PTFE wire insulation offers excellent chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, making it ideal for harsh environments, whereas PFA wire insulation combines similar chemical resistance with enhanced flexibility and ease of installation. Discover which material best fits Your specific application needs by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
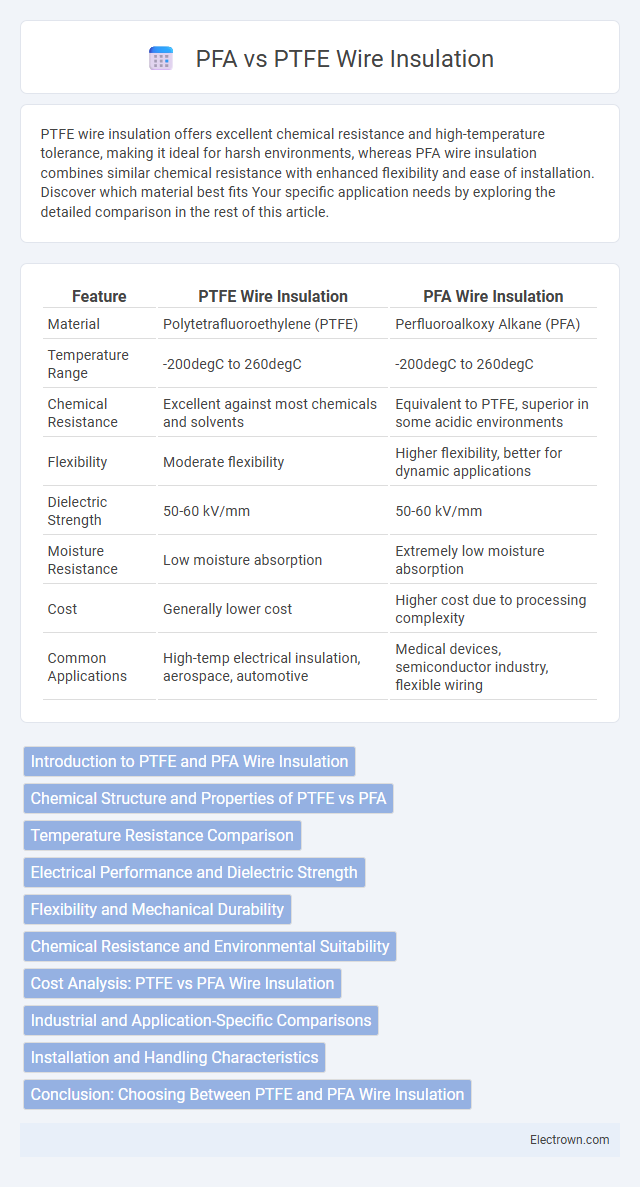
| Feature | PTFE Wire Insulation | PFA Wire Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Perfluoroalkoxy Alkane (PFA) |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 260degC | -200degC to 260degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against most chemicals and solvents | Equivalent to PTFE, superior in some acidic environments |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Higher flexibility, better for dynamic applications |
| Dielectric Strength | 50-60 kV/mm | 50-60 kV/mm |
| Moisture Resistance | Low moisture absorption | Extremely low moisture absorption |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to processing complexity |
| Common Applications | High-temp electrical insulation, aerospace, automotive | Medical devices, semiconductor industry, flexible wiring |
Introduction to PTFE and PFA Wire Insulation
PTFE and PFA wire insulation are both fluoropolymer materials known for their exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and electrical insulation properties. PTFE offers superior thermal stability up to 260degC and excellent dielectric strength, making it ideal for demanding industrial and aerospace applications. Your choice between PTFE and PFA wire insulation will depend on specific needs such as flexibility, processing ease, and environmental exposure.
Chemical Structure and Properties of PTFE vs PFA
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) consists of a linear polymer chain of carbon atoms fully fluorinated, creating a highly stable carbon-fluorine bond that provides exceptional chemical resistance and high thermal stability. PFA (perfluoroalkoxy alkane) differs by incorporating perfluoroalkoxy side chains, offering improved flexibility and melt-processability while maintaining similar chemical inertness and temperature tolerance. The molecular structure of PFA allows for easier fabrication methods like injection molding, whereas PTFE's rigid and highly crystalline structure results in superior mechanical strength and a higher melting point.
Temperature Resistance Comparison
PTFE wire insulation typically withstands continuous temperatures up to 260degC, making it suitable for high-heat applications, while PFA wire insulation offers slightly lower maximum service temperatures around 260degC but provides better flexibility and chemical resistance. Both materials excel in temperature resistance; however, PTFE is often preferred when maximum thermal endurance is critical for Your wiring needs. Choosing between PTFE and PFA depends on balancing temperature tolerance with mechanical properties and environmental exposure.
Electrical Performance and Dielectric Strength
PTFE wire insulation offers excellent electrical performance with a dielectric strength typically around 5000 V/mil, making it ideal for high-voltage applications requiring reliable insulation and minimal signal loss. PFA wire insulation provides slightly lower dielectric strength, approximately 4300 V/mil, but maintains superior chemical resistance and thermal stability under harsh conditions. Both materials ensure exceptional electrical insulation properties, with PTFE edging out in dielectric strength and PFA excelling in stable performance across wider temperature ranges.
Flexibility and Mechanical Durability
PTFE wire insulation offers excellent flexibility due to its unique molecular structure, allowing it to withstand repeated bending without cracking or breaking. PFA wire insulation, while also flexible, provides superior mechanical durability by resisting abrasion and maintaining performance in harsh environments. Your choice between PTFE and PFA will depend on whether you prioritize maximum flexibility or enhanced toughness under mechanical stress.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
PTFE wire insulation exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, with outstanding performance against aggressive chemicals, acids, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. PFA wire insulation offers similar chemical resistance but provides superior flexibility and withstands higher temperatures, enhancing its suitability for dynamic or high-temperature applications. Both materials show excellent environmental durability, but PTFE is often preferred in highly corrosive or chemically intense settings, while PFA excels in environments requiring higher mechanical stress resistance.
Cost Analysis: PTFE vs PFA Wire Insulation
PTFE wire insulation generally costs less than PFA due to its more established manufacturing processes and widespread availability. However, PFA offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, which may justify its higher price in demanding applications. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements in specific environments.
Industrial and Application-Specific Comparisons
PTFE wire insulation offers superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments such as chemical processing and aerospace applications. PFA insulation provides enhanced flexibility and excellent electrical properties, suitable for applications requiring frequent movement or tight bending, like robotics and semiconductor manufacturing. Your choice depends on balancing the demand for mechanical flexibility versus extreme resistance to chemicals and heat in your specific industrial application.
Installation and Handling Characteristics
PTFE wire insulation offers excellent flexibility and high-temperature resistance, making it suitable for complex installations requiring frequent bending and movement. PFA insulation provides enhanced chemical resistance and durability while maintaining good flexibility, ideal for harsh environments and prolonged mechanical stress during handling. Both materials allow for precise, secure termination, but PFA's slightly improved abrasion resistance often results in easier installation in demanding industrial applications.
Conclusion: Choosing Between PTFE and PFA Wire Insulation
PTFE wire insulation offers superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and excellent electrical properties, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. PFA wire insulation provides greater flexibility, enhanced mechanical strength, and continuous use temperatures around 260degC, suitable for dynamic environments requiring durability. Selecting between PTFE and PFA insulation depends on balancing chemical resistance, flexibility, and application-specific mechanical demands to optimize wire performance.
PTFE vs PFA wire insulation Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com