Remote IO systems offer flexible installation by transmitting signals over long distances without signal loss, while Local IO provides faster response times and reduces wiring complexity by processing signals near the control panel. Discover how to choose the best IO configuration for your specific automation needs in the rest of this article.
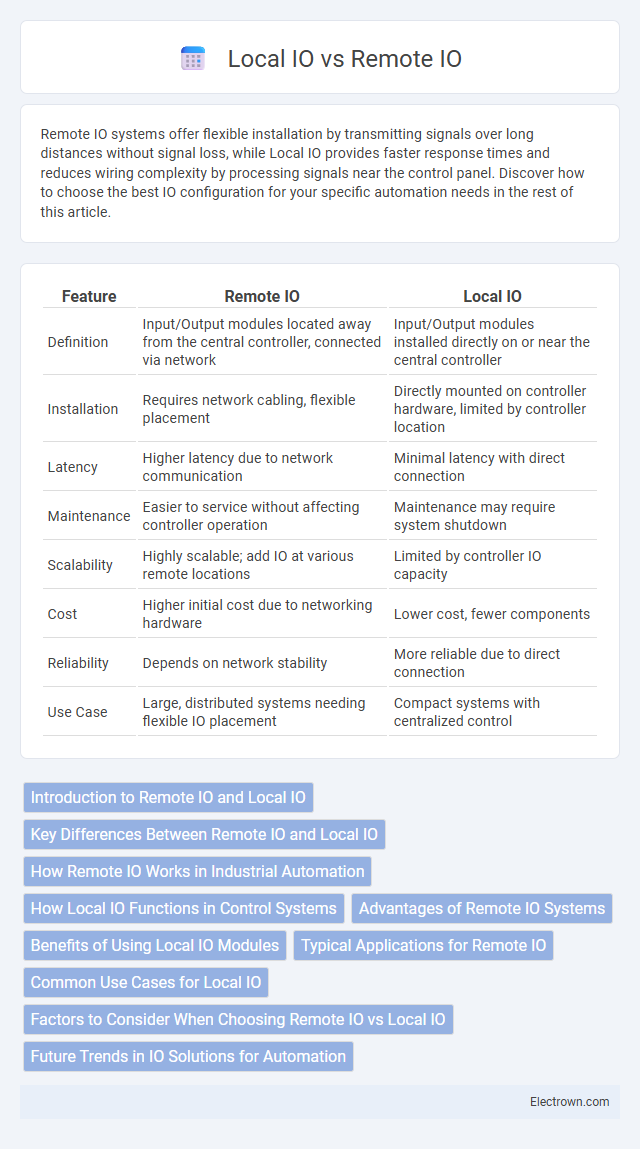
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Remote IO | Local IO |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Input/Output modules located away from the central controller, connected via network | Input/Output modules installed directly on or near the central controller |
| Installation | Requires network cabling, flexible placement | Directly mounted on controller hardware, limited by controller location |
| Latency | Higher latency due to network communication | Minimal latency with direct connection |
| Maintenance | Easier to service without affecting controller operation | Maintenance may require system shutdown |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; add IO at various remote locations | Limited by controller IO capacity |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to networking hardware | Lower cost, fewer components |
| Reliability | Depends on network stability | More reliable due to direct connection |
| Use Case | Large, distributed systems needing flexible IO placement | Compact systems with centralized control |
Introduction to Remote IO and Local IO
Remote IO systems extend control and data acquisition capabilities by connecting input/output devices over a network, offering increased scalability and flexibility in industrial automation environments. Local IO refers to input/output devices physically installed near the controller, providing faster response times and simpler wiring but limited expansion options. Selecting between Remote IO and Local IO depends on factors such as system size, communication distance, installation complexity, and application requirements.
Key Differences Between Remote IO and Local IO
Remote IO and Local IO differ primarily in physical placement, with Remote IO located away from the main controller and Local IO directly connected to it. Remote IO systems enhance scalability and reduce wiring complexity by communicating via fieldbus or Ethernet networks, whereas Local IO offers faster response times by processing signals on-site. The choice impacts system architecture, maintenance convenience, and latency, with Remote IO favored for distributed setups and Local IO preferred for critical timing control.
How Remote IO Works in Industrial Automation
Remote IO in industrial automation operates by connecting input/output modules to a central controller via communication networks, enabling data exchange over long distances. This setup allows sensors and actuators located remotely to transmit signals and receive commands without direct wiring to the controller, reducing installation costs and complexity. Your industrial system benefits from increased flexibility and scalability by integrating Remote IO for distributed control applications.
How Local IO Functions in Control Systems
Local IO functions in control systems by directly connecting sensors and actuators to the central controller, enabling real-time data acquisition and immediate response to process changes. This close proximity reduces latency and improves system reliability by minimizing communication delays and potential signal interference. Your control system benefits from precise and fast inputs and outputs, which are critical for maintaining optimal performance and safety.
Advantages of Remote IO Systems
Remote IO systems offer significant advantages such as increased installation flexibility by allowing devices to be placed closer to sensors and actuators, reducing wiring complexity and costs. They enhance system scalability and maintenance by enabling easier expansions and localized troubleshooting without disrupting the entire network. Your industrial automation setup benefits from improved data accuracy and faster response times through reduced signal degradation over long distances.
Benefits of Using Local IO Modules
Local IO modules offer faster data processing and lower latency compared to remote IO, enhancing real-time control and system responsiveness. They reduce network traffic and improve reliability by minimizing communication points and potential failure sources. Your automation systems benefit from easier maintenance and installation due to their close proximity to field devices.
Typical Applications for Remote IO
Remote IO is commonly used in large-scale industrial automation systems, where decentralized control and data acquisition are essential for efficient operation. Typical applications include distributed manufacturing plants, process control in oil and gas industries, and smart grid management, where sensors and actuators are spread across vast distances. Your control system benefits from reduced wiring costs and improved scalability by leveraging Remote IO to connect remote devices to a central controller.
Common Use Cases for Local IO
Local IO is commonly used in industrial automation systems where low latency and high-speed data processing are critical, such as in robotic control, motor drives, and safety systems. It enables direct connection of sensors and actuators to the main controller, ensuring faster response times and improved system reliability. Typical applications include assembly lines, packaging machines, and real-time monitoring in manufacturing environments.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Remote IO vs Local IO
Factors to consider when choosing Remote IO vs Local IO include system complexity, distance between control systems and field devices, and network reliability. Remote IO is ideal for expansive or distributed setups where reducing wiring costs and improving modularity are priorities, while Local IO suits compact systems with minimal latency requirements and direct device control. Your decision should balance installation costs, maintenance accessibility, and the specific performance demands of your automation environment.
Future Trends in IO Solutions for Automation
Remote IO is rapidly evolving with the integration of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies, enabling seamless data exchange and enhanced scalability for automation systems. Local IO maintains its relevance by offering low latency and high reliability essential for time-critical processes, yet emerging hybrid architectures combine both to optimize performance and flexibility. Your automation strategy should consider future trends like edge computing and increased cybersecurity measures that will shape the balance between remote and local IO solutions.
Remote IO vs Local IO Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com