Terminal blocks provide secure connections for individual wires, ensuring organized and reliable electrical circuitry, while distribution blocks distribute power from a single input to multiple outputs, simplifying complex wiring systems. Explore the full article to understand which solution best fits Your electrical installation needs and projects.
Table of Comparison
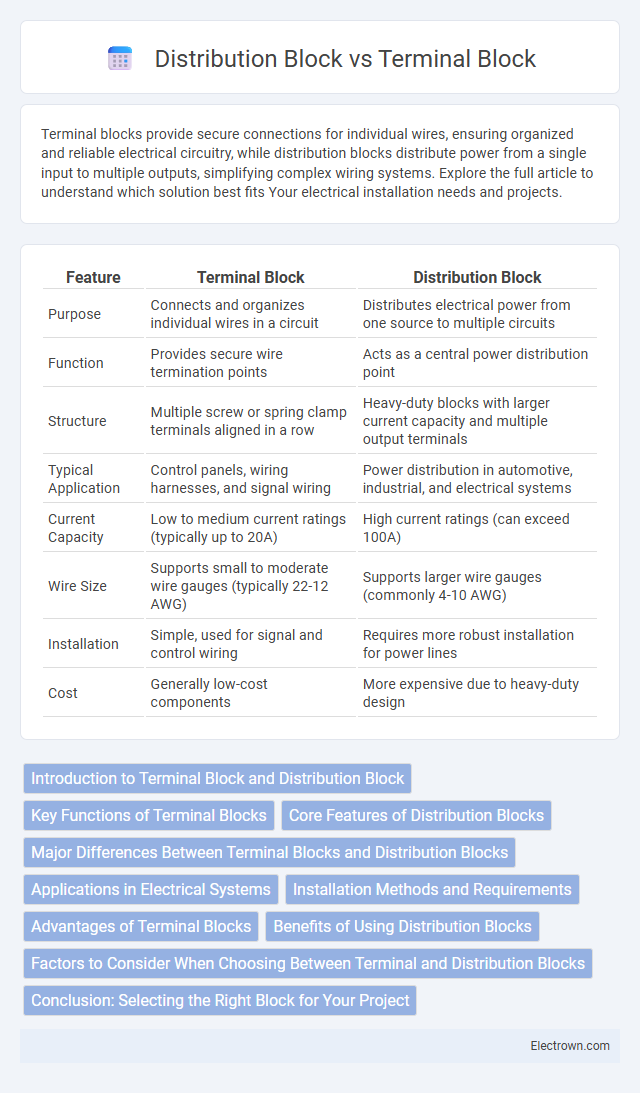
| Feature | Terminal Block | Distribution Block |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Connects and organizes individual wires in a circuit | Distributes electrical power from one source to multiple circuits |
| Function | Provides secure wire termination points | Acts as a central power distribution point |
| Structure | Multiple screw or spring clamp terminals aligned in a row | Heavy-duty blocks with larger current capacity and multiple output terminals |
| Typical Application | Control panels, wiring harnesses, and signal wiring | Power distribution in automotive, industrial, and electrical systems |
| Current Capacity | Low to medium current ratings (typically up to 20A) | High current ratings (can exceed 100A) |
| Wire Size | Supports small to moderate wire gauges (typically 22-12 AWG) | Supports larger wire gauges (commonly 4-10 AWG) |
| Installation | Simple, used for signal and control wiring | Requires more robust installation for power lines |
| Cost | Generally low-cost components | More expensive due to heavy-duty design |
Introduction to Terminal Block and Distribution Block
Terminal blocks provide secure and organized electrical connections by clamping wires between a metal strip and a screw or spring mechanism. Distribution blocks serve as centralized points for distributing electrical power from a single input to multiple output circuits, enhancing system organization and safety. Both components are essential in electrical panels for efficient wiring management and reliable circuit distribution.
Key Functions of Terminal Blocks
Terminal blocks serve as essential connectors that securely join electrical wires, ensuring safe and efficient transmission of electrical signals within circuits. They provide organized wire management, enabling easy identification, connection, and disconnection during maintenance or troubleshooting. Your electrical system benefits from terminal blocks by enhancing reliability and simplifying the installation process through their modular and standardized design.
Core Features of Distribution Blocks
Distribution blocks offer centralized power distribution with multiple output points, ensuring efficient management of electrical circuits in complex setups. These blocks provide high current-carrying capacity, secure connections, and easy integration into larger electrical panels, enhancing system reliability. Your electrical system benefits from improved organization and simplified maintenance when using distribution blocks compared to terminal blocks.
Major Differences Between Terminal Blocks and Distribution Blocks
Terminal blocks primarily serve as connection points to secure and organize multiple electrical wires, ensuring safe and efficient circuit connections. Distribution blocks distribute electrical power from a single input source across multiple output circuits, facilitating power management in electrical panels. The key differences lie in their function: terminal blocks focus on wire termination and circuit continuity, while distribution blocks emphasize power distribution and load balancing.
Applications in Electrical Systems
Terminal blocks are widely used in electrical systems to securely connect and organize multiple wires, ensuring safe and efficient circuit connections in control panels, machinery, and distribution boards. Distribution blocks serve as central points for distributing electrical power from a single input to multiple outputs, commonly utilized in power distribution systems, automotive wiring, and industrial equipment to manage voltage and current flow effectively. Both components enhance system reliability and maintenance by providing clear, organized wiring schemes in complex electrical installations.
Installation Methods and Requirements
Terminal blocks typically require mounting on DIN rails or panels with screws, ensuring secure and organized wire connections, while distribution blocks often feature modular installation with snap-on or bolt-down options for easy integration into electrical panels. Terminal block installation demands precise wire stripping and insertion into clamp terminals with adequate torque, whereas distribution blocks require proper conductor sizing and secure bolting to facilitate current distribution. Both systems necessitate compliance with electrical codes and sufficient space for heat dissipation to ensure safety and performance.
Advantages of Terminal Blocks
Terminal blocks offer enhanced organization and secure wire connections for complex electrical systems, making maintenance and troubleshooting more efficient. They provide modularity, allowing easy expansion or modification of circuits without disrupting existing wiring. Your electrical setup benefits from improved safety and reliable conductivity compared to distribution blocks, which typically handle simpler power distribution tasks.
Benefits of Using Distribution Blocks
Distribution blocks streamline electrical wiring by centralizing multiple connections, reducing clutter, and enhancing organization within control panels. They improve maintenance efficiency by allowing easier circuit identification and quick disconnection without disturbing other circuits. Your electrical systems benefit from improved safety and reliability through secure, stable connections that minimize the risk of loose wiring and electrical faults.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Terminal and Distribution Blocks
When choosing between terminal blocks and distribution blocks, consider current capacity, wiring complexity, and space constraints to ensure optimal electrical distribution and safety. Terminal blocks are ideal for organizing multiple wire connections in compact spaces, while distribution blocks efficiently split power from a single source to multiple circuits. Evaluating load requirements and installation environment helps determine the best option for reliable and efficient electrical system management.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Block for Your Project
Choosing between a terminal block and a distribution block depends on the project's wiring complexity and current handling requirements. Terminal blocks provide secure, individual wire connections ideal for organizing circuits, while distribution blocks efficiently distribute power from a single input to multiple outputs. Evaluate factors like load capacity, space constraints, and ease of maintenance to select the most suitable block for optimal electrical performance.
Terminal Block vs Distribution Block Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com