Proximity sensors detect the presence of nearby objects without physical contact, using electromagnetic fields or capacitive, inductive, or ultrasonic technologies, while photoelectric sensors rely on light beams to detect objects and measure distance or presence. Discover how understanding the differences between these sensors can optimize Your automation systems by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
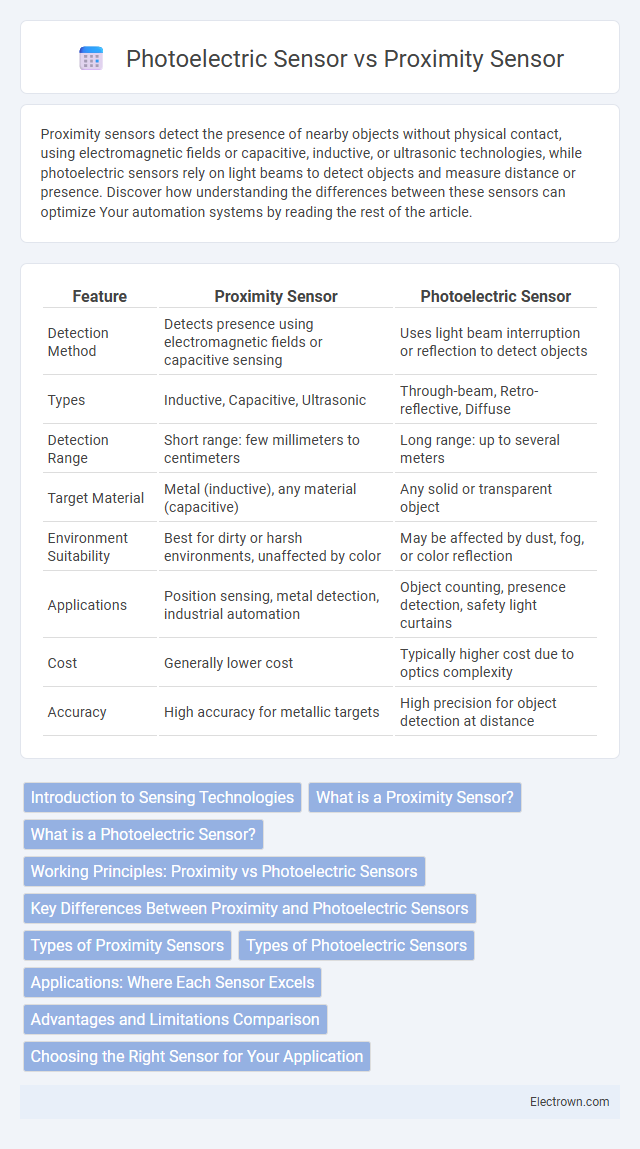
| Feature | Proximity Sensor | Photoelectric Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Method | Detects presence using electromagnetic fields or capacitive sensing | Uses light beam interruption or reflection to detect objects |
| Types | Inductive, Capacitive, Ultrasonic | Through-beam, Retro-reflective, Diffuse |
| Detection Range | Short range: few millimeters to centimeters | Long range: up to several meters |
| Target Material | Metal (inductive), any material (capacitive) | Any solid or transparent object |
| Environment Suitability | Best for dirty or harsh environments, unaffected by color | May be affected by dust, fog, or color reflection |
| Applications | Position sensing, metal detection, industrial automation | Object counting, presence detection, safety light curtains |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost due to optics complexity |
| Accuracy | High accuracy for metallic targets | High precision for object detection at distance |
Introduction to Sensing Technologies
Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of nearby objects without physical contact, using electromagnetic fields or capacitive sensing, making them ideal for applications requiring non-invasive detection. Photoelectric sensors operate by emitting and receiving light beams to identify object presence, distance, or changes in surface conditions, offering high precision in object detection and measurement. Both technologies play critical roles in automation, safety systems, and industrial process control by enabling accurate and reliable object sensing.
What is a Proximity Sensor?
