Limit switches provide precise mechanical feedback by physically contacting an object, ensuring reliable position detection in harsh environments, while proximity switches detect objects without contact using electromagnetic fields, offering faster response and longer life. Discover which switch suits your application best and explore their key differences in the following article.
Table of Comparison
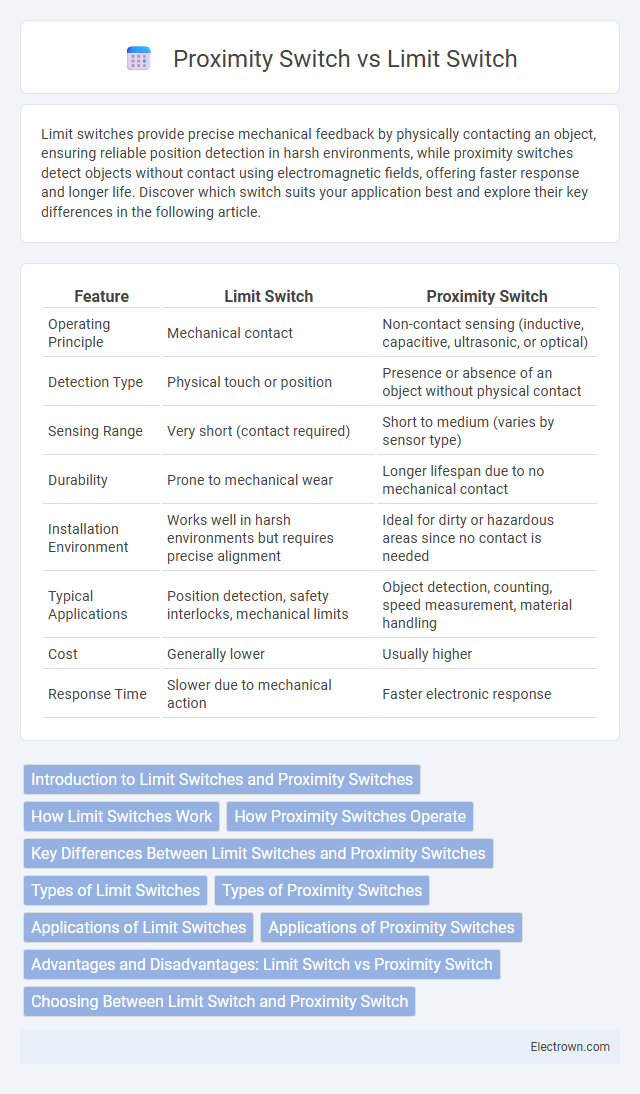
| Feature | Limit Switch | Proximity Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Mechanical contact | Non-contact sensing (inductive, capacitive, ultrasonic, or optical) |
| Detection Type | Physical touch or position | Presence or absence of an object without physical contact |
| Sensing Range | Very short (contact required) | Short to medium (varies by sensor type) |
| Durability | Prone to mechanical wear | Longer lifespan due to no mechanical contact |
| Installation Environment | Works well in harsh environments but requires precise alignment | Ideal for dirty or hazardous areas since no contact is needed |
| Typical Applications | Position detection, safety interlocks, mechanical limits | Object detection, counting, speed measurement, material handling |
| Cost | Generally lower | Usually higher |
| Response Time | Slower due to mechanical action | Faster electronic response |
Introduction to Limit Switches and Proximity Switches
Limit switches operate through physical contact to detect the presence or position of an object by mechanically actuating an internal switch. Proximity switches, such as inductive or capacitive sensors, detect objects without direct contact by sensing changes in electromagnetic fields or capacitance. Both types of switches play crucial roles in automation and control systems, enabling precise object detection and positioning.
How Limit Switches Work
Limit switches operate by physically contacting an object, triggering an internal mechanical action that opens or closes electrical contacts to control machinery or signal a position. These devices use a plunger, lever, or roller that moves when an object reaches a predetermined limit, ensuring precise control in automation systems. Your choice of limit switch depends on factors such as mechanical durability, environmental conditions, and response speed in comparison to proximity switches.
How Proximity Switches Operate
Proximity switches operate by detecting the presence or absence of an object without physical contact, using electromagnetic fields, capacitive sensing, or ultrasonic waves. Inductive proximity switches generate an electromagnetic field and detect changes when a metallic object enters this field, while capacitive types sense changes in the dielectric constant caused by non-metallic objects. Ultrasonic proximity switches emit high-frequency sound waves and measure the reflection time to identify nearby objects, enabling precise, contactless detection critical in automation and safety systems.
Key Differences Between Limit Switches and Proximity Switches
Limit switches physically detect the presence or absence of an object through direct contact, offering reliable mechanical feedback in industrial automation. Proximity switches sense objects without contact by using electromagnetic fields, inductive, capacitive, or ultrasonic sensors, enabling faster response times and reduced wear. Your choice depends on factors such as application environment, required sensing distance, and durability needs, as limit switches excel in harsh conditions while proximity switches provide non-contact detection.
Types of Limit Switches
Limit switches include various types such as plunger, lever, and roller, each designed for specific mechanical actuation. Plunger limit switches activate when a button is pressed directly, while lever and roller types respond to movement or rotation, offering flexibility in industrial automation. Selecting the right limit switch type enhances the precision and durability of your control system.
Types of Proximity Switches
Proximity switches include inductive, capacitive, ultrasonic, and photoelectric types, each detecting objects without physical contact. Inductive sensors excel at detecting metallic objects by generating an electromagnetic field, while capacitive sensors can sense both metallic and non-metallic materials through changes in capacitance. Ultrasonic switches use sound waves to detect distance and presence, whereas photoelectric sensors rely on light beams to identify objects, making them ideal for various industrial automation applications.
Applications of Limit Switches
Limit switches are extensively used in industrial automation for position detection and machine safety, often in conveyor systems to monitor object presence and end-of-travel limits. These switches ensure precise control in packaging machinery, robotics, and material handling equipment by providing reliable mechanical feedback. Their robust design allows operation in harsh environments, including manufacturing plants and automotive assembly lines, where accurate movement control is critical.
Applications of Proximity Switches
Proximity switches are widely used in industrial automation for detecting the presence or absence of objects without physical contact, making them ideal for conveyor systems, robotic arms, and safety devices. Their ability to operate in harsh environments with dust, dirt, or moisture enhances reliability in packaging, automotive, and food processing industries. You can improve production efficiency and equipment lifespan by integrating proximity switches into your automated control systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Limit Switch vs Proximity Switch
Limit switches offer reliable physical contact detection with clear on/off signals, making them ideal for simple mechanical systems, but they experience wear and require maintenance due to moving parts. Proximity switches provide non-contact detection with higher durability and faster response times, suitable for harsh environments, yet they can be more expensive and sensitive to metal interference. Your choice depends on whether durability and maintenance or cost-effectiveness and mechanical simplicity are the priority in your application.
Choosing Between Limit Switch and Proximity Switch
Choosing between a limit switch and a proximity switch depends on the application's environmental conditions, required durability, and sensing method. Limit switches provide mechanical contact detection ideal for harsh environments and precise position verification, while proximity switches offer non-contact sensing suitable for fast, wear-free operation and detecting metallic or non-metallic objects. Evaluating factors such as response time, maintenance needs, material compatibility, and installation complexity guides selecting the optimal switch type for industrial automation or safety systems.
Limit Switch vs Proximity Switch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com