Rigid PCBs offer solid and durable support for electronic components, making them ideal for applications requiring structural stability. Flex PCBs provide adaptable, space-saving solutions that enhance your device's design and functionality; explore the rest of the article to discover which type suits your project best.
Table of Comparison
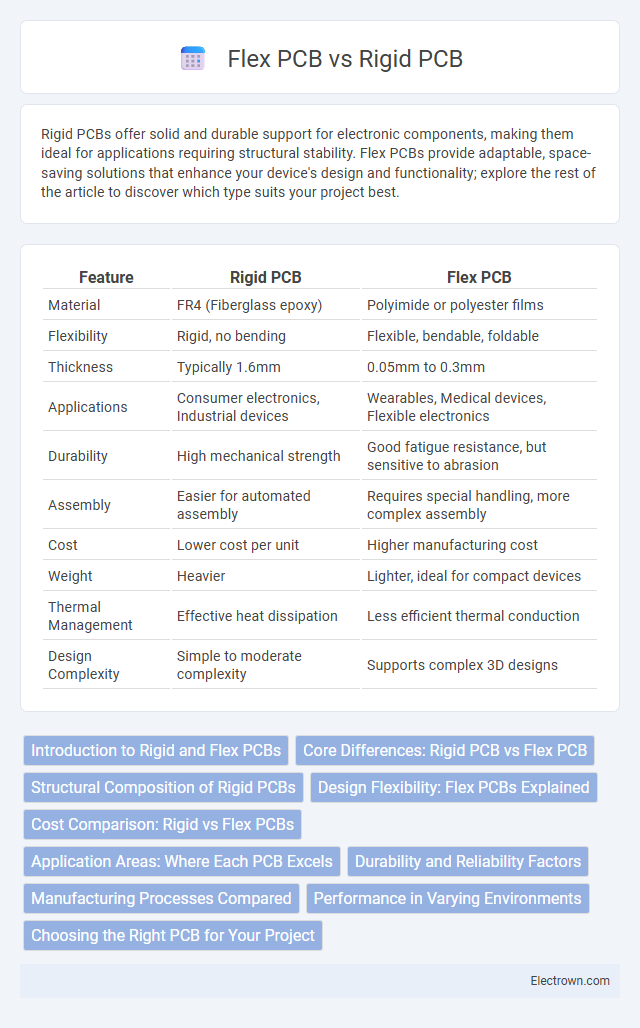
| Feature | Rigid PCB | Flex PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Material | FR4 (Fiberglass epoxy) | Polyimide or polyester films |
| Flexibility | Rigid, no bending | Flexible, bendable, foldable |
| Thickness | Typically 1.6mm | 0.05mm to 0.3mm |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, Industrial devices | Wearables, Medical devices, Flexible electronics |
| Durability | High mechanical strength | Good fatigue resistance, but sensitive to abrasion |
| Assembly | Easier for automated assembly | Requires special handling, more complex assembly |
| Cost | Lower cost per unit | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter, ideal for compact devices |
| Thermal Management | Effective heat dissipation | Less efficient thermal conduction |
| Design Complexity | Simple to moderate complexity | Supports complex 3D designs |
Introduction to Rigid and Flex PCBs
Rigid PCBs consist of a solid substrate that provides mechanical support and electrical connections, making them ideal for stable, high-density electronic circuits. Flex PCBs use flexible plastic substrates allowing them to bend and fold, which suits compact designs requiring dynamic movement or space-saving layouts. Your choice between rigid and flex PCBs depends on the application's durability, design complexity, and environmental adaptability requirements.
Core Differences: Rigid PCB vs Flex PCB
Rigid PCBs feature a solid, inflexible substrate made of materials like fiberglass, providing durability and dimensional stability, while Flex PCBs use flexible polyimide or polyester films that allow bending and folding. You should consider Flex PCBs for compact, dynamic applications requiring space-saving and adaptability, whereas Rigid PCBs suit environments needing structural rigidity and high mechanical strength. Core differences also encompass manufacturing complexity, cost variations, and electrical performance tailored to specific design needs.
Structural Composition of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs are composed of multiple layers of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin (FR4) materials, providing a sturdy and inflexible structure essential for robust electronic circuits. These layers are laminated together with copper traces etched on the surface, ensuring reliable electrical connectivity and mechanical support. Your choice of a rigid PCB ensures durability and stability in devices requiring firm component placement and resistance to mechanical stress.
Design Flexibility: Flex PCBs Explained
Flex PCBs offer superior design flexibility compared to rigid PCBs due to their ability to bend, fold, and conform to complex shapes and tight spaces, enabling innovative product designs. Materials like polyimide provide durability while maintaining flexibility, allowing better vibration resistance and space savings in compact electronic devices. This adaptability makes flex PCBs ideal for applications in wearable technology, aerospace, and medical devices where dynamic mechanical stress and lightweight construction are critical.
Cost Comparison: Rigid vs Flex PCBs
Rigid PCBs generally offer lower manufacturing costs compared to flex PCBs due to simpler materials and production processes, making them ideal for high-volume, cost-sensitive projects. Flex PCBs involve higher expenses caused by specialized substrates, intricate fabrication, and additional assembly steps required for their flexibility and durability. Evaluating your project's performance and design requirements will help determine if the cost premium of flex PCBs justifies their benefits over rigid PCBs.
Application Areas: Where Each PCB Excels
Rigid PCBs excel in applications requiring stable, durable circuit boards such as desktop computers, industrial machinery, and automotive electronics due to their solid structure and high component density. Flex PCBs are ideal for wearable devices, medical instruments, and aerospace equipment where space constraints, lightweight design, and the ability to bend or fold circuits are critical. Both types serve unique roles in electronics manufacturing, with rigid PCBs prioritizing robustness and flex PCBs enabling innovative, compact designs.
Durability and Reliability Factors
Rigid PCBs offer superior durability due to their solid substrate, making them ideal for applications requiring stable mechanical support and resistance to physical stress. Flex PCBs provide exceptional reliability in dynamic environments by accommodating bending and flexing without damaging the circuitry, reducing the risk of fractures in tight or moving spaces. Choosing between rigid and flex PCBs depends on specific durability needs and the reliability requirements of the device's operating conditions.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Rigid PCBs are manufactured using a solid, inflexible substrate such as fiberglass, with processes including layering, etching, drilling, and solder mask application, ensuring durability and stability for standard electronic assemblies. Flex PCBs involve flexible polymer materials like polyimide, requiring specialized manufacturing steps such as flexible substrate handling, precise laser cutting, and bend testing to maintain electrical integrity under dynamic conditions. Your choice between rigid and flex PCB manufacturing affects production complexity, material costs, and application suitability, particularly in devices demanding space-saving and mechanical resilience.
Performance in Varying Environments
Rigid PCBs offer stable performance in controlled environments due to their solid construction, making them ideal for applications with minimal mechanical stress. Flex PCBs excel in varying environments by providing superior durability and resistance to vibration, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical bending, which enhances reliability in dynamic conditions. Your choice between rigid and flex PCBs should consider the specific environmental stresses to optimize device performance and longevity.
Choosing the Right PCB for Your Project
Choosing the right PCB for your project depends on factors like design complexity, space constraints, and durability requirements. Rigid PCBs offer stability and ease of manufacturing, ideal for applications needing solid, fixed layouts, while Flex PCBs provide flexibility and lightweight design, perfect for compact or dynamic environments. Evaluate your project's mechanical stress, bending needs, and component density to determine whether a Rigid PCB or Flex PCB will optimize performance and reliability.
Rigid PCB vs Flex PCB Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com