Preventive maintenance in electronics involves scheduled inspections and part replacements to avoid equipment failure, while predictive maintenance uses real-time data and analytics to forecast issues before they occur, optimizing both uptime and resource use. Discover how these strategies can enhance Your electronic systems' reliability and efficiency throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
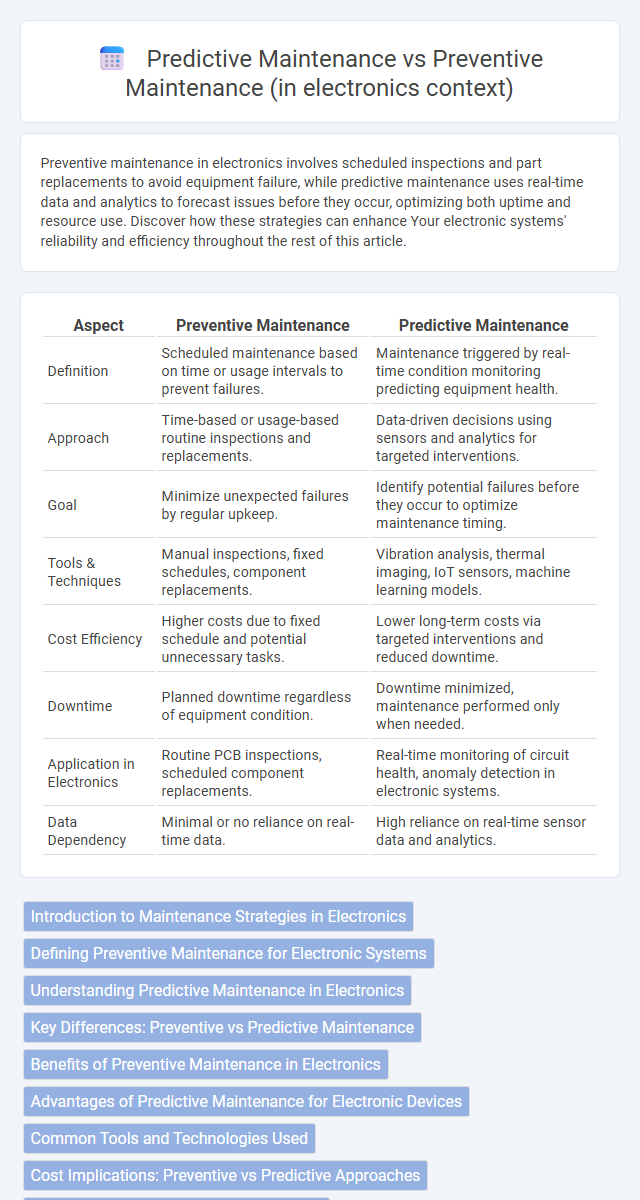
| Aspect | Preventive Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled maintenance based on time or usage intervals to prevent failures. | Maintenance triggered by real-time condition monitoring predicting equipment health. |
| Approach | Time-based or usage-based routine inspections and replacements. | Data-driven decisions using sensors and analytics for targeted interventions. |
| Goal | Minimize unexpected failures by regular upkeep. | Identify potential failures before they occur to optimize maintenance timing. |
| Tools & Techniques | Manual inspections, fixed schedules, component replacements. | Vibration analysis, thermal imaging, IoT sensors, machine learning models. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher costs due to fixed schedule and potential unnecessary tasks. | Lower long-term costs via targeted interventions and reduced downtime. |
| Downtime | Planned downtime regardless of equipment condition. | Downtime minimized, maintenance performed only when needed. |
| Application in Electronics | Routine PCB inspections, scheduled component replacements. | Real-time monitoring of circuit health, anomaly detection in electronic systems. |
| Data Dependency | Minimal or no reliance on real-time data. | High reliance on real-time sensor data and analytics. |
Introduction to Maintenance Strategies in Electronics
Preventive maintenance in electronics involves regularly scheduled inspections and component replacements to avoid unexpected failures, ensuring consistent device performance. Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and condition monitoring to forecast when a component might fail, optimizing repair timing and reducing downtime. Your choice between these strategies impacts system reliability, maintenance costs, and operational efficiency.
