Earth Leakage Relays detect leakage currents flowing to earth, protecting against electric shock and fire hazards by tripping when small leakage currents exceed a preset threshold, while Earth Fault Relays respond to unbalanced currents caused by faults in the earth path, ensuring system protection by isolating faulty sections. Understanding the differences between these relays is essential for enhancing your electrical safety and system reliability--read on to explore their distinct functions and applications.
Table of Comparison
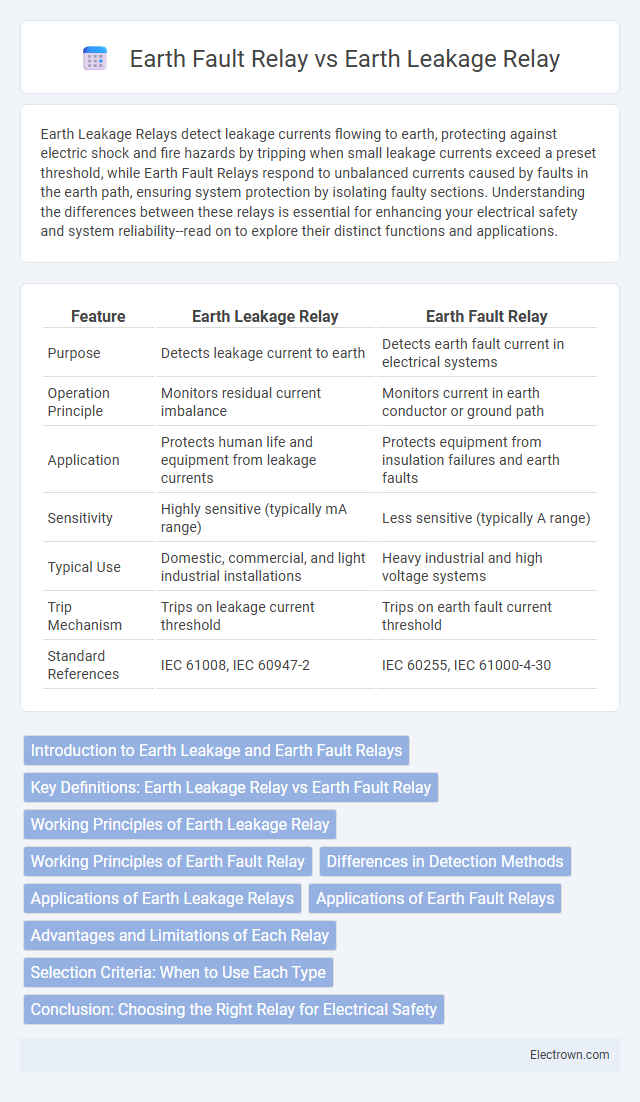
| Feature | Earth Leakage Relay | Earth Fault Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects leakage current to earth | Detects earth fault current in electrical systems |
| Operation Principle | Monitors residual current imbalance | Monitors current in earth conductor or ground path |
| Application | Protects human life and equipment from leakage currents | Protects equipment from insulation failures and earth faults |
| Sensitivity | Highly sensitive (typically mA range) | Less sensitive (typically A range) |
| Typical Use | Domestic, commercial, and light industrial installations | Heavy industrial and high voltage systems |
| Trip Mechanism | Trips on leakage current threshold | Trips on earth fault current threshold |
| Standard References | IEC 61008, IEC 60947-2 | IEC 60255, IEC 61000-4-30 |
Introduction to Earth Leakage and Earth Fault Relays
Earth Leakage Relays detect current leakage to earth caused by insulation failure or damaged wiring, typically at low magnitude, preventing electric shock and fire hazards. Earth Fault Relays monitor high-magnitude earth faults within power systems, protecting equipment from severe damage by isolating faulted circuits quickly. Understanding the role of these relays helps you enhance electrical safety and system reliability effectively.
