Polyolefin insulation offers superior chemical resistance, flexibility, and environmental friendliness compared to PVC insulation, which is commonly used for its cost-effectiveness and flame retardant properties. Explore the rest of the article to understand which insulation material best suits your specific application needs.
Table of Comparison
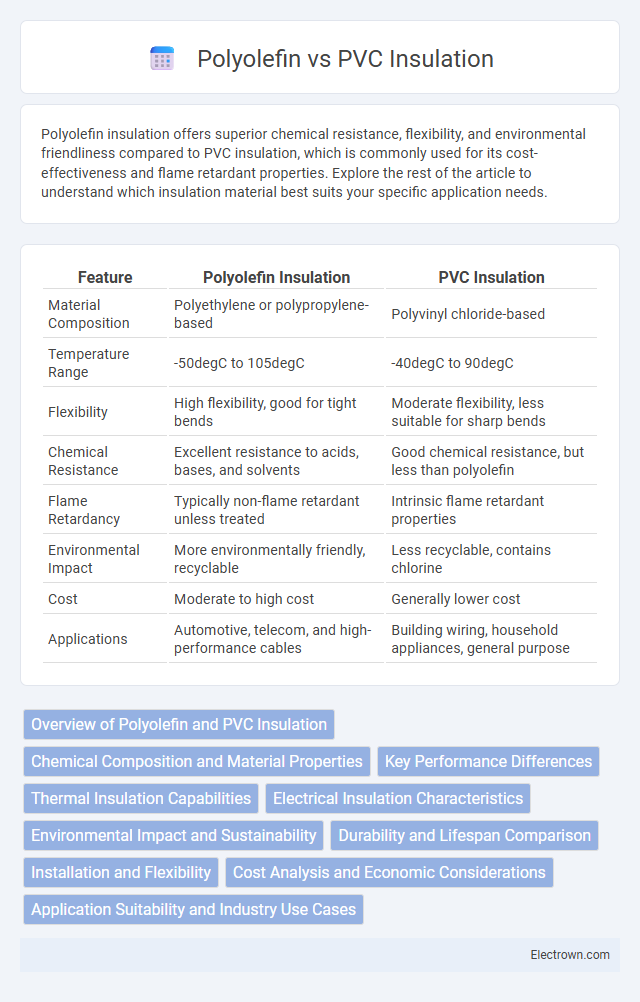
| Feature | Polyolefin Insulation | PVC Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyethylene or polypropylene-based | Polyvinyl chloride-based |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 105degC | -40degC to 90degC |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, good for tight bends | Moderate flexibility, less suitable for sharp bends |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Good chemical resistance, but less than polyolefin |
| Flame Retardancy | Typically non-flame retardant unless treated | Intrinsic flame retardant properties |
| Environmental Impact | More environmentally friendly, recyclable | Less recyclable, contains chlorine |
| Cost | Moderate to high cost | Generally lower cost |
| Applications | Automotive, telecom, and high-performance cables | Building wiring, household appliances, general purpose |
Overview of Polyolefin and PVC Insulation
Polyolefin insulation, derived from polymers like polyethylene and polypropylene, offers superior chemical resistance, flexibility, and low smoke emission compared to PVC insulation, which is made from polyvinyl chloride and is known for its durability and flame retardant properties. Polyolefin materials provide excellent electrical insulation and are preferred in applications requiring environmental resistance and lower toxicity during combustion. Your choice between polyolefin and PVC insulation should consider factors like operating temperature, mechanical stress, and safety standards relevant to the intended use.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Polyolefin insulation is primarily composed of polymerized olefins such as polyethylene or polypropylene, offering excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and high flexibility. PVC (polyvinyl chloride) insulation contains vinyl chloride monomers, providing durability, flame retardancy, and resistance to oils and chemicals but tends to be less flexible and more prone to plasticizer migration. The differences in chemical composition directly influence their thermal stability, environmental resistance, and mechanical properties, making polyolefins preferable for lightweight, flexible applications and PVC suitable for rugged, flame-resistant requirements.
Key Performance Differences
Polyolefin insulation offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility compared to PVC, making it ideal for harsh environments and applications requiring frequent bending. PVC insulation provides excellent flame retardancy and cost-effectiveness but may degrade under prolonged UV exposure and extreme temperatures. The choice between polyolefin and PVC depends on specific performance requirements such as thermal stability, durability, and environmental resistance.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Polyolefin insulation offers superior thermal insulation capabilities due to its low thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to temperature variations, maintaining performance in extreme heat and cold. PVC insulation provides adequate thermal insulation but tends to degrade faster under high-temperature exposure, limiting its effectiveness in demanding thermal environments. Choosing polyolefin insulation enhances energy efficiency and prolongs the lifespan of electrical cables in thermal-critical applications.
Electrical Insulation Characteristics
Polyolefin insulation offers superior electrical insulation properties with high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to electrical stress, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. PVC insulation provides decent electrical insulation but tends to have lower dielectric strength compared to polyolefin materials. The inherent chemical stability and moisture resistance of polyolefin enhance its electrical insulating performance over PVC in demanding environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyolefin insulation, derived from hydrocarbons such as polyethylene or polypropylene, offers enhanced environmental benefits due to its recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to PVC, which is chlorine-based and poses greater challenges in waste management and release of harmful dioxins during incineration. Polyolefin materials exhibit better sustainability by avoiding the generation of toxic additives like phthalates found in PVC, reducing long-term ecological risks. The adoption of polyolefin insulation aligns with global efforts to minimize plastic pollution and promote circular economy principles within the electrical and electronics industries.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Polyolefin insulation offers superior durability with excellent resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and chemicals, ensuring a longer lifespan compared to PVC insulation. PVC insulation, while cost-effective, tends to degrade faster under harsh conditions, making it less suitable for long-term applications. Choosing polyolefin can enhance your project's longevity by minimizing wear and maintenance needs.
Installation and Flexibility
Polyolefin insulation offers superior flexibility compared to PVC, making installation easier, especially in tight or complex spaces where bending and shaping are required. Its lightweight nature simplifies handling and reduces labor time, while PVC insulation is stiffer and may require more effort to fit around corners or irregular surfaces. Choosing polyolefin can enhance your project's efficiency and durability due to its elasticity and ease of installation.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Polyolefin insulation typically offers a lower initial cost compared to PVC, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale applications. Your decision should consider long-term economic factors such as durability and maintenance costs, where polyolefin often delivers superior performance and longevity. PVC insulation may incur higher replacement and environmental disposal costs, impacting the total cost of ownership.
Application Suitability and Industry Use Cases
Polyolefin insulation excels in automotive wiring, household appliances, and industrial cables due to its superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for environments requiring durability and safety. PVC insulation is widely used in building wiring, telecommunications, and consumer electronics because of its cost-effectiveness, flame retardance, and ease of processing. Both materials cater to specific industry standards and applications, with Polyolefin preferred where environmental resistance is critical, while PVC dominates in economic and standardized electrical installations.
Polyolefin vs PVC insulation Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com