Defining Preventive Maintenance for Electronic Systems
Preventive maintenance for electronic systems involves scheduled inspections and routine servicing to reduce the risk of unexpected failures and extend equipment lifespan. This approach includes tasks such as cleaning, firmware updates, and component replacements based on time intervals or usage cycles rather than device condition. Implementing preventive maintenance helps maintain system reliability and operational efficiency by addressing potential issues before they cause significant disruption.
Understanding Predictive Maintenance in Electronics
Predictive maintenance in electronics uses real-time data and advanced analytics to monitor device performance and detect anomalies before failures occur. Techniques such as vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and sensor data integration enable accurate forecasting of component wear and potential breakdowns. This approach minimizes unexpected downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of electronic equipment.
Key Differences: Preventive vs Predictive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance in electronics involves scheduled inspections and part replacements based on time or usage intervals to avoid failures, while predictive maintenance uses real-time data and sensor analytics to forecast equipment issues before they occur. Your electronics systems benefit from predictive maintenance by reducing downtime through condition-based monitoring, whereas preventive maintenance may lead to unnecessary replacements or missed early fault signs. Key differences include reliance on historical schedules versus real-time diagnostics and the potential for predictive maintenance to optimize resource use and extend component lifespan.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance in Electronics
Preventive maintenance in electronics ensures consistent device performance by scheduling regular inspections and component replacements before failures occur, reducing unexpected downtime and costly repairs. This proactive approach extends equipment lifespan and enhances reliability by detecting wear and potential issues early. Maintaining clean contacts, tightening connections, and updating software during preventive routines significantly improve system efficiency and safety.
Advantages of Predictive Maintenance for Electronic Devices
Predictive maintenance for electronic devices enables continuous monitoring of component health through real-time data analysis, reducing unexpected failures and downtime significantly. It optimizes maintenance schedules by predicting issues before they occur, minimizing unnecessary inspections and costs associated with routine preventive checks. Enhanced accuracy in forecasting device lifespan and performance deterioration extends equipment reliability and operational efficiency.
Common Tools and Technologies Used
Preventive maintenance in electronics typically employs scheduled inspections and tools such as thermal cameras, multimeters, and oscilloscopes to identify wear and potential failures before they occur. Predictive maintenance relies heavily on advanced technologies like vibration analysis sensors, infrared thermography, and machine learning algorithms to monitor real-time data and predict equipment malfunctions. Both approaches use specialized software platforms for data collection and analysis, but predictive maintenance incorporates IoT connectivity and big data analytics for more accurate forecasting.
Cost Implications: Preventive vs Predictive Approaches
Preventive maintenance typically incurs higher costs due to scheduled part replacements and routine inspections regardless of equipment condition, leading to potential unnecessary expenditures. Predictive maintenance uses real-time data and condition monitoring to address issues precisely when needed, resulting in lower overall maintenance costs and reduced downtime. Investment in advanced sensors and analytics for predictive maintenance often pays off by minimizing operational disruptions and extending equipment lifespan.
Selecting the Right Maintenance Strategy
Selecting the right maintenance strategy in electronics involves evaluating system complexity, operational costs, and failure criticality. Preventive maintenance schedules regular inspections and part replacements to reduce downtime but may incur unnecessary expenses. Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and condition monitoring, optimizing maintenance timing to prevent failures while minimizing resource use and maximizing equipment lifespan.
Future Trends in Electronic Maintenance Optimization
Future trends in electronic maintenance optimization emphasize the integration of predictive maintenance powered by IoT sensors and AI algorithms, enabling real-time monitoring and fault prediction to reduce downtime and extend device lifespan. Preventive maintenance remains essential for routine checks but increasingly complements data-driven predictive strategies that enhance efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Your electronic systems benefit from a hybrid approach leveraging machine learning models to optimize maintenance schedules and resource allocation.
Preventive Maintenance vs Predictive Maintenance (in electronics context) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com