ESD foam dissipates static electricity to protect sensitive electronic components, while antistatic foam reduces static buildup without actively discharging it, offering different levels of electrostatic protection. Discover how understanding the differences between ESD foam and antistatic foam can safeguard your electronic devices in this detailed comparison.
Table of Comparison
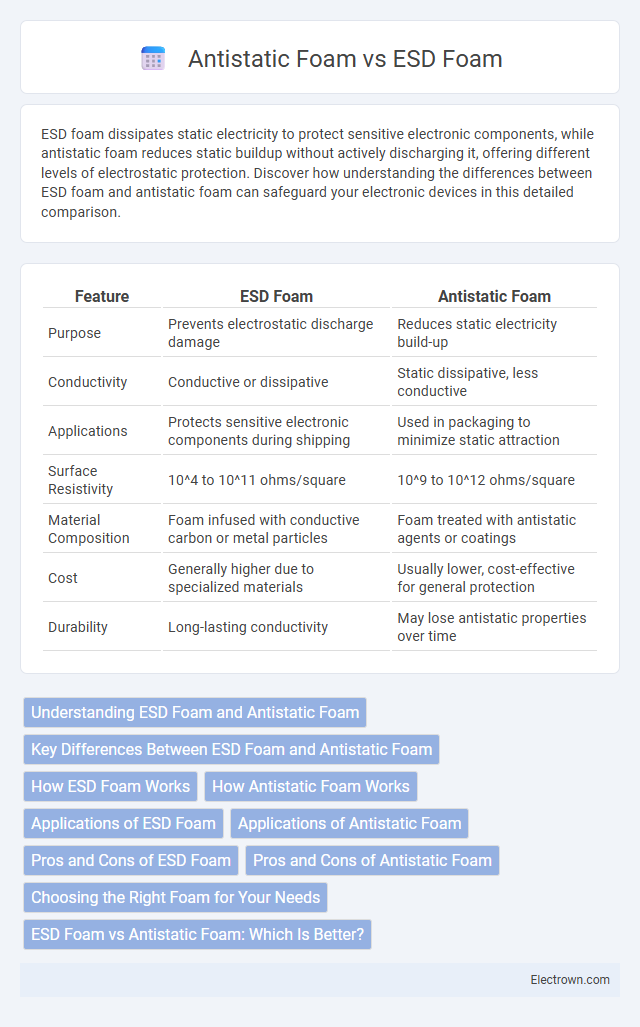
| Feature | ESD Foam | Antistatic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents electrostatic discharge damage | Reduces static electricity build-up |
| Conductivity | Conductive or dissipative | Static dissipative, less conductive |
| Applications | Protects sensitive electronic components during shipping | Used in packaging to minimize static attraction |
| Surface Resistivity | 10^4 to 10^11 ohms/square | 10^9 to 10^12 ohms/square |
| Material Composition | Foam infused with conductive carbon or metal particles | Foam treated with antistatic agents or coatings |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized materials | Usually lower, cost-effective for general protection |
| Durability | Long-lasting conductivity | May lose antistatic properties over time |
Understanding ESD Foam and Antistatic Foam
ESD foam protects sensitive electronic components by safely dissipating electrostatic charges, preventing damage caused by static electricity. Antistatic foam reduces static build-up on its surface but does not dissipate charges as effectively as ESD foam, making it less suitable for handling highly sensitive devices. Your choice between these foams depends on the level of electrostatic protection required for your application.
Key Differences Between ESD Foam and Antistatic Foam
ESD foam dissipates static electricity by safely grounding charges, making it ideal for protecting sensitive electronic components from electrostatic discharge damage. Antistatic foam, in contrast, merely reduces static buildup by preventing surface charge accumulation, offering basic protection without grounding capabilities. Your choice depends on the level of static control required--ESD foam for critical electronics and antistatic foam for less sensitive items.
How ESD Foam Works
ESD foam works by dissipating static electricity through its conductive or static dissipative properties, preventing electrostatic discharge that can damage sensitive electronic components. The foam contains carbon or metal particles, creating a controlled path for static charges to safely ground. This property makes ESD foam essential for packaging and protecting integrated circuits, circuit boards, and other sensitive electronics during storage and transit.
How Antistatic Foam Works
Antistatic foam works by incorporating conductive or dissipative materials that reduce static electricity buildup on its surface, preventing electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage to sensitive electronic components. It maintains a controlled surface resistivity, allowing static charges to slowly dissipate rather than accumulate, which is essential for safely packaging and handling delicate devices. Unlike ESD foam, which actively dissipates charges through embedded conductive pathways, antistatic foam primarily minimizes charge generation through its chemical composition and surface treatment.
Applications of ESD Foam
ESD foam is primarily used for protecting sensitive electronic components and devices from electrostatic discharge during shipping, storage, and handling. Its conductive properties prevent static buildup that can damage semiconductors, circuit boards, and microchips. You can rely on ESD foam for packaging, cushioning, and organizing electronic parts in manufacturing and assembly environments.
Applications of Antistatic Foam
Antistatic foam is widely used in the packaging and transportation of sensitive electronic components to prevent static charge buildup that can damage circuitry. It is ideal for protecting semiconductors, printed circuit boards, and delicate electronic assemblies during shipping and handling. This foam's ability to dissipate static electricity makes it essential in cleanroom environments and assembly lines where electrostatic discharge (ESD) control is critical.
Pros and Cons of ESD Foam
ESD foam effectively protects sensitive electronic components from electrostatic discharge by safely dissipating static electricity, making it essential for handling integrated circuits and semiconductors. Its main advantage is high electrostatic protection, but it can be more expensive and less durable compared to general antistatic foam, which only reduces static buildup without fully discharging static energy. While ESD foam offers superior protection in electronic manufacturing and shipping environments, it may require specific disposal methods due to its specialized materials.
Pros and Cons of Antistatic Foam
Antistatic foam reduces static electricity buildup, protecting sensitive electronic components from electrostatic discharge damage during storage and transport. It is less expensive than ESD foam and easier to handle, but offers limited protection against strong static events compared to ESD foam, which provides superior conductivity and grounding capabilities. However, antistatic foam can lose effectiveness over time and is not suitable for environments requiring stringent electrostatic control.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
ESD foam and antistatic foam serve different purposes in protecting electronic components from electrostatic discharge, with ESD foam specifically designed to safely dissipate static electricity and antistatic foam preventing static buildup on surfaces. When choosing the right foam for your needs, consider whether your primary concern is shielding delicate electronics from electrostatic damage (ESD foam) or simply reducing static attraction in packaging or storage (antistatic foam). Your selection should align with the sensitivity of your components and the environment in which they will be stored or transported.
ESD Foam vs Antistatic Foam: Which Is Better?
ESD foam provides superior protection by safely dissipating electrostatic discharge, making it ideal for sensitive electronic components, whereas antistatic foam primarily reduces static build-up without fully grounding charges. Your choice should depend on the level of electrostatic sensitivity of the items being stored or shipped, with ESD foam preferred for devices vulnerable to electrostatic damage. For basic static prevention with less critical electronics, antistatic foam may suffice, but ESD foam offers enhanced reliability for high-value or delicate components.
ESD foam vs antistatic foam Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com