CAN Bus offers a robust communication protocol widely used in automotive and industrial applications for real-time data exchange, while DeviceNet builds on CAN Bus by adding device-level networking capabilities and standardized profiles tailored for industrial automation. Explore this article to understand how these technologies compare and which is best suited for your specific application needs.
Table of Comparison
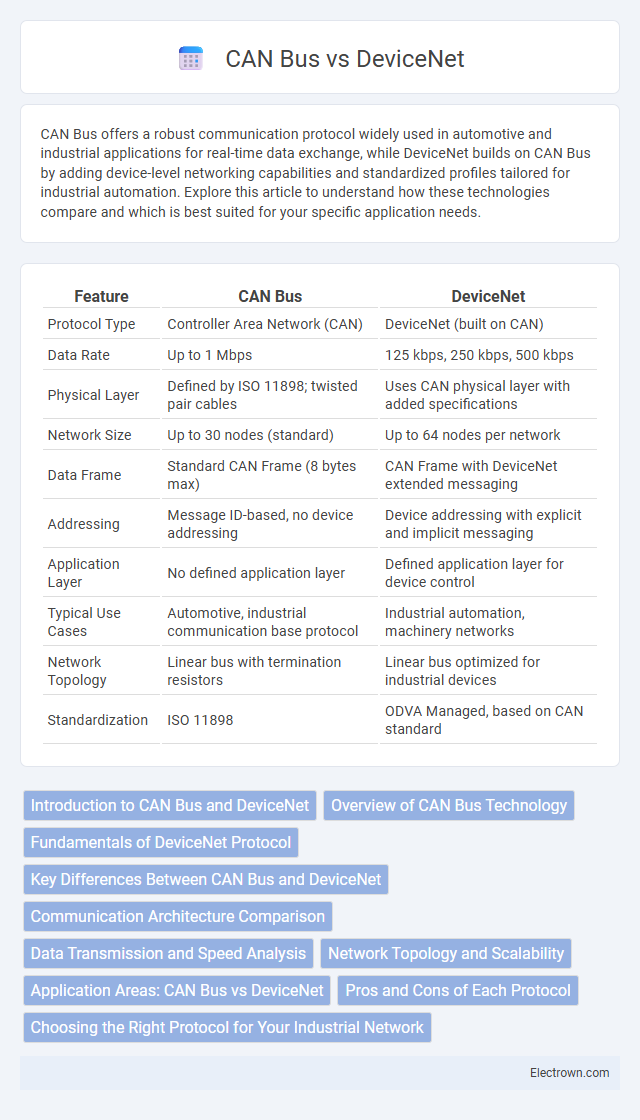
| Feature | CAN Bus | DeviceNet |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Controller Area Network (CAN) | DeviceNet (built on CAN) |
| Data Rate | Up to 1 Mbps | 125 kbps, 250 kbps, 500 kbps |
| Physical Layer | Defined by ISO 11898; twisted pair cables | Uses CAN physical layer with added specifications |
| Network Size | Up to 30 nodes (standard) | Up to 64 nodes per network |
| Data Frame | Standard CAN Frame (8 bytes max) | CAN Frame with DeviceNet extended messaging |
| Addressing | Message ID-based, no device addressing | Device addressing with explicit and implicit messaging |
| Application Layer | No defined application layer | Defined application layer for device control |
| Typical Use Cases | Automotive, industrial communication base protocol | Industrial automation, machinery networks |
| Network Topology | Linear bus with termination resistors | Linear bus optimized for industrial devices |
| Standardization | ISO 11898 | ODVA Managed, based on CAN standard |
Introduction to CAN Bus and DeviceNet
CAN Bus (Controller Area Network) is a robust vehicle bus standard designed for microcontrollers and devices to communicate without a host computer, widely used in automotive and industrial automation. DeviceNet is a communication protocol built on the CAN Bus physical layer, specifically developed for industrial automation applications, enabling easy integration of control devices and sensors. Both protocols facilitate efficient data exchange but DeviceNet adds a higher-level application layer for device interoperability in industrial networks.
