Star winding offers a neutral point and is ideal for distributing voltages, providing a stable and balanced load in three-phase systems, while delta winding delivers higher starting torque and can handle heavier loads without a neutral connection. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your choice between star and delta winding can impact electrical performance and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
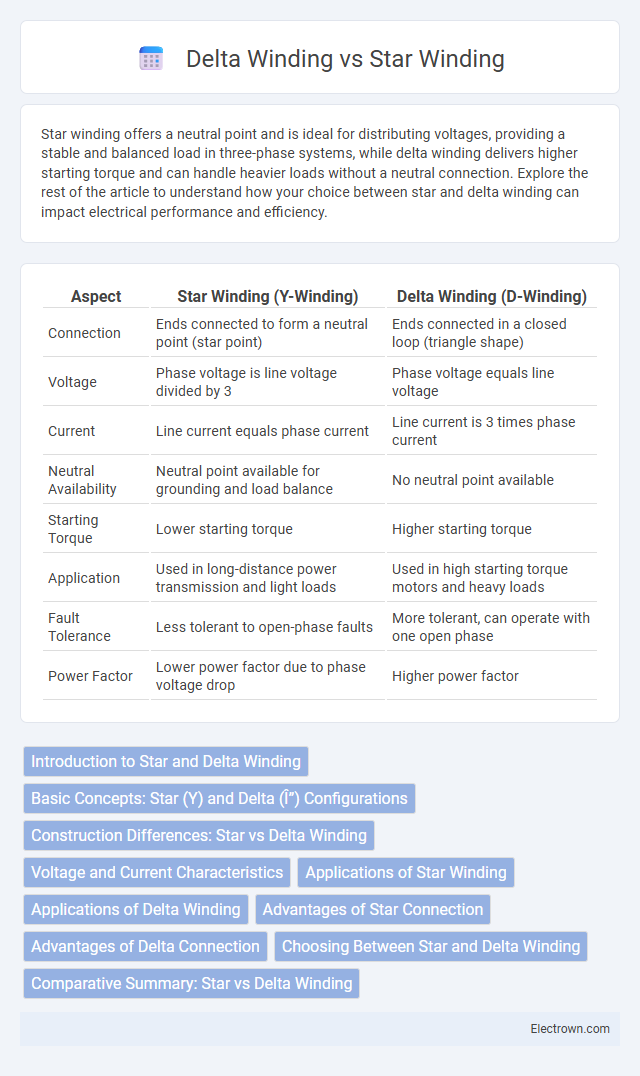
| Aspect | Star Winding (Y-Winding) | Delta Winding (D-Winding) |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | Ends connected to form a neutral point (star point) | Ends connected in a closed loop (triangle shape) |
| Voltage | Phase voltage is line voltage divided by 3 | Phase voltage equals line voltage |
| Current | Line current equals phase current | Line current is 3 times phase current |
| Neutral Availability | Neutral point available for grounding and load balance | No neutral point available |
| Starting Torque | Lower starting torque | Higher starting torque |
| Application | Used in long-distance power transmission and light loads | Used in high starting torque motors and heavy loads |
| Fault Tolerance | Less tolerant to open-phase faults | More tolerant, can operate with one open phase |
| Power Factor | Lower power factor due to phase voltage drop | Higher power factor |
Introduction to Star and Delta Winding
Star winding connects each coil end to a common neutral point, forming a Y-shaped configuration that enables phase voltages to be lower than line voltages. Delta winding connects coil ends in a closed loop, creating a triangular configuration where line voltage equals phase voltage, allowing for higher current handling. These fundamental distinctions influence voltage distribution, current flow, and applications in three-phase electrical systems.
Basic Concepts: Star (Y) and Delta (Δ) Configurations
Star (Y) winding connects each coil to a common neutral point, creating a three-phase system with line voltage 3 times the phase voltage and equal phase currents, ideal for balanced loads and providing neutral access. Delta (D) winding forms a closed loop where each coil connects end-to-end, generating line voltage equal to phase voltage and line current 3 times the phase current, suitable for high starting torque applications and unbalanced loads. Both configurations are essential in three-phase transformers and motors, influencing voltage, current relationships, and load distribution in electrical systems.
Construction Differences: Star vs Delta Winding
Star winding features each coil connected end-to-end to form a common neutral point, creating a Y-shape configuration, whereas delta winding connects coils in a closed loop, forming a triangular circuit. Star winding enables phase voltages to be lower than line voltages, beneficial for neutral load balancing and safety, unlike delta winding which provides equal phase and line voltages, allowing for higher current flow and robustness. You can identify construction differences by examining coil connections and terminal configurations that determine the motor or transformer's performance characteristics.
Voltage and Current Characteristics
Star winding configuration delivers a line voltage that is 3 times the phase voltage, while the line current equals the phase current, making it suitable for high-voltage, low-current applications. Delta winding provides a line current that is 3 times the phase current and a line voltage equal to the phase voltage, ideal for low-voltage, high-current scenarios. These distinctive voltage and current characteristics influence the choice between star and delta windings in three-phase electrical equipment for efficient performance under specific load conditions.
Applications of Star Winding
Star winding is widely used in electrical systems requiring a neutral point, such as in distribution transformers and three-phase power supplies, enabling stable voltage levels and fault detection. Your industrial motors benefit from star winding's ability to handle high starting currents with reduced voltage stress, improving efficiency and lifespan. This configuration is ideal for equipment demanding balanced loads and reliable operation under varying power conditions.
Applications of Delta Winding
Delta winding is commonly used in industrial motor applications where high starting torque is required, such as in compressors, pumps, and heavy machinery. It provides a robust solution for three-phase power systems, offering better phase current distribution and the ability to handle unbalanced loads efficiently. Delta connections are favored in power distribution networks for their capability to maintain voltage stability under fluctuating load conditions.
Advantages of Star Connection
Star winding offers several advantages such as providing a neutral point, which enhances system stability and fault detection. It allows the use of lower voltage ratings for insulation, making equipment more cost-effective and safer to operate. Your electrical system benefits from improved voltage balance and reduced phase currents, resulting in higher efficiency and reliability.
Advantages of Delta Connection
Delta winding offers higher power output and better efficiency in three-phase motors by providing a constant voltage across all phases. Its configuration allows for simpler fault detection and increased reliability during unbalanced load conditions. You benefit from improved starting torque and fault tolerance, making Delta connections ideal for heavy industrial applications.
Choosing Between Star and Delta Winding
When choosing between star and delta winding configurations, consider the application's voltage and current requirements, as star winding provides a neutral point for grounding and lower phase voltage, ideal for high-voltage, low-current situations. Delta winding delivers higher phase current and is better suited for heavy loads and motor starting where increased torque is needed. Your decision should balance efficiency, load type, and system protection needs to optimize performance and reliability.
Comparative Summary: Star vs Delta Winding
Star winding offers a neutral point and is generally used for long-distance power transmission due to its ability to handle high voltages with lower insulation requirements. Delta winding provides a closed-loop configuration suitable for high starting torque and balanced loads, often found in industrial motor applications. The choice between star and delta windings depends on factors like voltage levels, load characteristics, and the need for neutral connections.
Star Winding vs Delta Winding Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com