Key Definitions: Earth Leakage Relay vs Earth Fault Relay
Earth Leakage Relay detects leakage currents flowing to the ground, typically in the range of milliamperes, to prevent electric shock and fire hazards in electrical installations. Earth Fault Relay, on the other hand, monitors earth fault currents caused by insulation failures or faults in electrical equipment, usually at higher current levels than leakage relays, to protect transformers and generators. Both devices are essential for electrical safety but serve distinct roles based on the magnitude and nature of the earth current they monitor.
Working Principles of Earth Leakage Relay
Earth Leakage Relays operate by detecting residual currents flowing through the protective earth conductor, which indicate insulation failure or leakage in electrical systems. These relays compare the current balance between the line and neutral conductors using a current transformer, triggering a trip signal when the differential current exceeds a preset threshold. Your electrical system is safeguarded from potential shock hazards and equipment damage by promptly isolating circuits during unexpected earth leakage conditions.
Working Principles of Earth Fault Relay
Earth Fault Relays operate by detecting unbalanced currents caused by earth faults, using current transformers to monitor the difference between phase currents and neutral current. When this imbalance exceeds a set threshold, the relay triggers to isolate the faulty section, preventing equipment damage and safety hazards. Understanding your Earth Fault Relay's working principle ensures precise fault detection and timely protection in electrical systems.
Differences in Detection Methods
Earth Leakage Relay detects current leakage by measuring the imbalance between phase conductors and the neutral, identifying leakage currents flowing to the earth directly. Earth Fault Relay senses faults by detecting excess current flowing through the earth path, typically based on a specific threshold of fault current magnitude. The key difference lies in Earth Leakage Relay capturing any leakage current regardless of magnitude, while Earth Fault Relay targets significant fault currents indicative of serious earth faults.
Applications of Earth Leakage Relays
Earth Leakage Relays are primarily designed for detecting leakage currents to earth, enabling protection against electric shock and preventing fire hazards in residential, commercial, and industrial electrical installations. These relays are widely applied in low-voltage distribution systems, ensuring the safety of electrical equipment and personnel by quickly isolating faulty circuits when leakage thresholds are exceeded. You can find Earth Leakage Relays in applications such as motor protection, control panels, and sensitive electronic equipment where precise fault detection is crucial.
Applications of Earth Fault Relays
Earth Fault Relays are primarily used in power distribution systems to detect and isolate earth faults, preventing equipment damage and ensuring personnel safety. They protect transformers, generators, and motors by sensing earth current leakage, which indicates insulation failure or winding faults. Your electrical system's reliability improves significantly with the proper application of Earth Fault Relays in industrial, commercial, and residential installations.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Relay
Earth Leakage Relays offer the advantage of detecting low-level leakage currents quickly, enhancing protection against electrical shock and fire hazards by monitoring the difference between outgoing and returning currents. However, their sensitivity to transient currents can sometimes lead to nuisance tripping, limiting their application in environments with fluctuating loads. Earth Fault Relays provide robust detection of ground faults in high-current circuits and are less prone to nuisance trips but may have slower response times and less sensitivity to small leakage currents that could pose safety risks; understanding these trade-offs helps you select the appropriate relay for your electrical protection needs.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Each Type
Earth Leakage Relays are ideal for detecting low-level leakage currents in electrical installations, ensuring personnel safety and preventing fire hazards by quickly disconnecting faulty circuits. Earth Fault Relays are selected for systems requiring detection of phase-to-earth faults, commonly used in industrial and high-voltage applications to protect equipment from severe damage. Selection criteria depend on system sensitivity requirements, fault current levels, and specific protection zones; earth leakage devices suit residential and commercial settings, while earth fault relays serve heavy industrial networks.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Relay for Electrical Safety
Earth Leakage Relay detects leakage currents to ground, typically in the milliampere range, providing sensitive protection against electric shock and fire hazards. Earth Fault Relay monitors larger fault currents in power systems, primarily safeguarding equipment from damage due to insulation failures or faults to earth. Selecting the right relay depends on the required sensitivity and application context: Earth Leakage Relays suit personal safety in low-level leakage scenarios, while Earth Fault Relays are ideal for protecting electrical installations from substantial ground fault currents.
Earth Leakage Relay vs Earth Fault Relay Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com