A proximity sensor detects the presence or absence of objects within a predefined range without physical contact, commonly using electromagnetic fields or capacitive, inductive, or ultrasonic technologies. It is widely utilized in industrial automation, robotics, and security systems for object detection and position sensing. Unlike photoelectric sensors that rely on light beams, proximity sensors offer reliable detection in various environmental conditions and material types.
What is a Photoelectric Sensor?
A photoelectric sensor detects objects, changes in surface conditions, or environmental factors by emitting and receiving light, typically through infrared, visible, or laser beams. It operates on the principle of interrupting or reflecting a light beam to sense the presence or absence of an object within its detection range. Your choice between a photoelectric sensor and a proximity sensor depends on the required detection distance, material sensitivity, and environmental conditions in your application.
Working Principles: Proximity vs Photoelectric Sensors
Proximity sensors operate based on detecting changes in an electromagnetic field, capacitance, or inductance when a target object enters their sensing range, allowing non-contact detection of metallic or non-metallic objects. Photoelectric sensors function by emitting a light beam (often infrared) and monitoring the presence, absence, or interruption of this beam to detect an object's position or distance. The key distinction lies in proximity sensors relying on physical properties such as electromagnetic fields, while photoelectric sensors depend on optical detection through light signal interruption or reflection.
Key Differences Between Proximity and Photoelectric Sensors
Proximity sensors detect objects by sensing changes in the electromagnetic field or capacitance without physical contact, making them ideal for detecting metal or nearby objects. Photoelectric sensors use light beams--either through reflection or interruption--to detect the presence or distance of an object, providing longer detection ranges and the ability to sense transparent or small items. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right sensor based on object type, detection range, and environmental conditions.
Types of Proximity Sensors
Inductive, capacitive, ultrasonic, and magnetic are common types of proximity sensors, each designed to detect objects without physical contact. Inductive sensors excel at identifying metallic targets, while capacitive sensors sense both metallic and non-metallic materials by detecting changes in capacitance. Ultrasound transmits sound waves to measure distance or presence, and magnetic sensors detect changes in magnetic fields caused by nearby objects, offering diverse options depending on your application's needs.
Types of Photoelectric Sensors
Photoelectric sensors include through-beam, retroreflective, and diffuse types, each designed for specific sensing conditions and object detection needs. Through-beam sensors use separate transmitters and receivers, offering long-range detection with high accuracy, while retroreflective sensors employ a reflector to bounce light back for object sensing. Diffuse sensors detect objects by reflecting light directly from the target, making them ideal for short-range applications where surface texture and color vary.
Applications: Where Each Sensor Excels
Proximity sensors excel in detecting the presence or absence of objects without physical contact, making them ideal for applications such as metal detection in manufacturing lines, automated doors, and mobile devices. Photoelectric sensors are best suited for long-distance detection, object counting, and sorting tasks, especially in packaging, conveyor systems, and robotic automation where detecting transparent or small objects is crucial. Your choice depends on whether you need close-range, contactless detection or longer-range, precise object identification.
Advantages and Limitations Comparison
Proximity sensors offer non-contact detection with high durability and are ideal for metal object sensing in harsh environments, but their range is limited and sensitivity can be affected by target material and shape. Photoelectric sensors provide longer sensing distances and versatility for detecting various materials and transparent objects, though they are more susceptible to environmental conditions like dust, dirt, and ambient light interference. Choosing between these sensors depends on the specific application requirements, including detection range, target type, and environmental factors.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
Proximity sensors detect metallic and non-metallic objects without physical contact using electromagnetic fields or capacitive coupling, making them ideal for short-range detection in industrial automation. Photoelectric sensors use a light beam to identify objects over longer distances and provide high accuracy for transparent or small items, suitable for packaging and assembly lines. Selecting the right sensor depends on factors like target material, detection range, environmental conditions, and required precision, ensuring optimal performance and durability in your application.
Proximity Sensor vs Photoelectric Sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com