Flexible PCBs offer superior adaptability by conforming to complex shapes and enabling dynamic movement, while rigid PCBs provide enhanced durability and stability for fixed electronic assemblies. Discover the key differences and benefits of each to make the best choice for Your electronic projects in the full article.
Table of Comparison
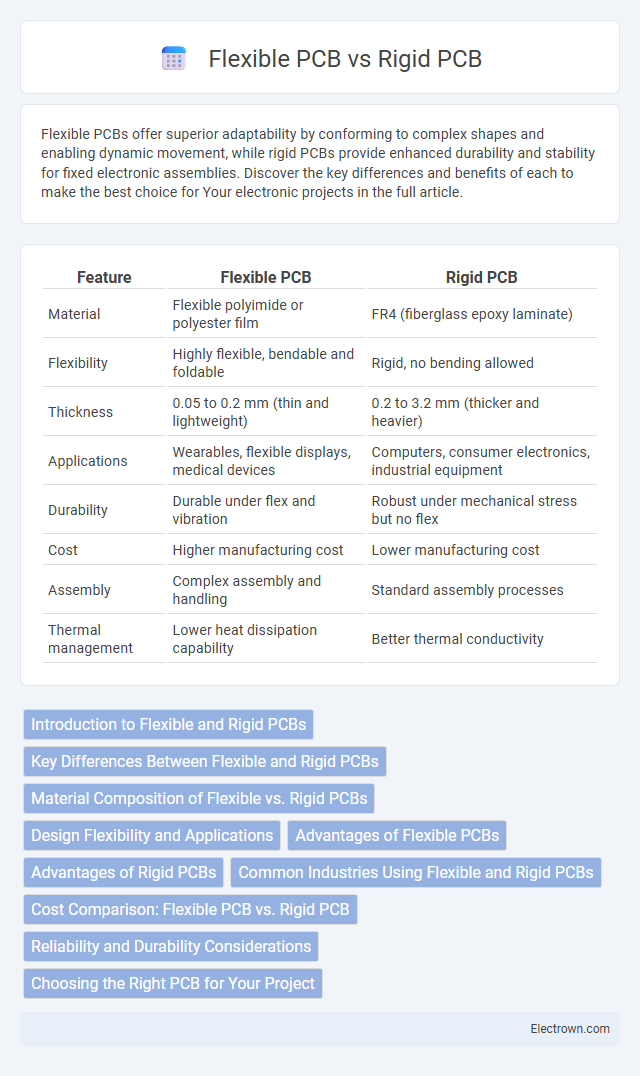
| Feature | Flexible PCB | Rigid PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Flexible polyimide or polyester film | FR4 (fiberglass epoxy laminate) |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, bendable and foldable | Rigid, no bending allowed |
| Thickness | 0.05 to 0.2 mm (thin and lightweight) | 0.2 to 3.2 mm (thicker and heavier) |
| Applications | Wearables, flexible displays, medical devices | Computers, consumer electronics, industrial equipment |
| Durability | Durable under flex and vibration | Robust under mechanical stress but no flex |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower manufacturing cost |
| Assembly | Complex assembly and handling | Standard assembly processes |
| Thermal management | Lower heat dissipation capability | Better thermal conductivity |
Introduction to Flexible and Rigid PCBs
Flexible PCBs, made from flexible plastic substrates such as polyimide, allow circuits to bend and conform to complex shapes, offering advantages in compact and dynamic electronic designs. Rigid PCBs use solid, inflexible materials like fiberglass to provide a stable platform for densely packed electronic components, ensuring durability and consistent performance. The choice between flexible and rigid PCBs depends on application requirements, including space constraints, mechanical stress, and electrical performance needs.
Key Differences Between Flexible and Rigid PCBs
Flexible PCBs are made from bendable materials like polyimide, allowing them to conform to complex shapes and reduce space in compact electronic devices, whereas rigid PCBs use solid substrates such as FR-4 for maximum stability and support. Flexible PCBs offer advantages in weight reduction and durability under dynamic conditions, while rigid PCBs provide superior mechanical strength and cost efficiency for standard applications. The key differences lie in their material composition, mechanical flexibility, and typical use cases in industries ranging from wearable technology to automotive electronics.
Material Composition of Flexible vs. Rigid PCBs
Flexible PCBs are made from polyimide or polyester films, which provide high flexibility, heat resistance, and durability, allowing them to bend or fold without damaging the circuitry. Rigid PCBs use fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate, such as FR4, ensuring a solid, stable base that supports complex, multi-layer circuit designs with enhanced mechanical strength. The difference in material composition directly impacts the application scope, with flexible PCBs suited for compact, wearable electronics and rigid PCBs ideal for robust, high-performance electronic devices.
Design Flexibility and Applications
Flexible PCBs offer superior design flexibility due to their ability to bend, fold, and conform to complex geometries, making them ideal for wearable devices, medical implants, and compact electronics. Rigid PCBs maintain a fixed, sturdy structure suitable for applications requiring high durability and stable component placement, such as computers, automotive control systems, and industrial machinery. The choice between flexible and rigid PCBs depends on specific application requirements, including space constraints, mechanical stress, and performance demands.
Advantages of Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs offer superior adaptability and space-saving benefits, enabling complex designs in compact electronic devices such as smartphones and wearable technology. Their ability to bend and twist reduces the need for connectors and solder joints, enhancing durability and reliability in dynamic applications like automotive and aerospace industries. Improved heat dissipation and lightweight construction further contribute to enhanced performance and energy efficiency compared to rigid PCBs.
Advantages of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs offer superior mechanical strength and durability, making them ideal for applications requiring stable and long-lasting circuit boards. They support higher component density and more complex circuit designs due to their solid substrate, enhancing performance in high-frequency and high-current environments. Their cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing contribute to widespread use in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial equipment.
Common Industries Using Flexible and Rigid PCBs
Flexible PCBs are widely used in industries like aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics due to their lightweight and adaptability to complex shapes. Rigid PCBs dominate automotive, industrial machinery, and telecommunications sectors where durability and high-performance stability are critical. Your choice between flexible and rigid PCBs depends on the specific mechanical and environmental demands of your application.
Cost Comparison: Flexible PCB vs. Rigid PCB
Flexible PCBs typically incur higher manufacturing costs due to their complex materials and production processes compared to rigid PCBs, which are more economical and widely used. However, flexible PCBs can reduce overall assembly and maintenance expenses by accommodating intricate designs and minimizing space, which can justify the initial investment. Your choice should consider both upfront costs and long-term savings based on the application's specific requirements.
Reliability and Durability Considerations
Flexible PCBs offer enhanced reliability in applications requiring dynamic bending and vibration resistance due to their ability to absorb mechanical stress without cracking. Rigid PCBs, while less adaptable to movement, provide superior durability in static environments with excellent structural integrity and resistance to physical damage. Selecting between flexible and rigid PCBs depends on the specific operational demands, balancing mechanical flexibility with long-term durability requirements.
Choosing the Right PCB for Your Project
Flexible PCBs offer lightweight, bendable designs ideal for compact or dynamic applications where space and movement are critical, while rigid PCBs provide durability and stability for high-performance, static electronic devices. Your choice depends on factors such as device form factor, mechanical stress tolerance, and production volume, with flexible PCBs excelling in wearable tech and rigid PCBs preferred in standard consumer electronics. Consider signal integrity requirements and assembly complexity to ensure optimal functionality and cost-efficiency for your project.
flexible PCB vs rigid PCB Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com