Glass-filled PTFE offers enhanced mechanical strength, improved wear resistance, and reduced thermal expansion compared to pure PTFE, making it ideal for high-load and high-temperature applications. To fully understand the benefits and best use cases of both materials, continue reading this detailed comparison.
Table of Comparison
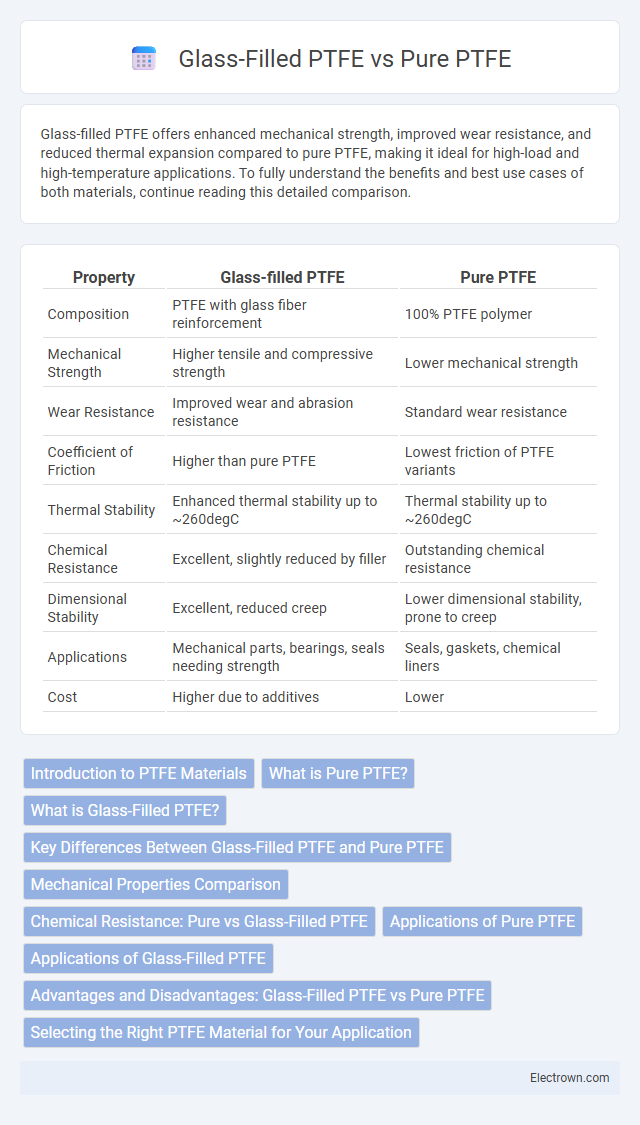
| Property | Glass-filled PTFE | Pure PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | PTFE with glass fiber reinforcement | 100% PTFE polymer |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher tensile and compressive strength | Lower mechanical strength |
| Wear Resistance | Improved wear and abrasion resistance | Standard wear resistance |
| Coefficient of Friction | Higher than pure PTFE | Lowest friction of PTFE variants |
| Thermal Stability | Enhanced thermal stability up to ~260degC | Thermal stability up to ~260degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, slightly reduced by filler | Outstanding chemical resistance |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent, reduced creep | Lower dimensional stability, prone to creep |
| Applications | Mechanical parts, bearings, seals needing strength | Seals, gaskets, chemical liners |
| Cost | Higher due to additives | Lower |
Introduction to PTFE Materials
Glass-filled PTFE offers enhanced mechanical strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability compared to Pure PTFE, which is renowned for its excellent chemical resistance and low friction properties. Pure PTFE remains a preferred choice in applications requiring high purity and maximum chemical inertness, while Glass-filled PTFE is ideal for engineering uses demanding improved load-bearing capacity and reduced deformation. Understanding the distinct properties of these PTFE materials enables optimal selection for specific industrial and engineering applications.
What is Pure PTFE?
Pure PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene, is a fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and high thermal stability, making it ideal for a variety of industrial applications. It is completely free of fillers or reinforcements, offering excellent electrical insulation and a smooth, non-stick surface. Unlike glass-filled PTFE, pure PTFE maintains maximum flexibility and superior corrosion resistance but has lower mechanical strength and wear resistance.
What is Glass-Filled PTFE?
Glass-filled PTFE is a composite material made by incorporating glass fibers into pure polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to enhance mechanical strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability. This modification significantly reduces the high creep and deformation tendencies found in pure PTFE while maintaining its excellent chemical resistance and low friction properties. Your applications requiring durable, low-friction components benefit from the improved performance glass-filled PTFE offers compared to pure PTFE.
Key Differences Between Glass-Filled PTFE and Pure PTFE
Glass-filled PTFE offers enhanced mechanical strength, improved wear resistance, and reduced thermal expansion compared to pure PTFE, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications. Pure PTFE provides superior chemical resistance and excellent electrical insulation but has lower tensile strength and can deform under high stress. The choice between glass-filled and pure PTFE depends on the balance between mechanical durability and chemical inertness required for specific use cases.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Glass-filled PTFE exhibits significantly enhanced mechanical properties compared to pure PTFE, including higher tensile strength, improved wear resistance, and reduced deformation under load. The addition of glass fibers increases stiffness and dimensional stability, making glass-filled PTFE ideal for applications requiring greater structural integrity and load-bearing capacity. Your choice between these materials should consider the balance between improved mechanical performance and potential changes in chemical resistance and flexibility.
Chemical Resistance: Pure vs Glass-Filled PTFE
Pure PTFE offers exceptional chemical resistance, withstanding most acids, bases, and solvents without degradation, making it ideal for highly corrosive environments. Glass-filled PTFE maintains good chemical resistance but may exhibit slightly reduced performance against strong alkalis and fluorinated compounds due to the glass filler content. Choosing between the two depends on balancing chemical resistance with enhanced mechanical properties provided by glass-filled PTFE in demanding applications.
Applications of Pure PTFE
Pure PTFE is widely used in applications requiring exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, such as in medical devices, food processing equipment, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Its low friction and non-stick properties make it ideal for seals, gaskets, and liners where purity and non-contamination are critical. Your choice of Pure PTFE ensures reliable performance in highly corrosive environments without compromising material integrity.
Applications of Glass-Filled PTFE
Glass-filled PTFE is extensively used in applications requiring enhanced mechanical strength, improved wear resistance, and reduced thermal expansion compared to pure PTFE. Common industries benefiting from glass-filled PTFE include automotive components, electrical insulators, and industrial machinery parts, where durability under stress and dimensional stability are critical. Your choice of glass-filled PTFE can significantly improve performance in high-load or high-friction environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Glass-Filled PTFE vs Pure PTFE
Glass-filled PTFE offers enhanced mechanical strength, improved wear resistance, and reduced creep compared to pure PTFE, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and dimensional stability. Pure PTFE provides superior chemical resistance and lower friction but is softer and more prone to deformation under load. Your choice depends on balancing the need for strength and wear resistance with chemical inertness and flexibility.
Selecting the Right PTFE Material for Your Application
Glass-filled PTFE offers enhanced mechanical strength, improved wear resistance, and reduced thermal expansion compared to pure PTFE, making it ideal for applications requiring higher structural integrity and dimensional stability. Pure PTFE excels in chemical resistance and electrical insulation, suitable for environments with aggressive chemicals or where minimal friction is crucial. Choosing between glass-filled and pure PTFE depends on balancing mechanical demands with chemical compatibility and electrical properties for optimal performance.
Glass-filled PTFE vs Pure PTFE Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com