Overview of CAN Bus Technology
CAN Bus technology is a robust communication protocol designed for real-time data exchange between microcontrollers and devices within automotive and industrial applications. It uses a multi-master, message-oriented transmission method that efficiently reduces wiring complexity and ensures reliable error detection and fault confinement. Your systems benefit from CAN Bus's high-speed data transfer rates, scalability, and standardized message formats, which make it a foundational technology for networks requiring deterministic communication and high reliability.
Fundamentals of DeviceNet Protocol
DeviceNet protocol is built on the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus physical layer, enabling robust, real-time communication between industrial devices. It employs a master-slave architecture with centralized control, using a token-passing mechanism to manage network access and prevent collisions. DeviceNet supports standardized object dictionaries, facilitating seamless device interoperability and simplified diagnostics within automation systems.
Key Differences Between CAN Bus and DeviceNet
CAN Bus operates as a low-level communication protocol primarily designed for real-time data exchange in automotive and industrial applications, offering a flexible and efficient message-based system. DeviceNet builds on the CAN Bus foundation by integrating higher-level protocols, enabling device-level networking with standardized device profiles, enhanced diagnostics, and simplified wiring in industrial automation environments. The key differences lie in DeviceNet's additional application layer, network management capabilities, and support for a broader range of device interoperability compared to the raw CAN Bus system.
Communication Architecture Comparison
CAN Bus employs a simple, multi-master broadcast communication architecture where all nodes share the same bus and messages are prioritized by identifier. DeviceNet extends CAN Bus by adding a higher-layer protocol and structured device profiles, organizing communication into producer-consumer and master-slave relationships for enhanced device interoperability and network management. Your choice depends on whether you need raw, flexible messaging with CAN Bus or standardized device integration and diagnostic capabilities offered by DeviceNet.
Data Transmission and Speed Analysis
CAN Bus operates with data transmission speeds up to 1 Mbps, providing a reliable and efficient communication protocol for real-time control systems. DeviceNet, built on the CAN Bus protocol, enhances data transmission by supporting speeds up to 500 kbps while integrating device-level networking features for industrial automation. Your choice between CAN Bus and DeviceNet should consider the required data speed, network size, and system complexity for optimal performance.
Network Topology and Scalability
CAN Bus utilizes a multi-master, broadcast communication system with a linear bus topology, enabling simple device connections and limited scalability primarily suitable for smaller networks. DeviceNet, built on CAN protocol, employs a bus topology with trunkline-dropline architecture, facilitating easier device addition and improved network scalability up to 64 nodes per segment and multiple segments via repeaters. The structured design of DeviceNet supports better organization and expansion in industrial automation environments compared to the more fundamental CAN Bus implementation.
Application Areas: CAN Bus vs DeviceNet
CAN Bus is widely used in automotive systems, industrial automation, and medical equipment for real-time communication and robust control. DeviceNet, built on the CAN protocol, is specifically designed for industrial automation environments, enabling seamless integration of sensors, actuators, and control devices on factory floors. Your choice depends on whether you need a versatile, general-purpose network (CAN Bus) or a standardized industrial network suited for device-level control and diagnostics (DeviceNet).
Pros and Cons of Each Protocol
CAN Bus offers high-speed data transmission and robust error handling, making it ideal for real-time automotive and industrial applications; however, it has limited message length and lacks standardized device profiles, which can complicate integration. DeviceNet builds on CAN Bus by incorporating standardized device profiles and network management features, enhancing interoperability and simplifying device integration in industrial automation; its complexity and higher implementation cost may be a drawback for simple applications. CAN Bus excels in low-cost, low-level communication scenarios, while DeviceNet provides a more comprehensive solution with added layers for device control and diagnostics in complex systems.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Industrial Network
Selecting the appropriate industrial network protocol depends on specific application requirements, with CAN Bus offering a simple, cost-effective solution for real-time control and DeviceNet providing enhanced network management and device-level diagnostics. CAN Bus excels in applications demanding high-speed communication and robustness in harsh environments, while DeviceNet supports complex device integration through its standardized communication layers and extensive device profiles. Evaluating factors such as network size, data throughput, diagnostic needs, and device interoperability ensures optimal protocol choice tailored to industrial automation goals.
CAN Bus vs DeviceNet Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com