Power factor correction improves energy efficiency by reducing reactive power flow in electrical systems, while harmonic filters mitigate distortions caused by non-linear loads to ensure cleaner power quality. Understanding the distinctions between these technologies can help you optimize your electrical system performance; explore the rest of the article to learn how to choose the right solution for your needs.
Table of Comparison
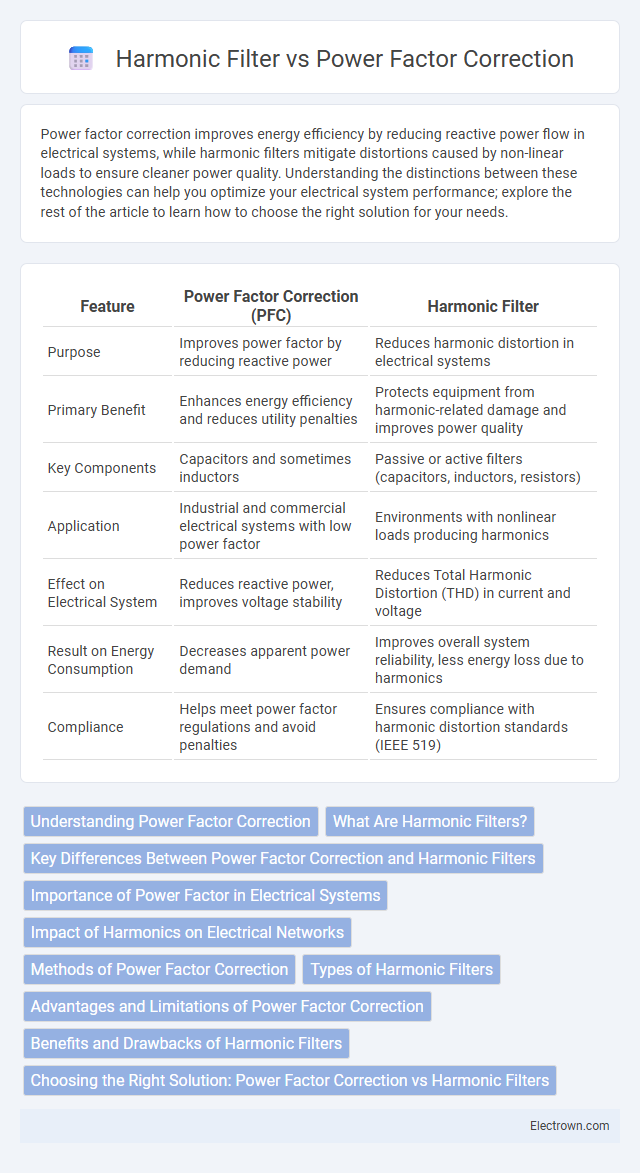
| Feature | Power Factor Correction (PFC) | Harmonic Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Improves power factor by reducing reactive power | Reduces harmonic distortion in electrical systems |
| Primary Benefit | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces utility penalties | Protects equipment from harmonic-related damage and improves power quality |
| Key Components | Capacitors and sometimes inductors | Passive or active filters (capacitors, inductors, resistors) |
| Application | Industrial and commercial electrical systems with low power factor | Environments with nonlinear loads producing harmonics |
| Effect on Electrical System | Reduces reactive power, improves voltage stability | Reduces Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) in current and voltage |
| Result on Energy Consumption | Decreases apparent power demand | Improves overall system reliability, less energy loss due to harmonics |
| Compliance | Helps meet power factor regulations and avoid penalties | Ensures compliance with harmonic distortion standards (IEEE 519) |
Understanding Power Factor Correction
Power Factor Correction improves the efficiency of electrical systems by reducing reactive power and enhancing voltage stability, directly impacting your energy savings and equipment longevity. Harmonic Filters address distortion caused by non-linear loads, ensuring cleaner power quality but do not correct the power factor itself. Understanding Power Factor Correction helps you optimize energy consumption and avoid penalties from utilities due to low power factor levels.
