Surge protectors safeguard your electronic devices from sudden voltage spikes, while lightning arresters primarily protect structures by diverting lightning strikes safely to the ground. Explore the key differences and find out which protection suits your needs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
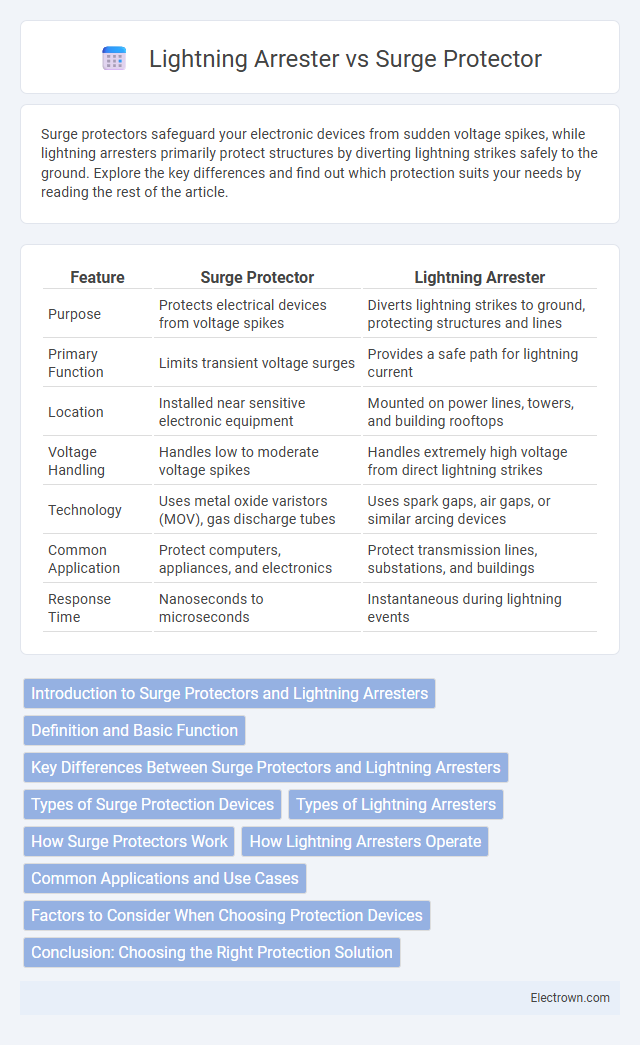
| Feature | Surge Protector | Lightning Arrester |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects electrical devices from voltage spikes | Diverts lightning strikes to ground, protecting structures and lines |
| Primary Function | Limits transient voltage surges | Provides a safe path for lightning current |
| Location | Installed near sensitive electronic equipment | Mounted on power lines, towers, and building rooftops |
| Voltage Handling | Handles low to moderate voltage spikes | Handles extremely high voltage from direct lightning strikes |
| Technology | Uses metal oxide varistors (MOV), gas discharge tubes | Uses spark gaps, air gaps, or similar arcing devices |
| Common Application | Protect computers, appliances, and electronics | Protect transmission lines, substations, and buildings |
| Response Time | Nanoseconds to microseconds | Instantaneous during lightning events |
Introduction to Surge Protectors and Lightning Arresters
Surge protectors safeguard electrical devices by limiting voltage spikes caused by power surges, typically from switching or lightning strikes. Lightning arresters protect power lines and equipment by redirecting high-voltage lightning currents safely to the ground, preventing damage. Both devices are essential for electrical safety but serve distinct roles in protecting against transient voltage events.
Definition and Basic Function
A surge protector is an electrical device designed to shield your electronic equipment from voltage spikes by limiting transient voltages and diverting excess current to the ground. A lightning arrester is specifically engineered to protect power systems and structures by safely channeling lightning strikes to the earth, preventing damage caused by high-voltage surges. Understanding the basic function of both devices helps you choose the appropriate protection for your electrical infrastructure.
Key Differences Between Surge Protectors and Lightning Arresters
Surge protectors are designed to safeguard electronic devices from voltage spikes caused by power surges, typically by diverting excess electricity to the ground, while lightning arresters primarily protect electrical power systems from direct lightning strikes by providing a low-resistance path to discharge high-voltage lightning currents safely. Surge protectors operate at lower voltage levels within homes or electronics, whereas lightning arresters are installed on power distribution systems and transmission lines to prevent insulation breakdown. The key difference lies in their application and operational response; surge protectors handle transient surges from electrical disturbances, and lightning arresters control extreme voltages from lightning events.
Types of Surge Protection Devices
Surge protection devices (SPDs) include voltage clamping types like Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) and gas discharge tubes (GDTs) designed to absorb and divert electrical surges, commonly used in surge protectors. Lightning arresters primarily use spark gaps to channel high-voltage lightning strikes safely to the ground, preventing damage to electrical systems. Both devices serve to protect against transient overvoltages but differ significantly in their mechanisms and application areas.
Types of Lightning Arresters
Lightning arresters are categorized into several types, including expulsion, valve, and polymer arresters, each designed to protect electrical equipment by diverting lightning surges safely to the ground. Expulsion arresters use a spark gap and blowout mechanism to extinguish the arc, suitable for medium-voltage systems, while valve arresters employ zinc oxide semiconductors for non-linear resistance, offering maintenance-free performance in high-voltage applications. Polymer arresters feature silicone rubber housing for enhanced weather resistance and lightweight design, providing reliable surge protection in harsh environmental conditions.
How Surge Protectors Work
Surge protectors safeguard electrical devices by diverting excess voltage from power surges, using components like metal oxide varistors (MOVs) that absorb and dissipate the spike. They respond to short-term voltage spikes caused by events such as lightning strikes, power outages, or switching surges, preventing damage to connected electronics. Unlike lightning arresters, which protect outdoor power lines by grounding high-voltage surges, surge protectors focus on regulating voltage within indoor electrical networks.
How Lightning Arresters Operate
Lightning arresters operate by safely diverting high-voltage lightning strikes away from electrical equipment and into the ground, preventing damage. They contain a non-linear resistor that remains non-conductive during normal operation but becomes conductive when voltage exceeds a certain threshold. Your electrical system is protected by these devices which quickly discharge the surge caused by lightning, maintaining system stability.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Surge protectors are commonly used in residential and commercial settings to safeguard electronic devices like computers, televisions, and home appliances from voltage spikes caused by power surges. Lightning arresters are primarily installed on power lines, telecommunications equipment, and industrial facilities to protect infrastructure by diverting lightning-induced surges safely to the ground. Your choice between these devices depends on the specific application: surge protectors shield sensitive electronics indoors, while lightning arresters defend critical outdoor electrical systems from lightning strikes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Protection Devices
When selecting between a surge protector and a lightning arrester, consider factors such as the intensity and frequency of electrical surges in your area, the specific vulnerabilities of your electrical system, and the level of protection required for your sensitive equipment. Surge protectors are ideal for minimizing transient voltage spikes caused by switching or minor surges, while lightning arresters are designed to handle high-energy strikes from lightning events. Your choice should align with the environmental risks, installation complexity, and compliance with local electrical standards to ensure optimal safety and performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Protection Solution
Selecting the appropriate protection device depends on the specific risk environment: surge protectors are ideal for guarding sensitive electronics against electrical surges caused by switching or minor lightning strikes, while lightning arresters provide robust defense during direct lightning strikes by safely diverting high voltage. Understanding the nature of electrical threats and site conditions ensures optimal investment in protection systems, minimizing equipment damage and downtime. Proper installation and regular maintenance further enhance the efficiency and lifespan of either protection solution.
Surge Protector vs Lightning Arrester Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com