Cu clad laminate offers superior electrical conductivity and thermal management ideal for high-performance electronic applications, while Al clad laminate provides excellent corrosion resistance and lighter weight suited for cost-effective and durability-focused projects. Explore the detailed comparison to determine which material best suits Your specific design needs.
Table of Comparison
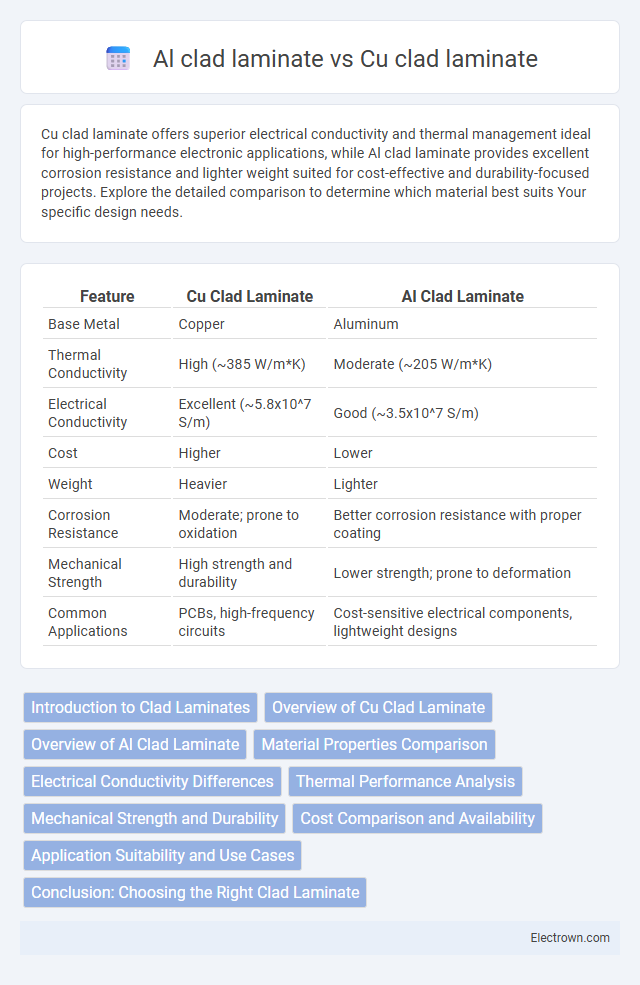
| Feature | Cu Clad Laminate | Al Clad Laminate |
|---|---|---|
| Base Metal | Copper | Aluminum |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (~385 W/m*K) | Moderate (~205 W/m*K) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent (~5.8x10^7 S/m) | Good (~3.5x10^7 S/m) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; prone to oxidation | Better corrosion resistance with proper coating |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and durability | Lower strength; prone to deformation |
| Common Applications | PCBs, high-frequency circuits | Cost-sensitive electrical components, lightweight designs |
Introduction to Clad Laminates
Clad laminates consist of a core substrate bonded with a metallic layer, commonly copper (Cu) or aluminum (Al), to enhance electrical and thermal conductivity. Cu clad laminates offer superior conductivity and solderability, making them ideal for high-performance printed circuit boards (PCBs). Al clad laminates provide lightweight and cost-effective solutions with excellent thermal dissipation, preferred in applications requiring heat management and reduced weight.
Overview of Cu Clad Laminate
Cu clad laminate offers exceptional electrical conductivity and thermal performance, making it ideal for high-frequency and high-power electronic applications. Its copper cladding provides superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength compared to Al clad laminate, ensuring longer PCB durability and reliability. Your choice of Cu clad laminate enhances signal integrity and heat dissipation, crucial for advanced circuit designs.
Overview of Al Clad Laminate
Al clad laminate consists of an aluminum core bonded with a reinforcing substrate, offering lightweight properties and excellent corrosion resistance compared to traditional copper-clad laminates. Its high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation make it ideal for high-frequency circuit applications and heat dissipation in power electronics. The aluminum base reduces overall PCB weight and cost, enhancing performance in aerospace and automotive industries.
Material Properties Comparison
Cu clad laminate offers superior electrical conductivity and excellent thermal management compared to Al clad laminate, making it ideal for high-frequency and heat-sensitive applications. Al clad laminate provides lower weight and cost benefits with moderate conductivity and thermal performance, suitable for lightweight or cost-sensitive designs. Your choice depends on prioritizing conductivity and thermal efficiency (Cu clad) versus weight reduction and budget (Al clad).
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Copper clad laminate offers superior electrical conductivity compared to aluminum clad laminate, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications. Copper's conductivity is approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, while aluminum's is significantly lower at around 3.77 x 10^7 S/m, affecting signal integrity and power efficiency. Your choice between these materials directly impacts the electrical performance and reliability of your circuit boards.
Thermal Performance Analysis
Cu clad laminate exhibits superior thermal conductivity compared to Al clad laminate, efficiently dissipating heat in high-power electronic applications. Your choice depends on the specific thermal management requirements; copper's thermal conductivity typically ranges around 400 W/m*K, whereas aluminum's is approximately 235 W/m*K. This difference makes Cu clad laminate ideal for applications demanding rapid heat transfer and enhanced reliability under thermal stress.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Cu clad laminate offers superior mechanical strength due to copper's higher tensile strength and better resistance to mechanical stress compared to aluminum. The durability of Cu clad laminates is enhanced by copper's excellent corrosion resistance and stable thermal conductivity, which reduces thermal fatigue over time. In contrast, Al clad laminates, while lighter and more cost-effective, may exhibit lower mechanical robustness and are more prone to oxidation, affecting long-term durability in demanding applications.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Cu clad laminate generally has higher material costs compared to Al clad laminate due to copper's higher market price and greater demand in electronics manufacturing. Aluminum clad laminates offer more cost-effective alternatives for applications requiring lighter weight and adequate conductivity, benefiting from aluminum's wider availability and lower price volatility. Availability of copper laminates is often limited by copper supply constraints, whereas aluminum laminates are more readily accessible through established industrial supply chains.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Cu clad laminate offers superior electrical conductivity and thermal performance, making it ideal for high-frequency circuits and power electronics in telecommunications, aerospace, and automotive industries. Al clad laminate provides lightweight strength and excellent corrosion resistance, commonly used in applications where weight reduction and durability are critical, such as in aerospace and lightweight structural components. Your choice depends on balancing electrical requirements with mechanical strength and weight constraints specific to your project's application.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clad Laminate
Selecting the appropriate clad laminate depends on your specific application requirements, with copper clad laminates offering superior electrical conductivity and excellent thermal performance ideal for high-frequency circuits. Aluminum clad laminates provide lightweight, cost-effective solutions with enhanced corrosion resistance suited for mechanical and structural uses. Evaluating factors such as conductivity, weight, cost, and environmental conditions will help you determine whether copper or aluminum clad laminate best fits your project's needs.
Cu clad laminate vs Al clad laminate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com