What Are Harmonic Filters?
Harmonic filters are specialized electrical components designed to reduce or eliminate harmonic distortions generated by nonlinear loads in power systems. These filters improve power quality by mitigating voltage and current harmonics, which can cause overheating, equipment malfunctions, and energy losses. Your electrical system benefits from harmonic filters by maintaining efficient operation and extending the lifespan of sensitive devices.
Key Differences Between Power Factor Correction and Harmonic Filters
Power Factor Correction (PFC) primarily improves electrical efficiency by reducing reactive power and maintaining voltage stability, while Harmonic Filters focus on eliminating harmonic distortion caused by non-linear loads to protect equipment and enhance power quality. PFC devices typically use capacitors and inductors to adjust power factor close to unity, whereas harmonic filters employ passive or active components designed to target specific harmonic frequencies. The key difference lies in their objectives: PFC targets reactive power compensation, whereas harmonic filters address distortion harmonics for a cleaner electrical signal.
Importance of Power Factor in Electrical Systems
Power factor correction improves energy efficiency by reducing reactive power in electrical systems, resulting in lower utility bills and enhanced equipment lifespan. Harmonic filters address distortion caused by non-linear loads, preventing equipment malfunctions and improved power quality. Maintaining a high power factor minimizes energy losses and ensures optimal performance in industrial and commercial electrical installations.
Impact of Harmonics on Electrical Networks
Harmonics in electrical networks cause voltage distortion, increased losses, and overheating of equipment, significantly reducing system efficiency and lifespan. Power factor correction improves energy efficiency by reducing reactive power but does not address harmonic distortion. Harmonic filters specifically target and mitigate harmonic currents, ensuring cleaner power quality and safeguarding sensitive devices in your electrical system.
Methods of Power Factor Correction
Methods of Power Factor Correction include using capacitors, synchronous condensers, and phase advancers to improve the power factor by compensating for reactive power. Capacitor banks are the most common solution, providing leading reactive power to counteract lagging inductive loads. You can enhance energy efficiency and reduce utility charges by choosing the appropriate correction method tailored to your electrical system's specific harmonic and reactive power characteristics.
Types of Harmonic Filters
Passive harmonic filters include single-tuned, double-tuned, and high-pass filters designed to target specific harmonic frequencies and improve power quality. Active harmonic filters use power electronics to dynamically inject counter-harmonic currents, effectively reducing a wide range of harmonics in real-time. You can optimize your electrical system by selecting the appropriate harmonic filter type based on the harmonic spectrum and load characteristics.
Advantages and Limitations of Power Factor Correction
Power Factor Correction (PFC) improves energy efficiency by reducing reactive power, leading to lower electricity costs and enhanced voltage stability in electrical systems. It faces limitations such as potential resonance issues and limited effectiveness in mitigating harmonic distortion compared to Harmonic Filters. While PFC primarily enhances power quality by optimizing power factor, it does not address harmonic currents, which Harmonic Filters specifically target.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Harmonic Filters
Harmonic filters reduce electrical noise and improve power quality by mitigating harmonic distortions caused by non-linear loads, enhancing equipment lifespan and reducing energy losses. However, they can be costly to install and maintain, require precise tuning for specific harmonic frequencies, and may introduce resonance issues if not properly designed. Despite these drawbacks, harmonic filters play a critical role in ensuring compliance with grid standards and preventing equipment malfunctions.
Choosing the Right Solution: Power Factor Correction vs Harmonic Filters
Choosing between Power Factor Correction (PFC) and Harmonic Filters depends on your electrical system's specific needs: PFC improves energy efficiency by reducing reactive power, while Harmonic Filters mitigate distortion caused by non-linear loads to protect sensitive equipment. Assess the power quality issues present, such as low power factor or harmonic distortion, to determine which solution enhances overall system performance. Implementing the right technology ensures optimal energy use, lower utility costs, and increased reliability for your facility.
Power Factor Correction vs Harmonic Filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com