COG (Chip on Glass) and COP (Chip on Plastic) display materials differ significantly in flexibility, cost, and durability, with COG offering superior optical clarity and COP being favored for bendable displays due to its lightweight and flexible properties. Understanding these distinctions can help you choose the most suitable technology for your specific display needs; read on to explore the detailed comparisons and applications of COG and COP materials.
Table of Comparison
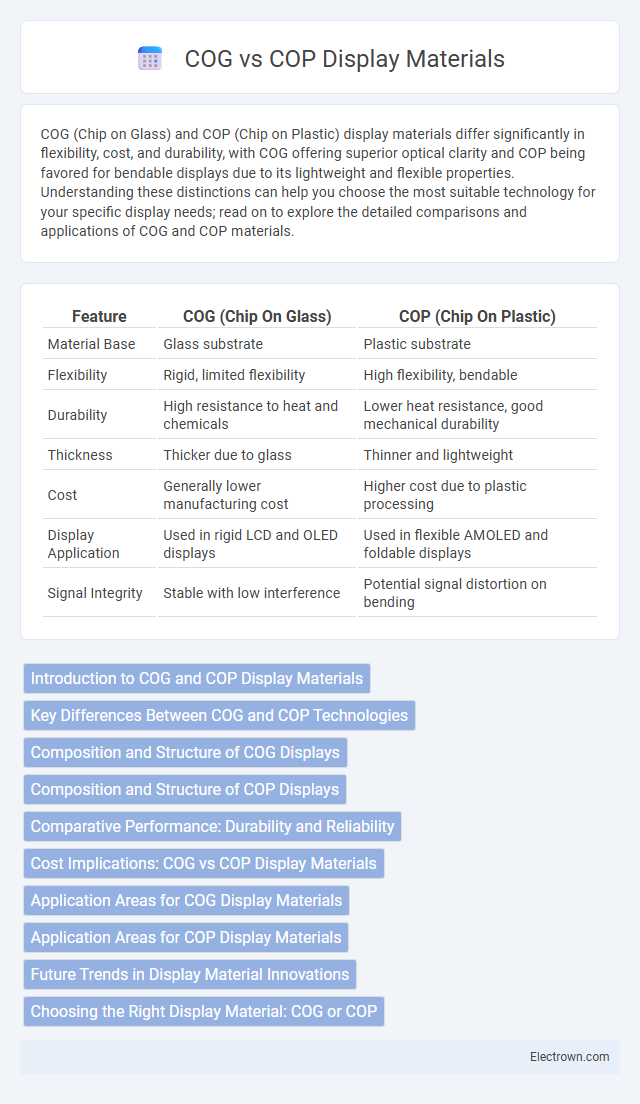
| Feature | COG (Chip On Glass) | COP (Chip On Plastic) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Base | Glass substrate | Plastic substrate |
| Flexibility | Rigid, limited flexibility | High flexibility, bendable |
| Durability | High resistance to heat and chemicals | Lower heat resistance, good mechanical durability |
| Thickness | Thicker due to glass | Thinner and lightweight |
| Cost | Generally lower manufacturing cost | Higher cost due to plastic processing |
| Display Application | Used in rigid LCD and OLED displays | Used in flexible AMOLED and foldable displays |
| Signal Integrity | Stable with low interference | Potential signal distortion on bending |
Introduction to COG and COP Display Materials
COG (Chip on Glass) and COP (Chip on Plastic) are advanced display technologies used in modern electronic devices. COG integrates the semiconductor chip directly onto the glass substrate, providing high-resolution displays with improved electrical performance and compact design. COP places the chip on a flexible plastic substrate, enabling lightweight, bendable screens suited for wearable devices and flexible displays.
Key Differences Between COG and COP Technologies
COG (Chip On Glass) and COP (Chip On Plastic) technologies differ primarily in substrate material and flexibility; COG mounts the integrated circuit directly on glass, offering superior display clarity and durability, while COP attaches the chip to a plastic substrate, enabling thinner, more flexible displays suited for curved or wearable devices. COG generally provides better thermal conductivity and lower production costs for rigid displays, whereas COP supports advanced design aesthetics and lightweight applications but may involve higher manufacturing complexity. The choice between COG and COP depends on application requirements such as display form factor, durability, and cost constraints.
Composition and Structure of COG Displays
COG (Chip on Glass) displays feature integrated circuit chips directly mounted on the glass substrate, enhancing compactness and reducing internal connections. The structure typically consists of a thin-film transistor (TFT) array on glass with a flexible printed circuit (FPC) attached, providing improved signal transmission and reliability. This composition contrasts with COP (Chip on Plastic) displays, where the chip is mounted on a flexible plastic substrate, resulting in different mechanical properties and manufacturing processes.
Composition and Structure of COP Displays
COP displays consist of a flexible circuit film laminated directly onto the display panel, eliminating the need for traditional rigid substrates found in COG technology. This structure results in a thinner, lighter display module with improved durability and better resistance to mechanical stress. Your device benefits from enhanced flexibility and a more compact design when using COP displays compared to COG counterparts.
Comparative Performance: Durability and Reliability
COG (Chip on Glass) displays offer superior durability due to their integrated construction, reducing the risk of damage from external impacts and environmental stress compared to COP (Chip on Plastic) displays. COP displays, while flexible and lightweight, tend to exhibit lower reliability over time due to plastic's susceptibility to deformation and thermal expansion. The enhanced durability of COG technology makes it preferable for applications requiring long-term reliability and resistance to harsh conditions.
Cost Implications: COG vs COP Display Materials
COG (Chip on Glass) display materials typically offer lower manufacturing costs due to reduced packaging and simplified assembly processes compared to COP (Chip on Plastic), which involves more complex material handling and bonding techniques. COP displays may incur higher costs driven by enhanced flexibility and durability requirements but can provide better performance and design versatility. Understanding these cost implications helps you make informed decisions about trade-offs between budget constraints and display quality in your electronic projects.
Application Areas for COG Display Materials
COG (Chip on Glass) display materials are extensively used in compact, high-resolution devices such as smartphones, smartwatches, and wearable medical devices due to their minimal thickness and enhanced durability. Their superior electrical performance and space-saving design make them ideal for applications requiring slim profiles and high pixel density. If you seek efficient integration of display components in your compact electronics, COG materials offer a reliable solution for optimizing device performance and aesthetics.
Application Areas for COP Display Materials
COP display materials excel in high-performance electronic devices due to their excellent optical clarity, flexibility, and thermal stability, making them ideal for smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. Their superior mechanical properties support curved and foldable screens, expanding application areas in next-generation displays. You benefit from enhanced durability and lightweight design when choosing COP for advanced display technology in consumer electronics.
Future Trends in Display Material Innovations
COG (Chip on Glass) and COP (Chip on Plastic) display materials are evolving with advancements in flexible, lightweight, and transparent substrates to enhance device durability and visual performance. Emerging trends highlight the integration of ultra-thin flexible OLEDs and improved barrier coatings that extend lifespan and support curved or foldable screens. Your choice of display technology will benefit from future innovations emphasizing sustainability and enhanced energy efficiency in COG and COP materials.
Choosing the Right Display Material: COG or COP
Choosing between COG (Chip on Glass) and COP (Chip on Plastic) display materials depends on application-specific requirements such as flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. COG is ideal for rigid displays with excellent electrical performance and compact integration due to its direct chip attachment on glass substrates. COP offers superior flexibility and lightweight properties, making it suitable for foldable or wearable devices where plastic substrate advantages are critical.
COG vs COP display materials Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com