Wet contacts use an external voltage source with electrical current flowing through the contacts, while dry contacts, also known as volt-free contacts, operate without supplying any voltage, merely opening or closing a circuit. Understanding the differences between wet and dry contacts is essential for selecting the right switch type for your application--explore the details in the rest of the article.
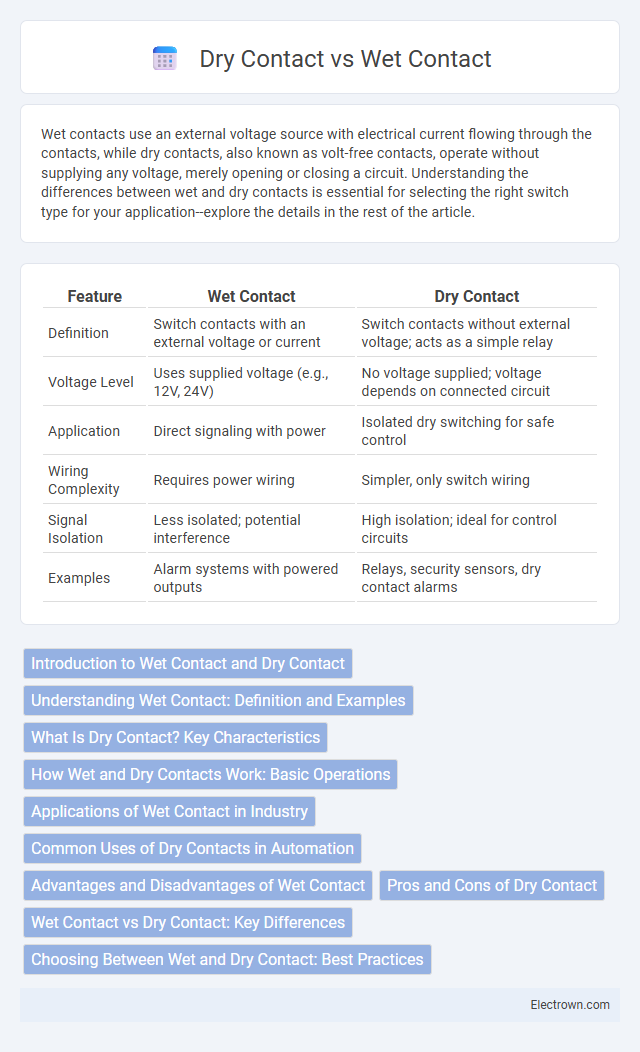
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wet Contact | Dry Contact |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Switch contacts with an external voltage or current | Switch contacts without external voltage; acts as a simple relay |
| Voltage Level | Uses supplied voltage (e.g., 12V, 24V) | No voltage supplied; voltage depends on connected circuit |
| Application | Direct signaling with power | Isolated dry switching for safe control |
| Wiring Complexity | Requires power wiring | Simpler, only switch wiring |
| Signal Isolation | Less isolated; potential interference | High isolation; ideal for control circuits |
| Examples | Alarm systems with powered outputs | Relays, security sensors, dry contact alarms |
Introduction to Wet Contact and Dry Contact
Wet contact refers to a switching mechanism where the relay contacts are connected to a power source, supplying voltage to the load when activated, commonly used in automation and control systems. Dry contact, also known as a volt-free contact, operates without an external voltage, simply acting as a switch that opens or closes a circuit without supplying power. Understanding the distinction is crucial for selecting appropriate relay types in electrical and electronic applications to ensure compatibility and safety.
Understanding Wet Contact: Definition and Examples
Wet contact refers to a type of electrical switch or relay contact that has an external voltage source applied to it, ensuring a measurable voltage is present when the contact is closed. Common examples of wet contacts include switch outputs connected directly to a power supply or sensor outputs providing a specific voltage signal. These contacts enable reliable detection in control systems by supplying a defined voltage level for status monitoring.
What Is Dry Contact? Key Characteristics
Dry contact, also known as a voltage-free contact, is an electrical switch or relay contact that does not supply voltage or current; it operates purely as a mechanical switch to open or close a circuit. Key characteristics include isolation from the controlling circuit, allowing it to interface safely with devices regardless of voltage or current levels, and reliable operation in low-voltage control applications. Dry contacts are commonly used in alarm systems, HVAC controls, and industrial automation for signaling and control functions without introducing electrical noise or interference.
How Wet and Dry Contacts Work: Basic Operations
Wet contacts operate by utilizing an external power source to energize the contact points, allowing electrical current to flow when the switch closes, ensuring a reliable signal in industrial control systems. Dry contacts, in contrast, function as simple mechanical switches without supplying voltage or current; they rely on your external circuit to provide power, offering isolation and flexibility for low-voltage control applications. Understanding these basic operations helps you select the appropriate contact type for monitoring and controlling electrical devices effectively.
Applications of Wet Contact in Industry
Wet contact sensors are widely utilized in industrial automation for monitoring electrical circuits where they directly interface with voltage sources, enabling reliable control of machinery, conveyor belts, and safety interlocks. These contacts ensure enhanced electrical isolation and longevity in harsh industrial environments such as manufacturing plants and process control systems. Their applications include motor starters, relay outputs, and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) inputs that require consistent voltage signaling for accurate equipment operation.
Common Uses of Dry Contacts in Automation
Dry contacts are commonly used in automation systems to interface with relays, sensors, and control circuits without supplying power, ensuring safe and isolated switching. They serve critical roles in monitoring equipment status, triggering alarms, and controlling motor starters or PLC inputs by providing voltage-free signals. This makes dry contacts essential for reliable signal transmission and fault detection in industrial automation environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wet Contact
Wet contact relays use an external power source to energize the contact, offering clear signal integrity and reliable operation in noisy electrical environments. They reduce contact wear and corrosion due to the controlled voltage and current, extending relay lifespan and maintenance intervals. However, wet contact relays may require additional wiring and power consumption, increasing system complexity and cost compared to dry contact alternatives.
Pros and Cons of Dry Contact
Dry contact switches operate without an external voltage, offering a safer and more reliable signal transmission in sensitive control systems. They reduce the risk of electrical interference and corrosion, extending the lifespan of your equipment. However, dry contacts may require additional components for signal conditioning, which can increase system complexity and installation costs.
Wet Contact vs Dry Contact: Key Differences
Wet contact uses an external voltage source to detect closed circuit states, making it suitable for interfacing with devices requiring powered signals. Dry contact operates as a simple switch with no voltage applied, relying on mechanical closure to complete the circuit, ideal for low-voltage or signaling applications. Understanding the key differences between wet and dry contacts enables you to select the appropriate sensor type for your control or monitoring system.
Choosing Between Wet and Dry Contact: Best Practices
Choosing between wet contact and dry contact depends on the specific requirements of your system, including voltage levels, environmental conditions, and signal integrity needs. Wet contact is preferred when a reliable, voltage-driven signal is needed to avoid false triggering in noisy environments, while dry contact excels in applications requiring isolated, voltage-free switching for safer interfacing with control circuits. Evaluating your application's voltage tolerance, signal clarity, and electrical isolation needs will ensure the best practice in selecting the appropriate contact type.
Wet Contact vs Dry Contact Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com