful to the environment during disposal. Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density but require more complex recycling processes due to the presence of hazardous materials like lithium and cobalt. You can reduce your ecological footprint by choosing batteries with established recycling programs and supporting advancements in sustainable battery technology.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
NiMH batteries typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to Li-ion, making them a budget-friendly option for applications like power tools and hybrid vehicles. Li-ion batteries dominate the market due to their higher energy density, longer lifespan, and declining manufacturing costs, fueling rapid adoption in electric vehicles and portable electronics. Understanding these cost dynamics can help you make informed decisions based on current market trends and long-term value.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Needs
NiMH batteries offer reliable performance with a lower cost and better safety profile, making them ideal for devices with moderate power requirements and frequent recharging cycles. Li-ion batteries provide higher energy density, longer lifespan, and lighter weight, perfect for high-performance gadgets and portable electronics demanding extended usage. Evaluating your device's power consumption and usage patterns helps you choose the right battery for your needs.
NiMH vs Li-ion Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com