FR-1 and FR-4 are types of materials used for printed circuit boards, with FR-1 being a phenolic paper-based substrate offering lower mechanical strength and heat resistance, while FR-4 is a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate known for higher durability and better electrical insulation. Understanding the differences in performance and application can help you choose the right PCB material for your project needs, so continue reading to discover detailed comparisons and use cases.
Table of Comparison
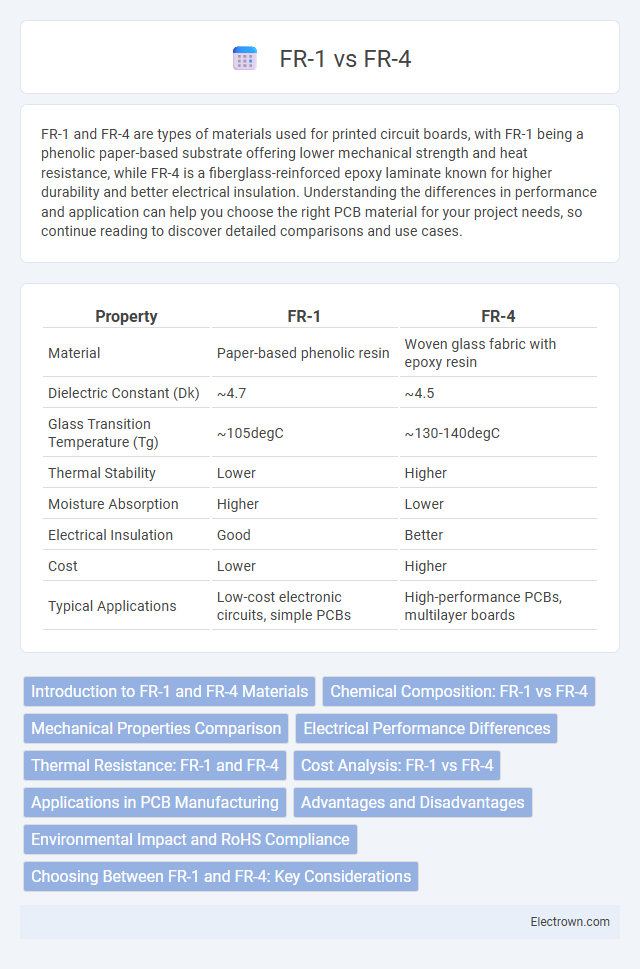
| Property | FR-1 | FR-4 |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Paper-based phenolic resin | Woven glass fabric with epoxy resin |
| Dielectric Constant (Dk) | ~4.7 | ~4.5 |
| Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) | ~105degC | ~130-140degC |
| Thermal Stability | Lower | Higher |
| Moisture Absorption | Higher | Lower |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Better |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Low-cost electronic circuits, simple PCBs | High-performance PCBs, multilayer boards |
Introduction to FR-1 and FR-4 Materials
FR-1 and FR-4 are widely used printed circuit board (PCB) substrates, each with distinct properties suitable for various applications. FR-1 is a phenolic paper-based laminate known for its low cost and basic electrical insulation, commonly used in low-frequency or hobbyist electronics. FR-4, made from woven fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin, offers superior flame resistance, mechanical strength, and higher dielectric performance, making it the industry standard for most professional and high-frequency PCB designs.
Chemical Composition: FR-1 vs FR-4
FR-1 and FR-4 are both standard printed circuit board (PCB) materials with distinct chemical compositions impacting their performance. FR-1 is made from phenolic resin bonded to paper, providing basic insulation properties suitable for low-frequency applications. FR-4 consists of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder, offering superior mechanical strength, higher thermal resistance, and better electrical insulation for high-frequency and high-reliability electronics.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
FR-1 exhibits lower mechanical strength and rigidity compared to FR-4, making it less suitable for high-stress applications. FR-4 features superior tensile strength and dimensional stability due to its fiberglass reinforcement, enabling better resistance to bending and impact. The enhanced mechanical properties of FR-4 contribute to its widespread use in demanding electronic circuit boards and industrial components.
Electrical Performance Differences
FR-1 and FR-4 differ significantly in electrical performance, with FR-4 offering superior dielectric strength and lower signal loss due to its epoxy resin composition and woven fiberglass reinforcement. FR-1, composed of phenolic paper, exhibits higher dielectric constant and greater signal attenuation, making it less suitable for high-frequency applications. The enhanced insulation resistance and thermal stability of FR-4 improve signal integrity in demanding electronic circuits compared to FR-1.
Thermal Resistance: FR-1 and FR-4
FR-1 and FR-4 differ significantly in thermal resistance, with FR-4 offering a higher heat tolerance due to its epoxy resin and fiberglass composition, making it suitable for applications requiring greater durability and heat dissipation. FR-1, made from paper impregnated with phenolic resin, has a lower thermal resistance, limiting its use in high-temperature environments. Your choice between these materials should consider the operating temperature demands of your electronic components to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Cost Analysis: FR-1 vs FR-4
FR-1 phenolic paper laminates typically cost significantly less than FR-4 epoxy fiberglass materials, making FR-1 a budget-friendly option for basic, low-frequency electronic applications. The higher price of FR-4 is justified by its superior thermal resistance, mechanical strength, and electrical performance, which are critical in complex, high-reliability circuits. Cost analysis must weigh FR-1's affordability against FR-4's durability and long-term performance benefits in demanding environments.
Applications in PCB Manufacturing
FR-1 is commonly used for low-cost, single-layer PCBs found in consumer electronics and simple control circuits, offering moderate thermal resistance suitable for less demanding applications. FR-4, a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate, is the industry standard for multi-layer PCBs in advanced electronics due to its high mechanical strength, superior thermal stability, and excellent electrical insulation properties. FR-4's characteristics make it ideal for complex, high-performance applications such as computer motherboards, telecommunications equipment, and automotive electronics.
Advantages and Disadvantages
FR-1 offers cost-effective advantages with good electrical insulating properties and is suitable for low-frequency applications, but has lower heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to FR-4. FR-4 provides superior thermal stability, mechanical durability, and electrical performance, making it ideal for high-frequency and high-temperature environments, though it is more expensive and heavier. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with the performance requirements of your specific electronic or PCB project.
Environmental Impact and RoHS Compliance
FR-1 material, made from phenolic paper laminate, generally has a lower environmental impact due to its simpler composition and biodegradability compared to FR-4, which is a fiberglass epoxy laminate with a more complex manufacturing process releasing more pollutants. FR-4, while offering enhanced durability and electrical performance, often contains brominated flame retardants and other substances subject to strict RoHS regulations, requiring careful compliance measures. Both materials must adhere to RoHS standards restricting hazardous substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and specific flame retardants to minimize environmental and health risks in electronic production.
Choosing Between FR-1 and FR-4: Key Considerations
Choosing between FR-1 and FR-4 hinges on electrical performance, thermal resistance, and application requirements. FR-4, a fiberglass epoxy laminate, offers higher flame retardancy, mechanical strength, and temperature tolerance up to around 130degC, ideal for high-speed circuits and durable electronics. FR-1, a phenolic paper laminate, is cost-effective with moderate electrical insulation but lower heat resistance, suitable for simple, low-budget projects where advanced thermal and mechanical properties are less critical.
FR-1 vs FR-4 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com