Epoxy resin offers superior adhesive strength and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance coatings and bonding applications, while polyurethane provides greater flexibility and UV resistance, suited for outdoor and impact-resistant uses. Discover which material best matches Your project needs by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
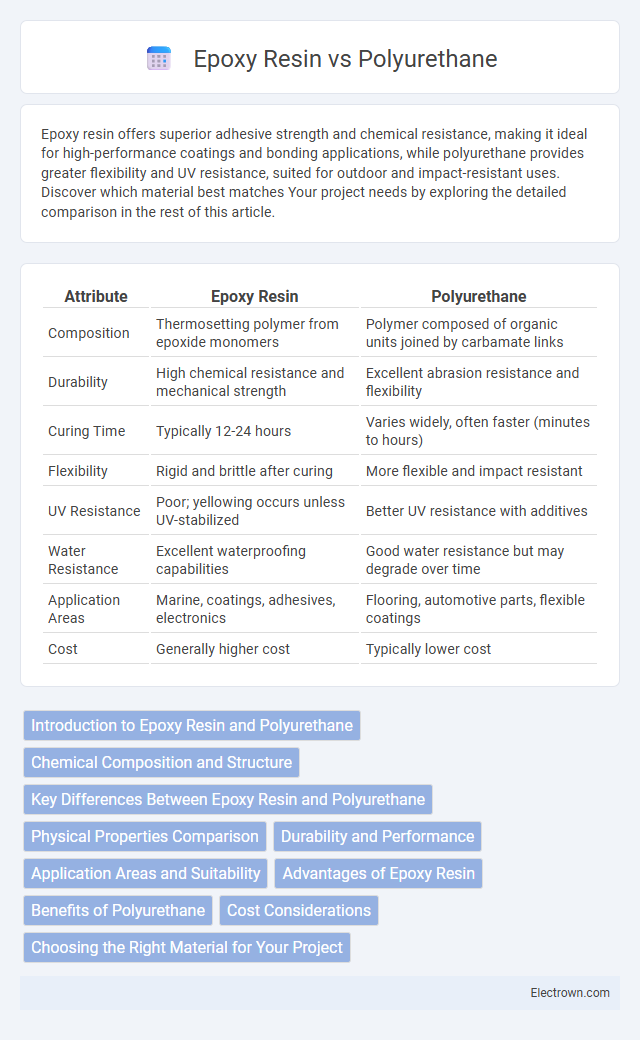
| Attribute | Epoxy Resin | Polyurethane |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Thermosetting polymer from epoxide monomers | Polymer composed of organic units joined by carbamate links |
| Durability | High chemical resistance and mechanical strength | Excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility |
| Curing Time | Typically 12-24 hours | Varies widely, often faster (minutes to hours) |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle after curing | More flexible and impact resistant |
| UV Resistance | Poor; yellowing occurs unless UV-stabilized | Better UV resistance with additives |
| Water Resistance | Excellent waterproofing capabilities | Good water resistance but may degrade over time |
| Application Areas | Marine, coatings, adhesives, electronics | Flooring, automotive parts, flexible coatings |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Typically lower cost |
Introduction to Epoxy Resin and Polyurethane
Epoxy resin is a thermosetting polymer known for its strong adhesive properties, chemical resistance, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for coatings, adhesives, and composite materials. Polyurethane, a versatile polymer available in flexible or rigid forms, offers outstanding elasticity, abrasion resistance, and moisture tolerance, commonly used in foams, sealants, and coatings. Your choice between epoxy resin and polyurethane depends on the specific application requirements such as durability, flexibility, and environmental exposure.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Epoxy resin consists of epoxide groups that react with hardeners to form a highly cross-linked, thermosetting polymer known for its strong adhesion and chemical resistance. Polyurethane features urethane linkages created by the reaction of polyols and isocyanates, resulting in a versatile polymer with elastomeric or rigid properties depending on formulation. Understanding these distinct chemical structures helps you choose the ideal material based on required flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance.
Key Differences Between Epoxy Resin and Polyurethane
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and hardness, making it ideal for durable coatings and structural repairs. Polyurethane provides greater flexibility, UV resistance, and abrasion resistance, suitable for applications requiring elasticity and outdoor exposure. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right material based on your project's durability, flexibility, and environmental demands.
Physical Properties Comparison
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion, hardness, and chemical resistance compared to polyurethane, making it ideal for heavy-duty coatings and structural applications. Polyurethane excels in flexibility, impact resistance, and UV stability, providing better wear and weather resistance for outdoor or high-movement surfaces. Understanding these physical properties helps you choose the right material for your specific durability and environmental exposure needs.
Durability and Performance
Epoxy resin offers exceptional durability with strong resistance to chemicals, moisture, and mechanical stress, making it ideal for high-performance industrial applications. Polyurethane excels in flexibility and abrasion resistance, providing superior impact absorption and wear protection in dynamic environments. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize rigid strength and chemical resistance (epoxy) or enhanced elasticity and toughness (polyurethane).
Application Areas and Suitability
Epoxy resin exhibits superior chemical resistance and strong adhesion, making it ideal for applications like industrial coatings, adhesives, and marine environments where durability and moisture resistance are critical. Polyurethane's flexibility and abrasion resistance suit applications such as automotive parts, flexible seals, and coatings requiring elasticity and impact absorption. Selecting between epoxy resin and polyurethane depends on the specific project demands, with epoxy favoring structural strength and chemical exposure, while polyurethane excels in flexible, wear-resistant uses.
Advantages of Epoxy Resin
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesive strength, excellent chemical resistance, and exceptional durability compared to polyurethane, making it ideal for industrial and marine applications. Its low shrinkage and high mechanical properties ensure long-lasting, precise finishes, especially in flooring and coating projects. When choosing materials for your project, epoxy resin provides better structural integrity and resistance to environmental stressors.
Benefits of Polyurethane
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to epoxy resin, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and shock absorption. Its excellent UV resistance enhances longevity in outdoor environments, preventing yellowing and degradation over time. Polyurethane also provides strong adhesive properties with a faster curing time, allowing for efficient manufacturing and repair processes.
Cost Considerations
Epoxy resin generally offers a more cost-effective solution for small to medium-scale projects due to its lower material costs and ease of application. Polyurethane tends to be more expensive upfront but provides enhanced flexibility and durability, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Evaluating total lifecycle costs and specific project requirements is crucial when choosing between epoxy resin and polyurethane coatings.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Epoxy resin offers superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and a glossy finish, making it ideal for projects requiring durability and a smooth surface. Polyurethane provides greater flexibility, abrasion resistance, and UV stability, which suits applications exposed to outdoor elements or frequent wear. Understanding your project's requirements for strength, flexibility, and environmental exposure helps determine whether epoxy resin or polyurethane is the best choice for your needs.
Epoxy resin vs Polyurethane Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com